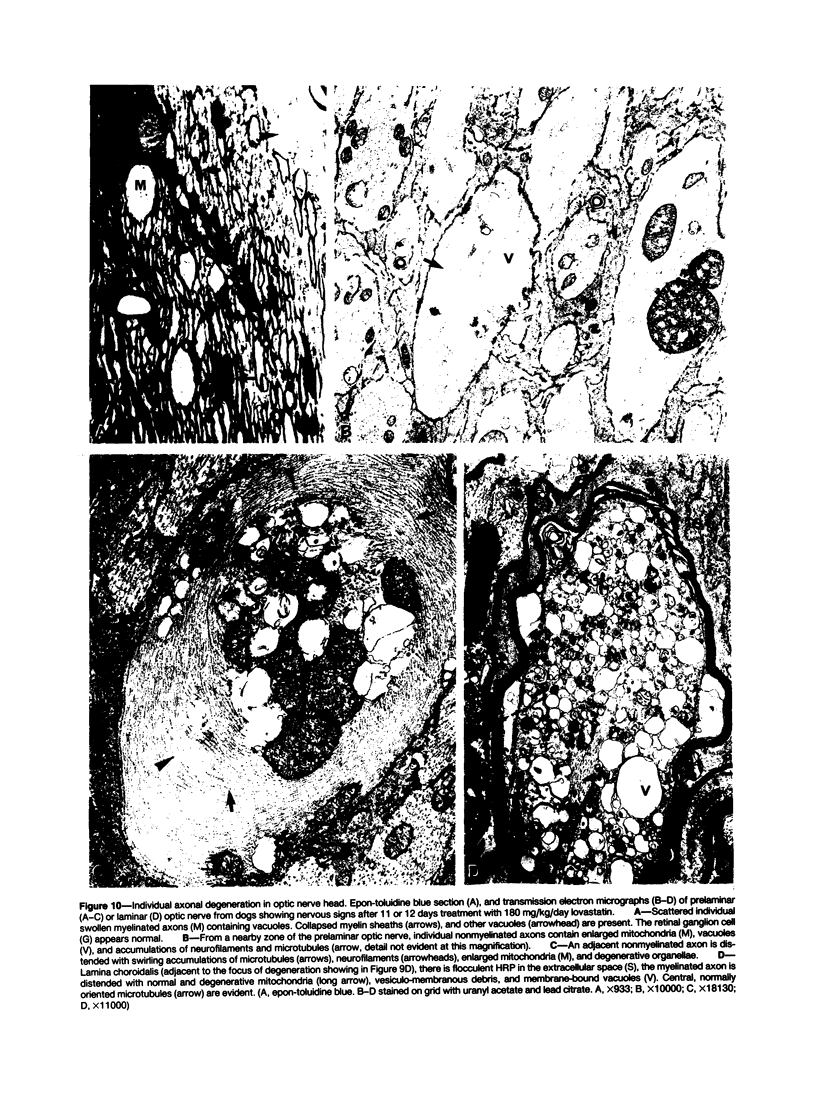
Abstract
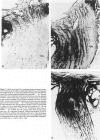
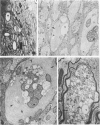
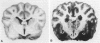
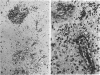
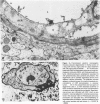
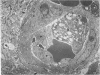
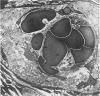
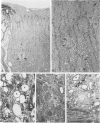
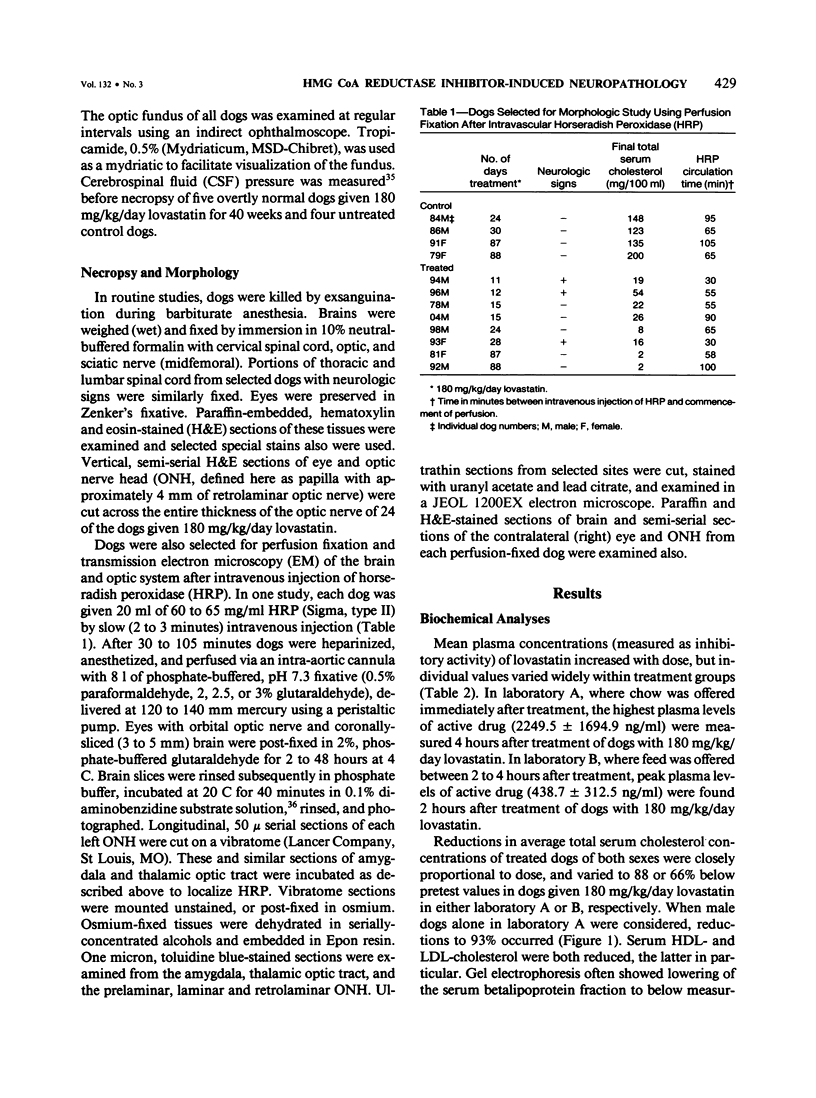
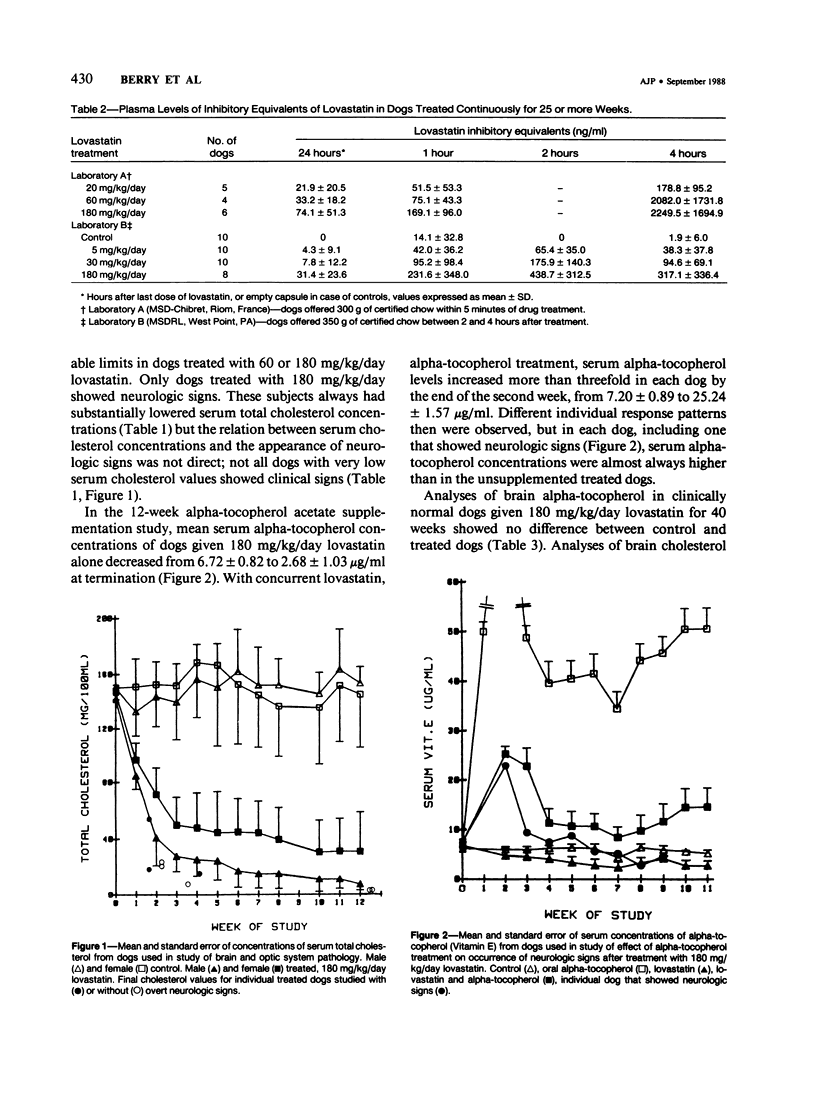
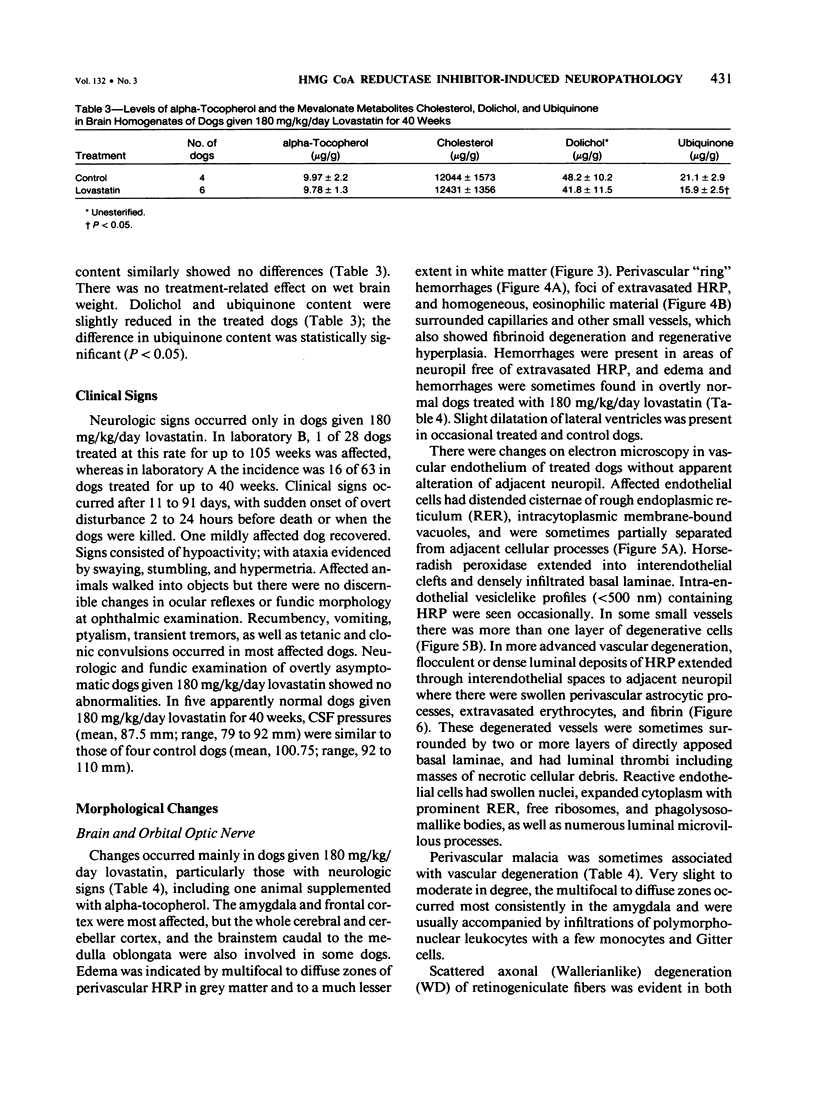
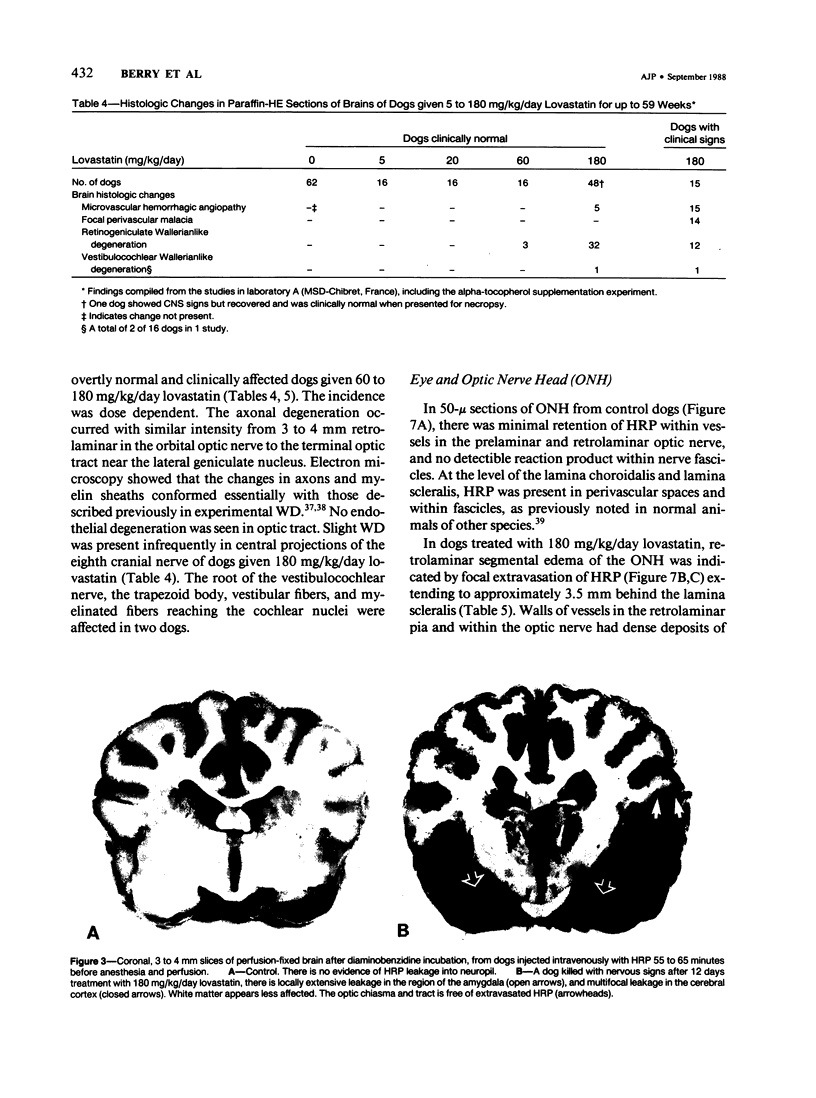
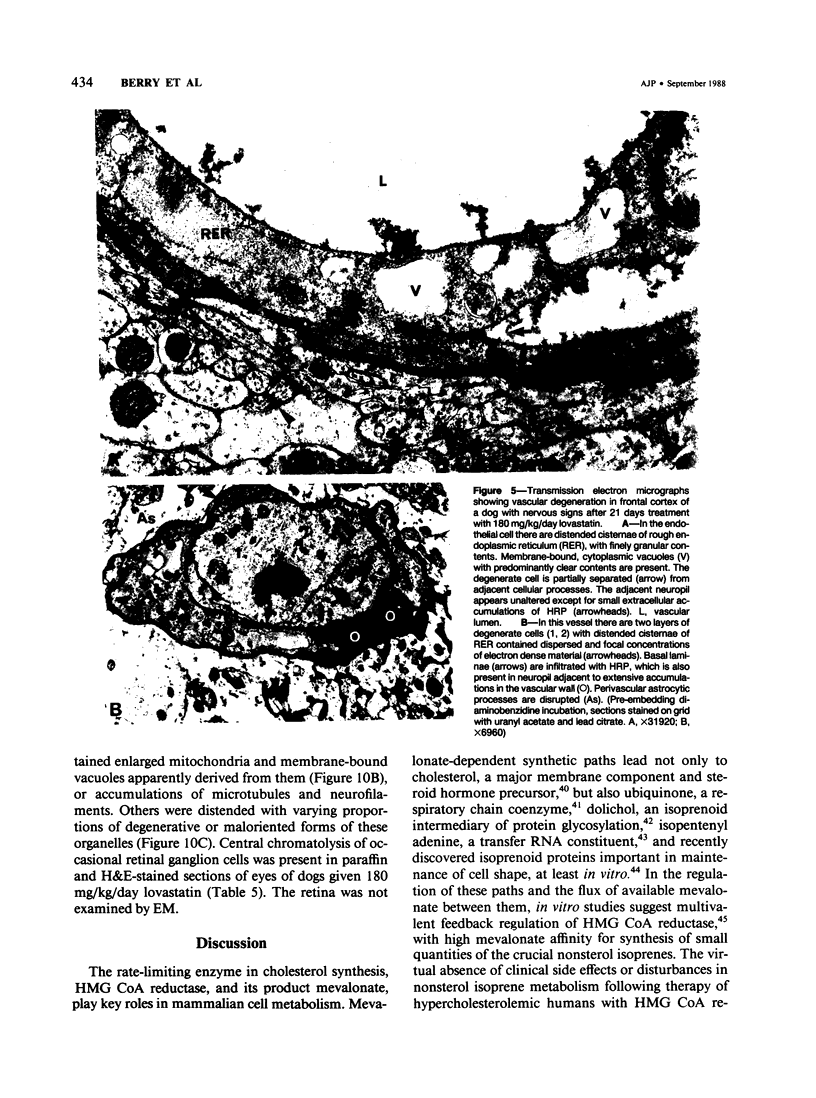
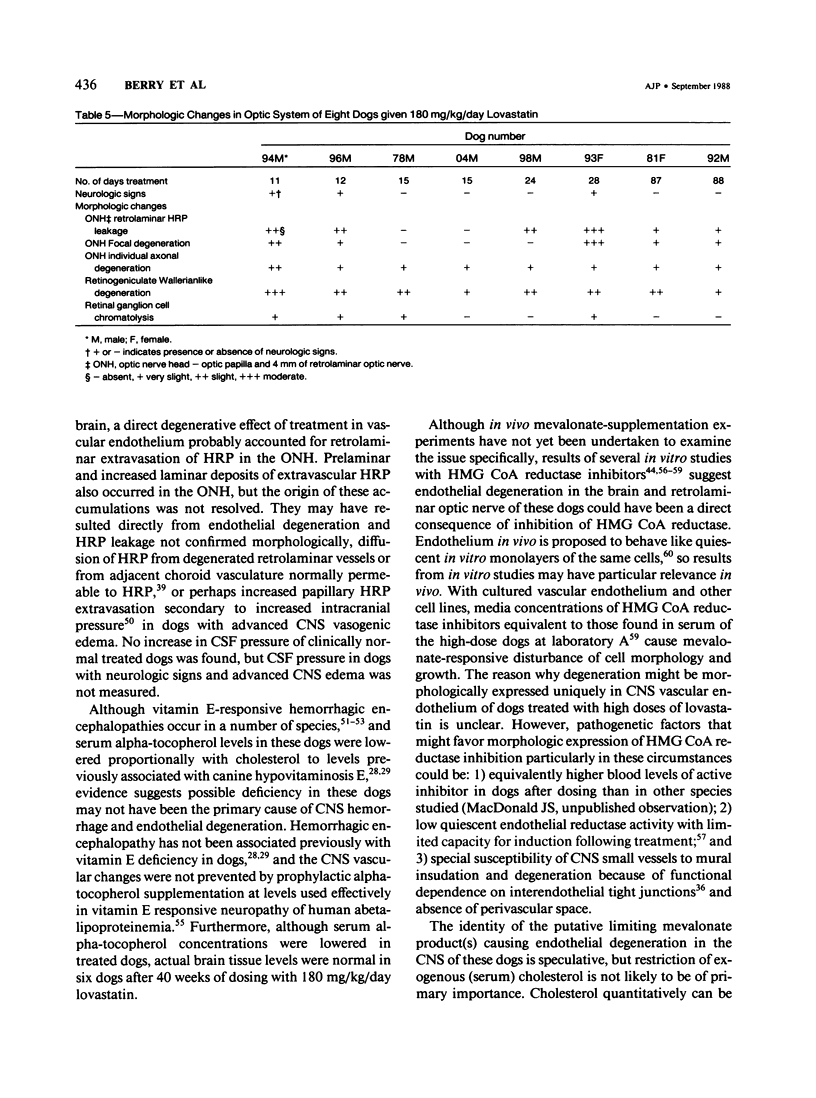
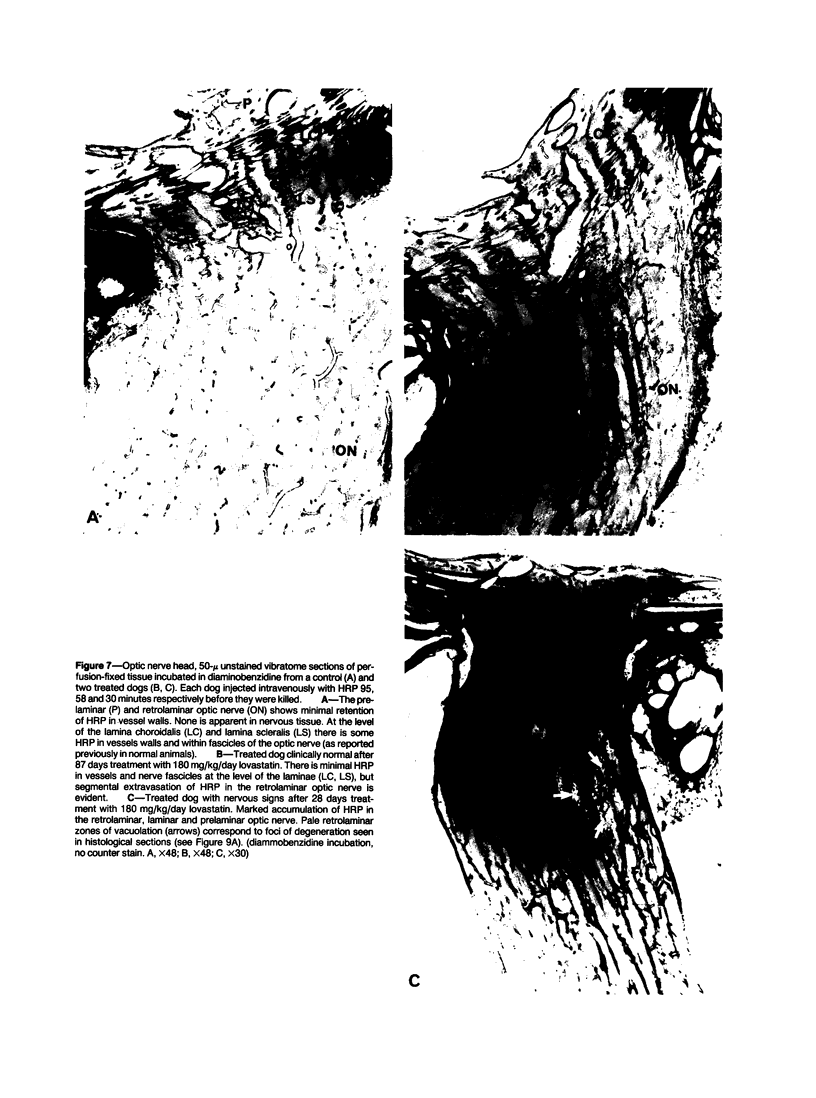
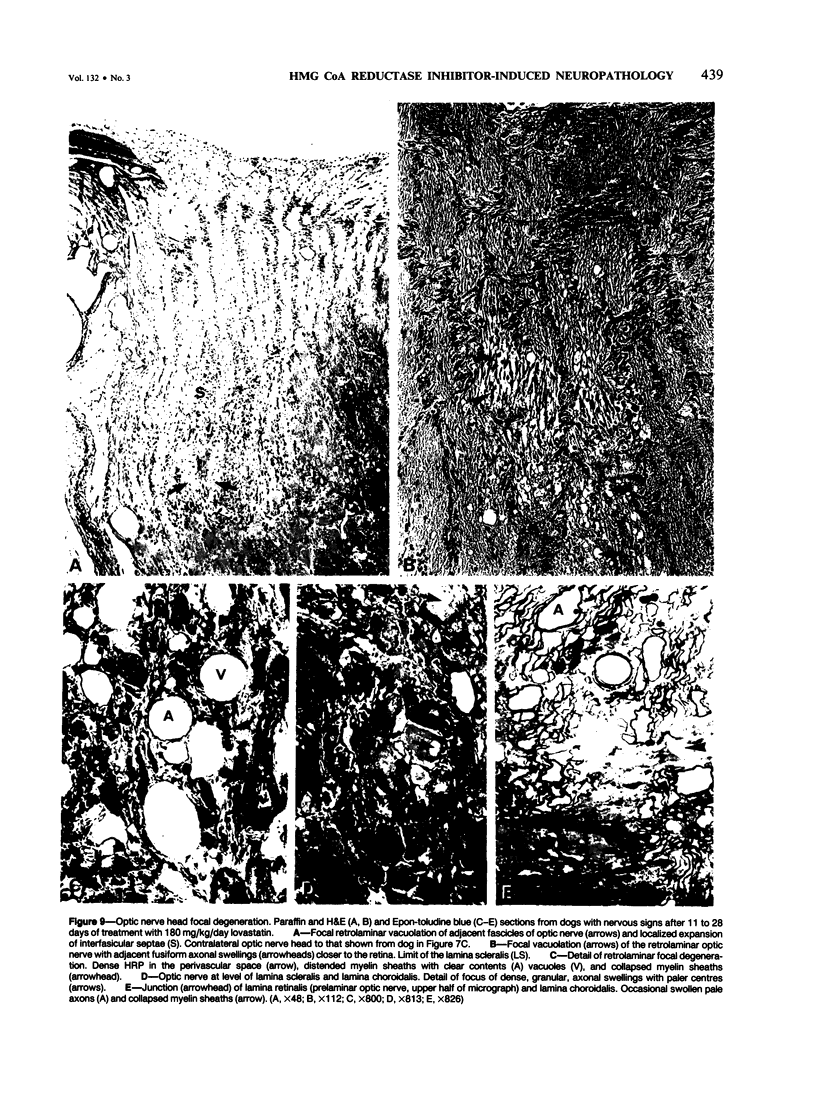
The cholesterol lowering compound lovastatin, a competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (EC 1.1.1.34 HMG CoA reductase), was given in nine separate experiments to normocholesterolemic dogs at rates up to 180 times the maximum therapeutic dose in man (1 mg/kg/day). Mean serum total cholesterol concentrations were reduced as much as 88% below normal. Clinical evidence of neurotoxicity occurred in up to 37% of animals given 180 mg/kg/day lovastatin for 11 or more days, especially in one laboratory where the dosing regime resulted in higher concentrations of plasma drug levels. Dogs receiving 60 mg/kg/day or less never exhibited neurologic signs. The central nervous system (CNS) of affected dogs exhibited endothelial degeneration and hemorrhagic encephalopathy. Focal extravasation of horseradish peroxidase occurred frequently (6/8) in the retrolaminar optic nerve of asymptomatic or clinically affected dogs given 180 mg/kg/day lovastatin, with endothelial degeneration and discrete optic nerve degenerative lesions interpreted as ischemic. The association between the degree of hypocholesterolemia and occurrence of clinical signs was not exact. Total brain cholesterol was similar in treated and control dogs. Hypocholesterolemic dogs had proportionally lowered serum concentrations of alpha-tocopherol, but oral supplementation of this vitamin did not prevent the neurologic syndrome. Endothelial degeneration in the CNS and optic nerve may have reflected in vitro morphologic effects of HMG CoA reductase inhibitors due to extreme inhibition