Abstract
OBJECTIVES--To examine general practitioner consultations by demographic and socioeconomic variables and to derive a method of measuring the impact of relative deprivation on general practitioner workload. DESIGN--The study was based on general practitioner consultations reported in the general household surveys of 1983-7, covering a sample of 129,987 individuals in Great Britain. Odds ratios for general practitioner consultations were obtained for selected variables among children (0-15 years), men (16-64), women (16-64), and elderly people (greater than or equal to 65). These were then used to derive deprivation indices specific to electoral wards for use in general practice. SETTING--Great Britain, with particular findings illustrated by English electoral wards and the conurbations of London, Manchester, Merseyside, and the West Midlands. RESULTS--Council tenure increased the likelihood of consultation significantly in all four groups. Odds ratios were raised in children, men, and women with no access to a car. Birth in the New Commonwealth or Pakistan yielded high odds ratios in men, women, and elderly people but not in children. Marginally increased consultation rates were evident in the manual socioeconomic groups in women, elderly people, and children with a single parent mother. The deprivation indices for general practice derived using these odds ratios varied substantially among English electoral wards with, for example, anticipated general practitioner consultations in the electoral ward of Hulme, Manchester, being 24% higher than the average ward in England as a result of local attributes, and consultations in the Cheam South ward of Sutton, London, 11% lower than average. CONCLUSION--This deprivation index for general practice overcomes several shortcomings expressed about the underprivileged area score, which has been adopted in the 1990 contract as a basis for allocating deprivation supplements to general practitioners. The proposed index can be applied nationwide.
Full text
PDF
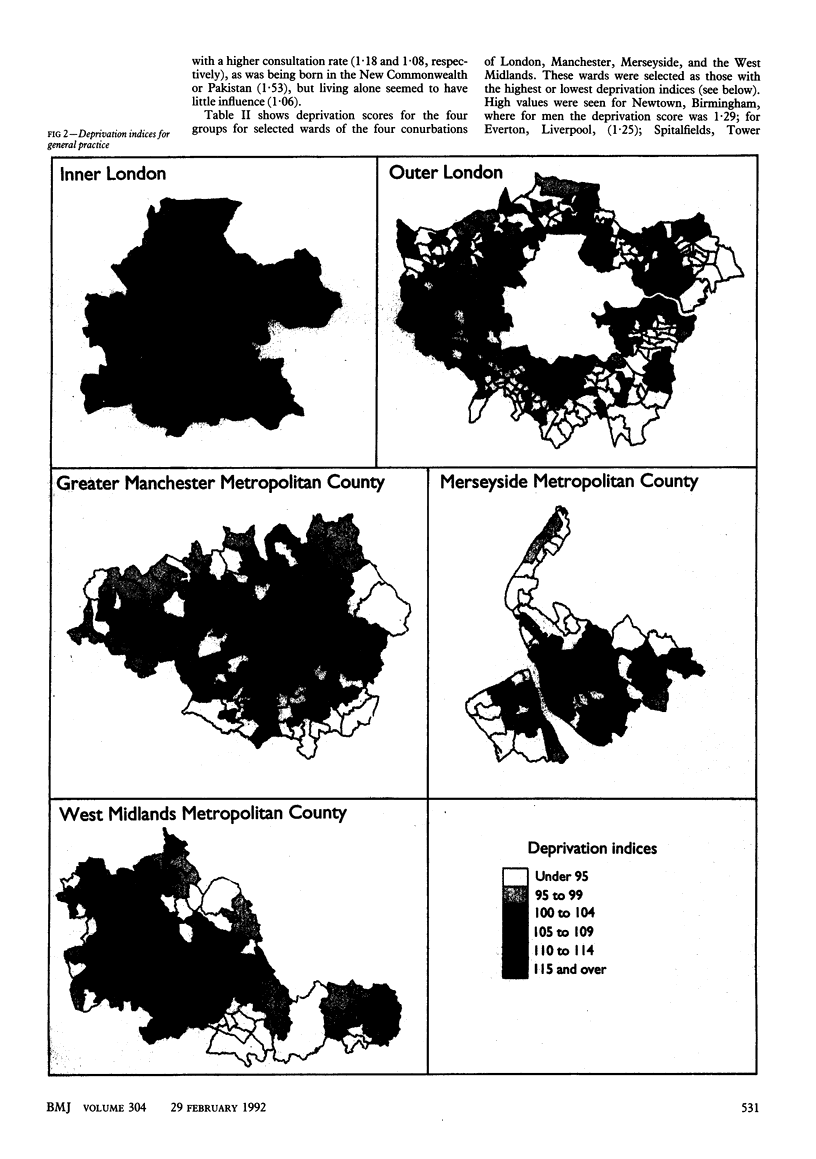
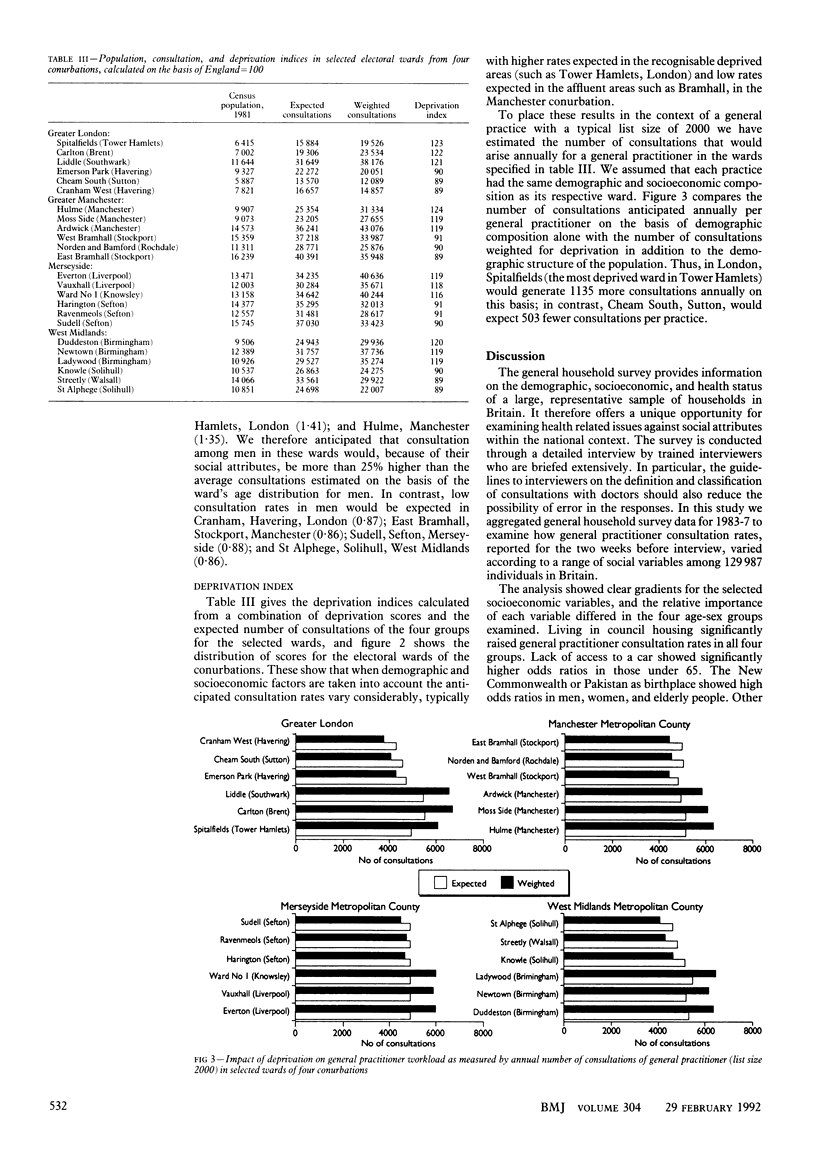


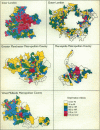
