Abstract
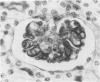
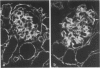
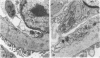
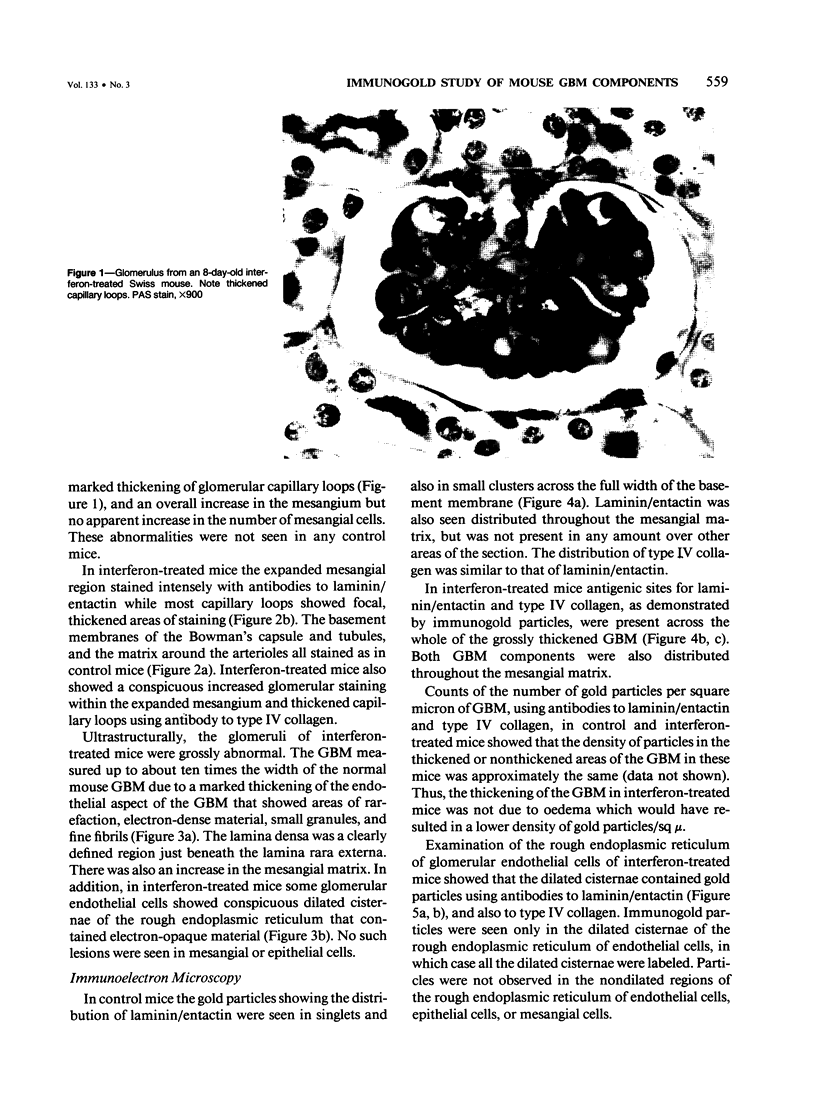
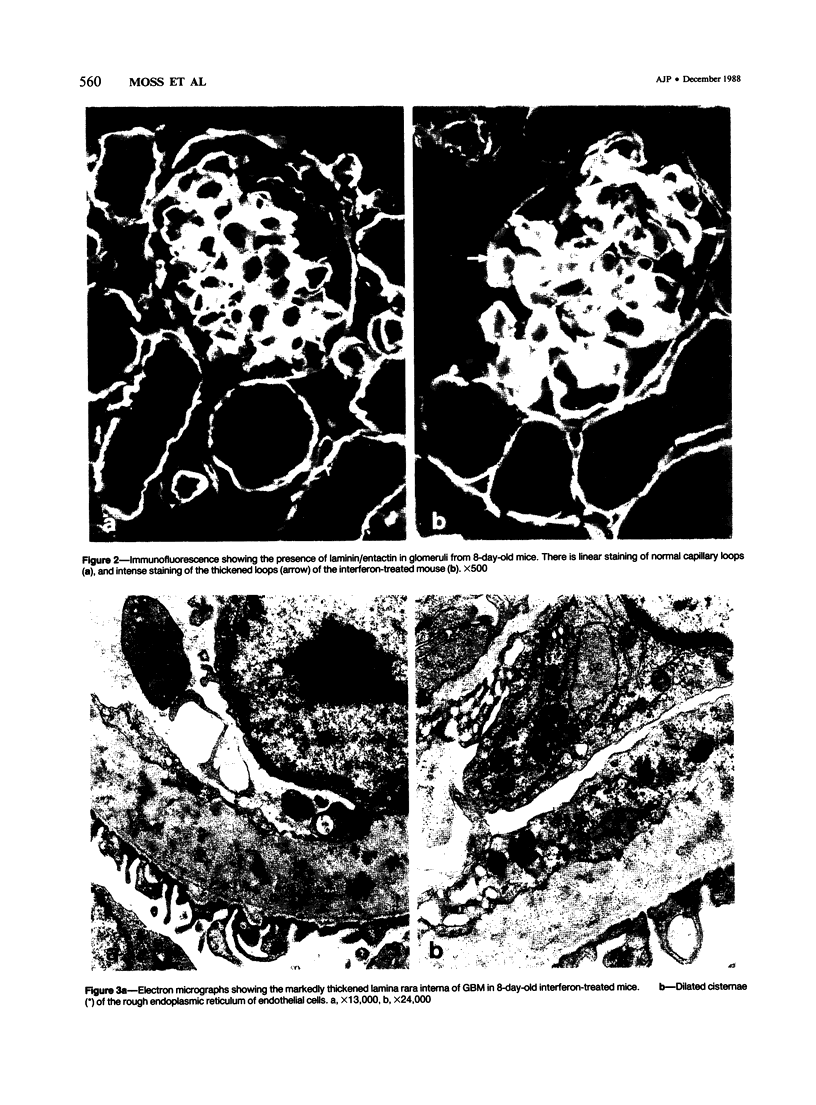
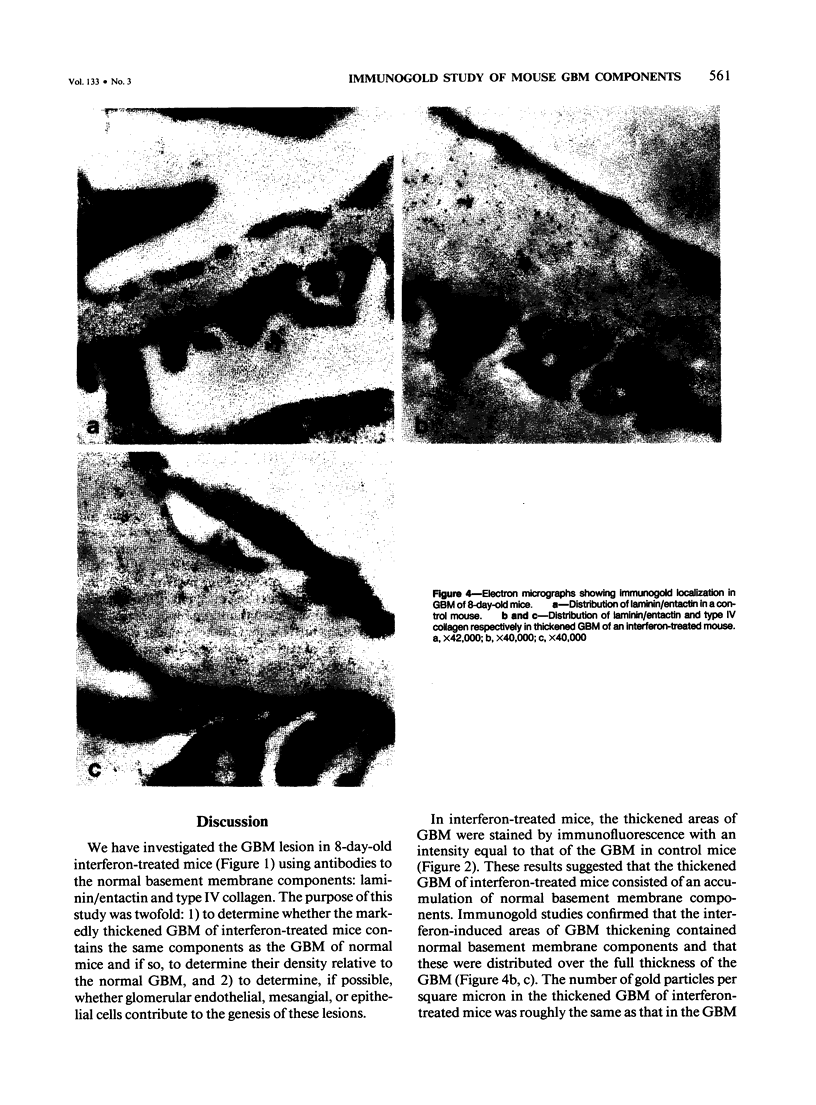
Newborn Swiss mice were injected daily for the first week of life with mouse interferon alpha/beta. This treatment resulted in a delay in the maturation of the kidney and the development of glomerular abnormalities. The width of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) was increased up to tenfold and was characterized by a marked thickening of the endothelial aspect of the GBM. The endothelial cells lining the capillary loops were also abnormal with many dilated regions of the rough endoplasmic reticulum that contained amorphous electron-opaque material. Immunogold studies showed that type IV collagen and laminin/entactin were distributed throughout the thickened GBM, and also within the dilated rough endoplasmic reticulum of the endothelial cells. These results show that the interferon-induced lesion within the glomerulus is associated with an accumulation of normal GBM components and that endothelial cells are involved in this pathologic process.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamson D. R. Origin of the glomerular basement membrane visualized after in vivo labeling of laminin in newborn rat kidneys. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1988–2000. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J. Accumulation of newly synthesized mRNAs in response to human fibroblast (beta) interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4763–4766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Broeze R. J., Lengyel P. Accumulation of an mRNA and protein in interferon-treated Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):523–525. doi: 10.1038/279523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Aguet M., Morel-Maroger L., Woodrow D., Puvion-Dutilleul F., Guillon J. C., Maury C. Electrophoretically pure mouse interferon inhibits growth, induces liver and kidney lesions, and kills suckling mice. Am J Pathol. 