of nonsterol isoprene synthesis. Retinogeniculate axonal (Wallerianlike) degeneration occurred in ≥12% of dogs given 60 mg/kg/day or more lovastatin, with central chromatolysis of occasional retinal ganglion cells. These neuroaxonal changes may have been secondary to vascular effects, but superimposed direct neurotoxic action at the high dosage levels of lovastatin could not be excluded. There was no evidence of drug induced adverse effects in the CNS of dogs given up to 30 mg/kg/day lovastatin for 2 years.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. W., Chen J., Kuron G., Hunt V., Huff J., Hoffman C., Rothrock J., Lopez M., Joshua H., Harris E. Mevinolin: a highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Grundy S. M., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Mevinolin and colestipol stimulate receptor-mediated clearance of low density lipoprotein from plasma in familial hypercholesterolemia heterozygotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4124–4128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch K. The biological synthesis of cholesterol. Science. 1965 Oct 1;150(3692):19–28. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3692.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W., Broadwell R. D. The morphological approach to the study of normal and abnormal brain permeability. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;69:41–54. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3264-0_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Multivalent feedback regulation of HMG CoA reductase, a control mechanism coordinating isoprenoid synthesis and cell growth. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jul;21(5):505–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böke W., Voigt G. J. Circulatory disorders of the optic nerve. Ophthalmologica. 1980;180(2):88–100. doi: 10.1159/000308960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancilla P. A., Frommes S. P., Kahn L. E., DeBault L. E. Regeneration of cerebral microvessels: a morphologic and histochemical study after local freeze-injury. Lab Invest. 