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balarajan R., Yuen P., Machin D. Socioeconomic differentials in the uptake of medical care in Great Britain. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1987 Sep;41(3):196–199. doi: 10.1136/jech.41.3.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balarajan R., Yuen P., Soni Raleigh V. Ethnic differences in general practitioner consultations. BMJ. 1989 Oct 14;299(6705):958–960. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6705.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney T. Workload of general practitioners. BMJ. 1989 Sep 23;299(6702):753–754. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6702.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr-Hill R. A., Sheldon T. Designing a deprivation payment for general practitioners: the UPA(8) wonderland. BMJ. 1991 Feb 16;302(6773):393–396. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6773.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstairs V., Morris R. Deprivation and health. BMJ. 1989 Dec 9;299(6713):1462–1462. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6713.1462-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillam S. J., Jarman B., White P., Law R. Ethnic differences in consultation rates in urban general practice. BMJ. 1989 Oct 14;299(6705):953–957. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6705.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson A., Foy C., Sandhu B. Comparison of two scores for allocating resources to doctors in deprived areas. BMJ. 1989 Nov 4;299(6708):1142–1144. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6708.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman B. Identification of underprivileged areas. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 May 28;286(6379):1705–1709. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6379.1705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone A. E., Jewell J. A., Robson J. Twenty four hour care in inner cities: two years' out of hours workload in east London general practice. BMJ. 1989 Aug 5;299(6695):368–370. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6695.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle M. The quality divide in primary care. BMJ. 1989 Aug 19;299(6697):470–471. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6697.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot R. J. Underprivileged areas and health care planning: implications of use of Jarman indicators of urban deprivation. BMJ. 1991 Feb 16;302(6773):383–386. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6773.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P., Balarajan R. Unemployment and patterns of consultation with the general practitioner. BMJ. 1989 May 6;298(6682):1212–1214. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6682.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]