1981 Mar;102(3):396–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I. Can interferon induce disease? Interferon. 1982;4:95–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Maury C., Tovey M., Morel-Maroger L., Pontillon F. Progressive glomerulonephritis in mice treated with interferon preparations at birth. Nature. 1976 Sep 30;263(5576):420–422. doi: 10.1038/263420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Morel-Maroger L., Châtelet F., Maury C., Tovey M., Bandu M. T., Buywid J., Delauche M. Delay in growth and the development of nephritis in rats treated with interferon preparations in the neonatal period. Am J Pathol. 1979 May;95(2):329–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Maury C., Chouroulinkov I. Lethality of interferon preparations for newborn mice. Nature. 1975 Nov 6;258(5530):76–78. doi: 10.1038/258076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribaudo G., Toniato E., Engel D. A., Lengyel P. Interferons as gene activators. Characteristics of an interferon-activatable enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11878–11883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie G. W., Leblond C. P., Cournil I., Martin G. R. Immunohistochemical evidence for the intracellular formation of basement membrane collagen (type IV) in developing tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Dec;28(12):1267–1274. doi: 10.1177/28.12.6164715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie G. W., Leblond C. P., Martin G. R. Intracellular localization of basement membrane precursors in the endodermal cells of the rat parietal yolk sac. II. Immunostaining for type IV collagen and its precursors. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Oct;30(10):983–990. doi: 10.1177/30.10.6752264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie G. W., Leblond C. P., Martin G. R., Silver M. H. Intracellular localization of basement membrane precursors in the endodermal cells of the rat parietal yolk sac. III. Immunostaining for laminin and its precursors. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Oct;30(10):991–998. doi: 10.1177/30.10.6752265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liesi P. Laminin in cultured mouse C1300 neuroblastoma cells: immunocytochemical localization by pre- and postembedding electron microscope procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jun;31(6):755–764. doi: 10.1177/31.6.6841971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel-Maroger L., Sloper J. C., Vinter J., Woodrow D., Gresser I. An ultrastructural study of the development of nephritis in mice treated with interferon in the neonatal period. Lab Invest. 1978 Nov;39(5):513–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayyar R. P., Volini F. I., Borke J. L. The role of visceral epithelial, endothelial and mesangial cells in the formation and turnover of glomerular basement membrane. Ren Physiol. 1980;3(1-6):212–219. doi: 10.1159/000172763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semoff S., Hogan B. L., Hopkins C. R. Localization of fibronectin, laminin-entactin, and entactin in Reichert's membrane by immunoelectron microscopy. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1171–1175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman L., Revel M. Interferon-dependent induction of mRNA activity for (2'-5')oligo-isoadenylate synthetase. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):98–100. doi: 10.1038/288098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Begon-Lours J., Gresser I. A method for the large scale production of potent interferon preparations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jul;146(3):809–815. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]