1979 Jan;40(1):74–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castelli W. P., Garrison R. J., Wilson P. W., Abbott R. D., Kalousdian S., Kannel W. B. Incidence of coronary heart disease and lipoprotein cholesterol levels. The Framingham Study. JAMA. 1986 Nov 28;256(20):2835–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. W. Role of cholesterol metabolism in cell growth. Fed Proc. 1984 Jan;43(1):126–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiswick M. L., Johnson M., Woodhall C., Gowland M., Davies J., Toner N., Sims D. Protective effect of vitamin E on intraventricular haemorrhage in the newborn. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;101:186–200. doi: 10.1002/9780470720820.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. C., Massoglia S. L., Gospodarowicz D. Feedback regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in vascular endothelial cells. Separate sterol and non-sterol components. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11106–11112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook R. D., Ghetti B., Wiśniewski H. M. The pattern of Wallerian degeneration in the optic nerve of newborn kittens: an ultrastructural study. Brain Res. 1974 Jul 26;75(2):261–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90746-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook R. D. Observations on glial cells within myelin sheaths in degenerating optic nerves. J Neurocytol. 1974 Dec;3(6):737–751. doi: 10.1007/BF01097195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLahunta A. Small animal neurologic examination. Vet Clin North Am. 1971 Jan;1(1):191–206. doi: 10.1016/s0091-0279(71)50014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East C., Grundy S. M., Bilheimer D. W. Normal cholesterol levels with lovastatin (mevinolin) therapy in a child with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia following liver transplantation. JAMA. 1986 Nov 28;256(20):2843–2848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A., Lan S. F., Fogelman A. M. Alterations in the rates of synthesis and degradation of rat liver 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase produced by cholestyramine and mevinolin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10219–10222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo A., Kuroda M., Tsujita Y. ML-236A, ML-236B, and ML-236C, new inhibitors of cholesterogenesis produced by Penicillium citrinium. