Abstract
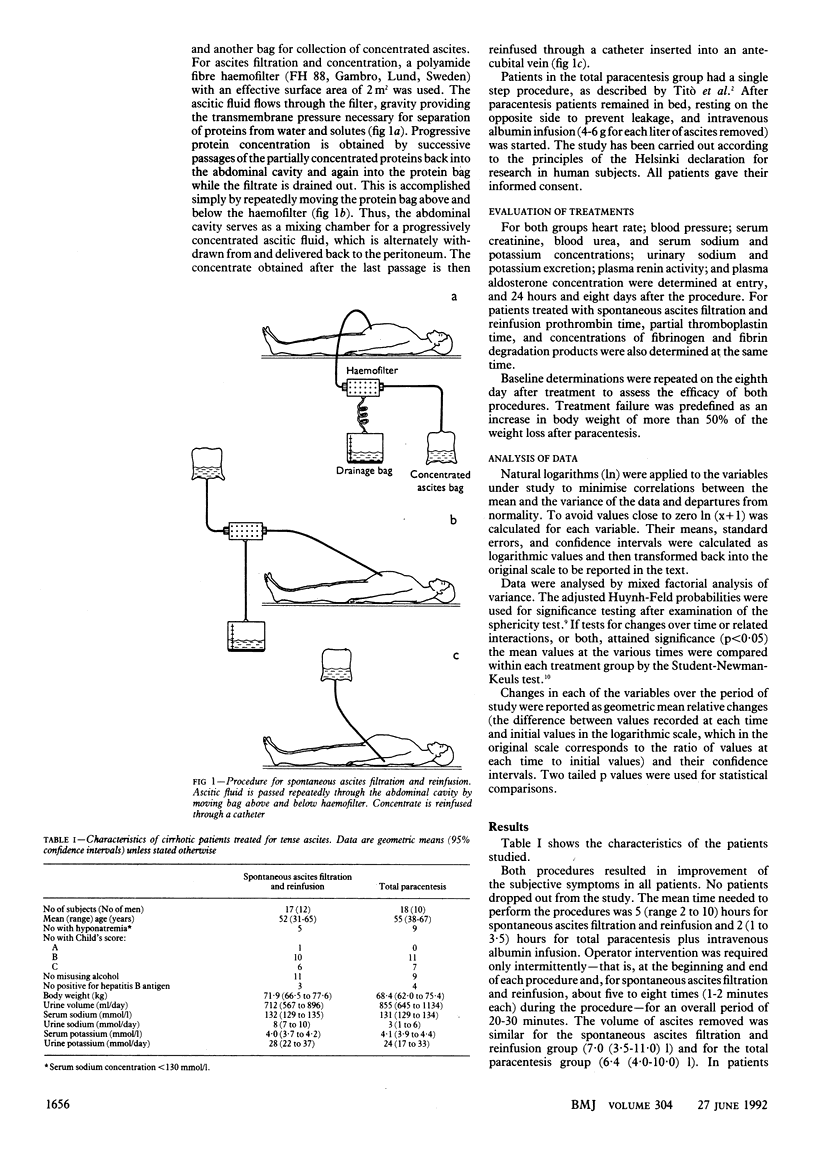
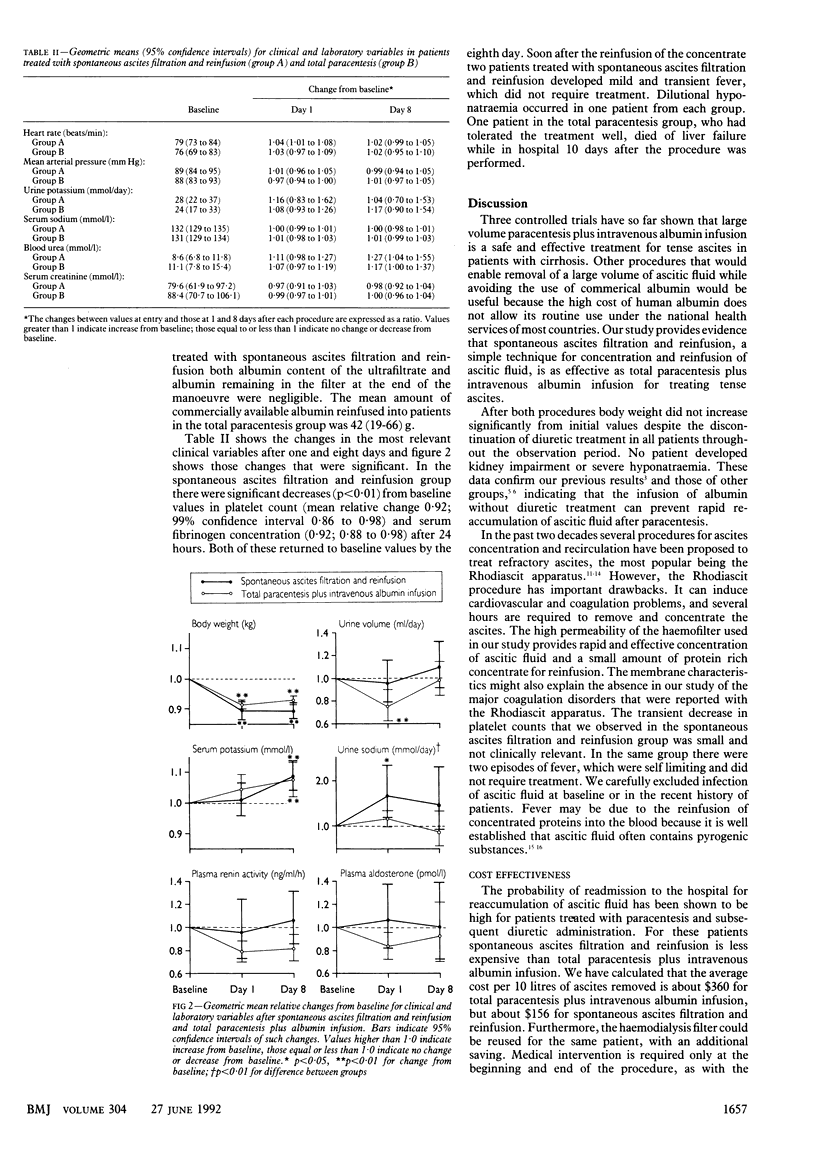
OBJECTIVE--To compare the effectiveness and safety of spontaneous ascites filtration and reinfusion and total paracentesis plus intravenous albumin infusion in cirrhotic patients with tense ascites. DESIGN--Randomised trial of the two treatments. SETTING--Teaching hospital and district general hospital in Milan. PATIENTS--45 consecutive cirrhotic patients with recurrent tense ascites and urinary sodium excretion rate less than 20 mmol/day. 35 fulfilled admission criteria and completed the study. 17 received spontaneous ascites filtration and 18 paracentesis plus albumin infusion. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Body weight; urinary volume; serum and urinary electrolyte, serum fibrinogen, and plasma aldosterone concentrations; and plasma renin activity before the procedure and 24 hours and eight days afterwards. RESULTS--Both procedures were effective in all patients. Weight decreased in both groups and showed no substantial increase after eight days. In patients receiving ascites filtration, values decreased significantly (p less than 0.01) after 24 hours for platelet count (mean relative change 0.92; 99% confidence interval 0.86 to 0.98) and serum fibrinogen concentration (0.92; 0.88 to 0.98) but returned to pretreatment values after eight days; no laboratory and clinical signs of disseminated intravascular coagulation were noted. Three patients in this group had fever, which receded spontaneously. One patient in each group had dilutional hyponatraemia. CONCLUSIONS--Spontaneous ascites filtration and reinfusion is an effective treatment for tense ascites. Reinfusion of the patient's concentrated proteins provides savings without compromising safety.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansley J. D., Bethel R. A., Bowen P. A., 2nd, Warren W. D. Effect of peritoneovenous shunting with the Le Veen valve on ascites, renal function, and coagulation in six patients with intractable ascites. Surgery. 1978 Feb;83(2):181–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginès P., Titó L., Arroyo V., Planas R., Panés J., Viver J., Torres M., Humbert P., Rimola A., Llach J. Randomized comparative study of therapeutic paracentesis with and without intravenous albumin in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jun;94(6):1493–1502. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90691-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginés P., Arroyo V., Quintero E., Planas R., Bory F., Cabrera J., Rimola A., Viver J., Camps J., Jiménez W. Comparison of paracentesis and diuretics in the treatment of cirrhotics with tense ascites. Results of a randomized study. Gastroenterology. 1987 Aug;93(2):234–241. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)91007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortenson R. A., Lawton R. L. Surgical treatment for intractable ascites. Am J Surg. 1968 Dec;116(6):929–931. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(68)90469-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planas R., Ginès P., Arroyo V., Llach J., Panés J., Vargas V., Salmerón J. M., Ginès A., Toledo C., Rimola A. Dextran-70 versus albumin as plasma expanders in cirrhotic patients with tense ascites treated with total paracentesis. Results of a randomized study. Gastroenterology. 1990 Dec;99(6):1736–1744. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90481-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runyon B. A., Canawati H. N., Akriviadis E. A. Optimization of ascitic fluid culture technique. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1351–1355. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90372-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salerno F., Badalamenti S., Incerti P., Tempini S., Restelli B., Bruno S., Bellati G., Roffi L. Repeated paracentesis and i.v. albumin infusion to treat 'tense' ascites in cirrhotic patients. A safe alternative therapy. J Hepatol. 1987 Aug;5(1):102–108. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salerno F., Badalamenti S., Lorenzano E., Moser P., Incerti P. Randomized comparative study of hemaccel vs. albumin infusion after total paracentesis in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites. Hepatology. 1991 Apr;13(4):707–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff E. R. Paracentesis: a safe and effective form of therapy. Hepatology. 1987 May-Jun;7(3):591–592. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D. M., McCain J. R., Bonkovsky H. L., Wells J. O., Hartle D. K., Galambos J. T. Effects of therapeutic paracentesis on systemic and hepatic hemodynamics and on renal and hormonal function. Hepatology. 1987 May-Jun;7(3):423–429. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart H. L., Triger D. R. A randomised prospective trial comparing daily paracentesis and intravenous albumin with recirculation in diuretic refractory ascites. J Hepatol. 1990 Mar;10(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(90)90051-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawes R. L., Jr, Sydorak G. R., Kennedy P. A., Brown W. H., Scribner R. G., Beare J. P., Harris E. J. Coagulopathy associated with peritoneovenous shunting. Am J Surg. 1981 Jul;142(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(81)80011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titó L., Ginès P., Arroyo V., Planas R., Panés J., Rimola A., Llach J., Humbert P., Badalamenti S., Jiménez W. Total paracentesis associated with intravenous albumin management of patients with cirrhosis and ascites. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jan;98(1):146–151. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91303-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde J. T., Cooper P., Kennedy H. J., Triger D. R., Preston F. E. Coagulation disturbances following ascites recirculation. J Hepatol. 1990 Mar;10(2):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(90)90055-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. P., Davidson A. R., Henderson J., Williams R. Ascites reinfusion using Rhodiascit apparatus--clinical experience and coagulation abnormalities. Postgrad Med J. 1975 Aug;51(598):583–587. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.51.598.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


