Abstract
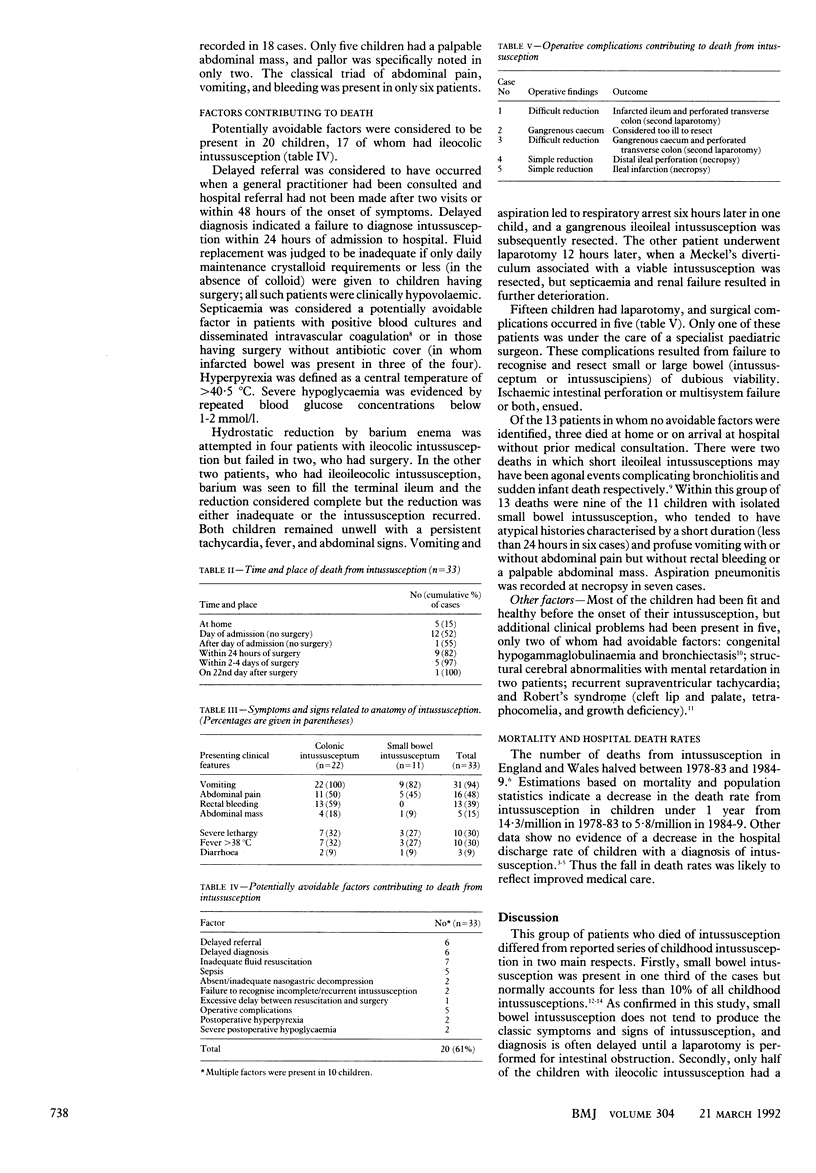
OBJECTIVE--To assess the incidence of potentially avoidable factors contributing to death of children with intussusception. DESIGN--Review of children who died with intussusception in England and Wales between 1984 and 1989 from data of the Office of Population Censuses and Surveys, case notes, coroners' records, and necropsy reports. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Unambiguous objective criteria such as failure to diagnose intussusception within 24 hours of admission. RESULTS--33 children died of acute intussusception in England and Wales between 1984 and 1989 compared with 67 in the previous six years. Their median age was 7 months (range 2 months to 12 years), and two thirds were boys. Half of the deaths occurred at home or soon after arrival at hospital but 15 patients had surgery. Potentially avoidable factors contributing to death were identified in 20 (61%) children, all but three of whom had ileocolic intussusception. These factors were excessive delay in diagnosis, inadequate intravenous fluid and antibiotic therapy, delay in recognising recurrent or residual intussusception after hydrostatic reduction, and surgical complications. Of the 13 patients in whom no avoidable factors were identified, there were nine of 11 children with isolated small bowel intussusception, who tended to have atypical presentations. CONCLUSION--Although the mortality from intussusception has declined, there remains ample opportunity for improved management.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beasley S. W., Auldist A. W., Stokes K. B. Recurrent intussusception: barium or surgery? Aust N Z J Surg. 1987 Jan;57(1):11–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1987.tb01231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce J., Huh Y. S., Cooney D. R., Karp M. P., Allen J. E., Jewett T. C., Jr Intussusception: evolution of current management. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1987 Sep-Oct;6(5):663–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennison W. M., Shaker M. Intussusception in infancy and childhood. Br J Surg. 1970 Sep;57(9):679–684. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800570912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ein S. H., Stephens C. A. Intussusception: 354 cases in 10 years. J Pediatr Surg. 1971 Feb;6(1):16–27. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(71)90663-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ein S. H., Stephens C. A., Minor A. The painless intussusception. J Pediatr Surg. 1976 Aug;11(4):563–564. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(76)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklöf O., Hartelius H. Reliability of the abdominal plain film diagnosis in pediatric patients with suspected intussusception. Pediatr Radiol. 1980 Jul;9(4):199–206. doi: 10.1007/BF01092945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch S. J., Magill H. L., Benator R. M., Parvey L. S., Hixson S. D. Pseudoreduction of intussusception: is ileal reflux the end point? Gastrointest Radiol. 1985;10(2):181–183. doi: 10.1007/BF01893098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund G. L., Johnson J. F., Strife J. L. Ileocolic intussusception: extensive reflux of air preceding pneumatic reduction. Radiology. 1990 Jan;174(1):187–189. doi: 10.1148/radiology.174.1.2294546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey R. W., Sodhi S. K., Johnson W. R. Two children with lethargy and intussusception. Ann Emerg Med. 1990 Apr;19(4):390–392. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(05)82343-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison I. F., Olayiwola B., Young D. G. Intussusception in infancy and childhood. Br J Surg. 1980 Mar;67(3):209–212. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800670314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon J. R. Multiple "agonal" intussusception of the small bowel. J Ir Med Assoc. 1974 Mar 9;67(5):134–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palder S. B., Ein S. H., Stringer D. A., Alton D. Intussusception: barium or air? J Pediatr Surg. 1991 Mar;26(3):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(91)90501-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger H. G., Buchan R. Deaths in children with acute appendicitis. Br Med J. 1969 Nov 22;4(5681):466–470. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5681.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger H. G., Fahy L. T., van Mourik G. A., Bush G. H. Deaths in children with a diagnosis of acute appendicitis in England and Wales 1980-4. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Nov 14;295(6608):1233–1235. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6608.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pracros J. P., Tran-Minh V. A., Wright C. Ultrasound in diagnosis of intussusception. Lancet. 1985 Sep 28;2(8457):733–734. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92979-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparnon A. L., Little K. E., Morris L. L. Intussusception in childhood: a review of 139 cases. Aust N Z J Surg. 1984 Aug;54(4):353–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1984.tb05332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steyn J., Kyle J. Epidemiology of Acute Intussusception. Br Med J. 1961 Jun 17;1(5241):1730–1732. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5241.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West K. W., Stephens B., Vane D. W., Grosfeld J. L. Intussusception: current management in infants and children. Surgery. 1987 Oct;102(4):704–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