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Dec;29(12):1346–1348. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo A., Tsujita Y., Kuroda M., Tanzawa K. Effects of ML-236B on cholesterol metabolism in mice and rats: lack of hypocholesterolemic activity in normal animals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 21;575(2):266–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks K. P., Barbu V. D., Witte L. D., Weinstein I. B., Goodman D. S. Effects of mevinolin and mevalonate on cell growth in several transformed cell lines. J Cell Physiol. 1986 May;127(2):216–222. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041270205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks K. P., Witte L. D., Goodman D. S. Relationship between mevalonate and mitogenesis in human fibroblasts stimulated with platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1546–1551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust J. R., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Synthesis of delta 2-isopentenyl tRNA from mevalonate in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6546–6548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough D. P., Hemming F. W. The characterization and stereochemistry of biosynthesis of dolichols in rat liver. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):163–166. doi: 10.1042/bj1180163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes K. C., Nielsen S. W., Rousseau J. E., Jr Vitamin E deficiency and fat stress in the dog. J Nutr. 1969 Oct;99(2):196–209. doi: 10.1093/jn/99.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayreh S. S. Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Arch Neurol. 1981 Nov;38(11):675–678. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510110035002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkind P., Charles N. C., Pearson J. Histopathology of ischemic optic neuropathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970 Jan;69(1):78–90. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(70)91859-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner I., Gabbiani G. Vascular endothelium: recent advances and unanswered questions. Lab Invest. 1982 Nov;47(5):409–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jago M. V., Payne A. L., Peterson J. E., Bagust T. J. Inhibition of glycosylation by corynetoxin, the causative agent of annual ryegrass toxicity: a comparison with tunicamycin. Chem Biol Interact. 1983 Jul 15;45(2):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(83)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. B., Cavanagh J. B. Comparison between the early changes in isoniazid intoxication and the chromatolytic response to nerve ligation in spinal ganglion cells of the rat. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1981 Nov-Dec;7(6):489–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1981.tb00248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeler R. F., Young S. Role of vitamin E in the etiology of spontaneous hemorrhagic necrosis of the central nervous system of fetal hamsters. Teratology. 1979 Aug;20(1):127–132. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420200116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L., Jaramillo J. J., Brown M. S. Regulatory role for hepatic low density lipoprotein receptors in vivo in the dog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroon P. A., Hand K. M., Huff J. W., Alberts A. W. The effects of mevinolin on serum cholesterol levels of rabbits with endogenous hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 1982 Jul;44(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(82)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda M., Tsujita Y., Tanzawa K., Endo A. Hypolipidemic effects in monkeys of ML-236B, a competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Lipids. 1979 Jun;14(6):585–589. doi: 10.1007/BF02533537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz H. J., Short E. C., Jr Pathogenesis of edema disease in swine: pathologic effects of hemolysin, autolysate, and endotoxin of Escherichia coli (O141). Am J Vet Res. 1976 Jan;37(1):15–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi H., Haba T., Tatami R., Miyamoto S., Sakai Y., Wakasugi T., Watanabe A., Koizumi J., Takeda R. Effect of an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methyglutaryl coenzyme A reductase on serum lipoproteins and ubiquinone-10-levels in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 27;305(9):478–482. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108273050902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi H., Sakai T., Sakai Y., Yoshimura A., Watanabe A., Wakasugi T., Koizumi J., Takeda R. Reduction of serum cholesterol in heterozygous patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Additive effects of compactin and cholestyramine. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 17;308(11):609–613. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303173081101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. V., Jr, Panner B. J. Regenerating capillary basement membrane in skeletal muscle wounds. Ultrastructural and histochemical study. Lab Invest. 1972 Jan;26(1):100–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod D., Marshall J., Kohner E. M. Role of axoplasmic transport in the pathophysiology of ischaemic disc swelling. Br J Ophthalmol. 1980 Apr;64(4):247–261. doi: 10.1136/bjo.64.4.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minsker D. H., MacDonald J. S., Robertson R. T., Bokelman D. L. Mevalonate supplementation in pregnant rats suppresses the teratogenicity of mevinolinic acid, an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase. Teratology. 1983 Dec;28(3):449–456. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420280316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D. P., Lloyd J. K., Wolff O. H. The role of vitamin E in the treatment of the neurological features of abetalipoproteinaemia and other disorders of fat absorption. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1985;8 (Suppl 1):88–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01800666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T., Poduslo S. E. Myelination in rat brain: changes in myelin composition during brain maturation. J Neurochem. 1973 Oct;21(4):759–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese T. S., Karnovsky M. J. Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):207–217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum W. I. Aspects of endothelial malfunction and function in cerebral microvessels. Lab Invest. 1986 Sep;55(3):252–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux C., Dupuis R., Horvath C., Talbot J. N. Teratogenic effect of an inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis (AY 9944) in rats: correlation with maternal cholesterolemia. J Nutr. 1980 Nov;110(11):2310–2312. doi: 10.1093/jn/110.11.2310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. A., Glomset J. A., Wight T. N., Habenicht A. J., Ross R. A study of the Influence of mevalonic acid and its metabolites on the morphology of swiss 3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):144–153. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. A., Schneider C. J., Glomset J. A. Evidence for post-translational incorporation of a product of mevalonic acid into Swiss 3T3 cell proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10175–10180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I. I., Kawka D. W., Kazazis D. M., Alberts A. W., Chen J. S., Huff J. W., Ness G. C. Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase-containing hepatocytes are distributed periportally in normal and mevinolin-treated rat livers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5556–5560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. E., Hasinoff C. M. Inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis and myelin formation. Lipids. 1970 Aug;5(8):665–671. doi: 10.1007/BF02531432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spohn M., Davison A. N. Cholesterol metabolism in myelin and other subcellular fractions of rat brain. J Lipid Res. 1972 Sep;13(5):563–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., De Paul L. D. Myelin degeneration in sciatic nerve of rats treated with hypocholesteremic drug AY9944. Lab Invest. 1972 May;26(5):534–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Zagoren J. C. Degeneration of oligodendroglia in the central nervous system of rats treated with AY9944 or triparanol. Lab Invest. 1974 Nov;31(5):503–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. L., Lamden M. P., Tappel A. L. Sensitive fluorometric method for tissue tocopherol analysis. Lipids. 1976 Jul;11(7):530–538. doi: 10.1007/BF02532898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobert J. A., Bell G. D., Birtwell J., James I., Kukovetz W. R., Pryor J. S., Buntinx A., Holmes I. B., Chao Y. S., Bolognese J. A. Cholesterol-lowering effect of mevinolin, an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase, in healthy volunteers. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):913–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI110530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso M. O., Hayreh S. S. Optic disc edema in raised intracranial pressure. III. A pathologic study of experimental papilledema. Arch Ophthalmol. 1977 Aug;95(8):1448–1457. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1977.04450080158022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso M. O., Shih C. Y., McLean I. W. Is there a blood-brain barrier at the optic nerve head? Arch Ophthalmol. 1975 Sep;93(9):815–825. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1975.01010020703008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujita Y., Kuroda M., Shimada Y., Tanzawa K., Arai M., Kaneko I., Tanaka M., Masuda H., Tarumi C., Watanabe Y. CS-514, a competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase: tissue-selective inhibition of sterol synthesis and hypolipidemic effect on various animal species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 11;877(1):50–60. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujita Y., Kuroda M., Tanzawa K., Kitano N., Endo A. Hypolipidemic effects in dogs of ML-236B, a competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Atherosclerosis. 1979 Mar;32(3):307–313. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(79)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vleet J. F. Experimentally induced vitamin E-selenium deficiency in the growing dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1975 Apr 15;166(8):769–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Ito T., Saeki M., Kuroda M., Tanzawa K., Mochizuki M., Tsujita Y., Arai M. Hypolipidemic effects of CS-500 (ML-236B) in WHHL-rabbit, a heritable animal model for hyperlipidemia. Atherosclerosis. 1981 Jan-Feb;38(1-2):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentz P. W., Cross R. E., Savory J. An integrated approach to lipid profiling: enzymatic determination of cholesterol and triglycerides with a centrifugal analyzer. Clin Chem. 1976 Feb;22(2):188–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]