Abstract
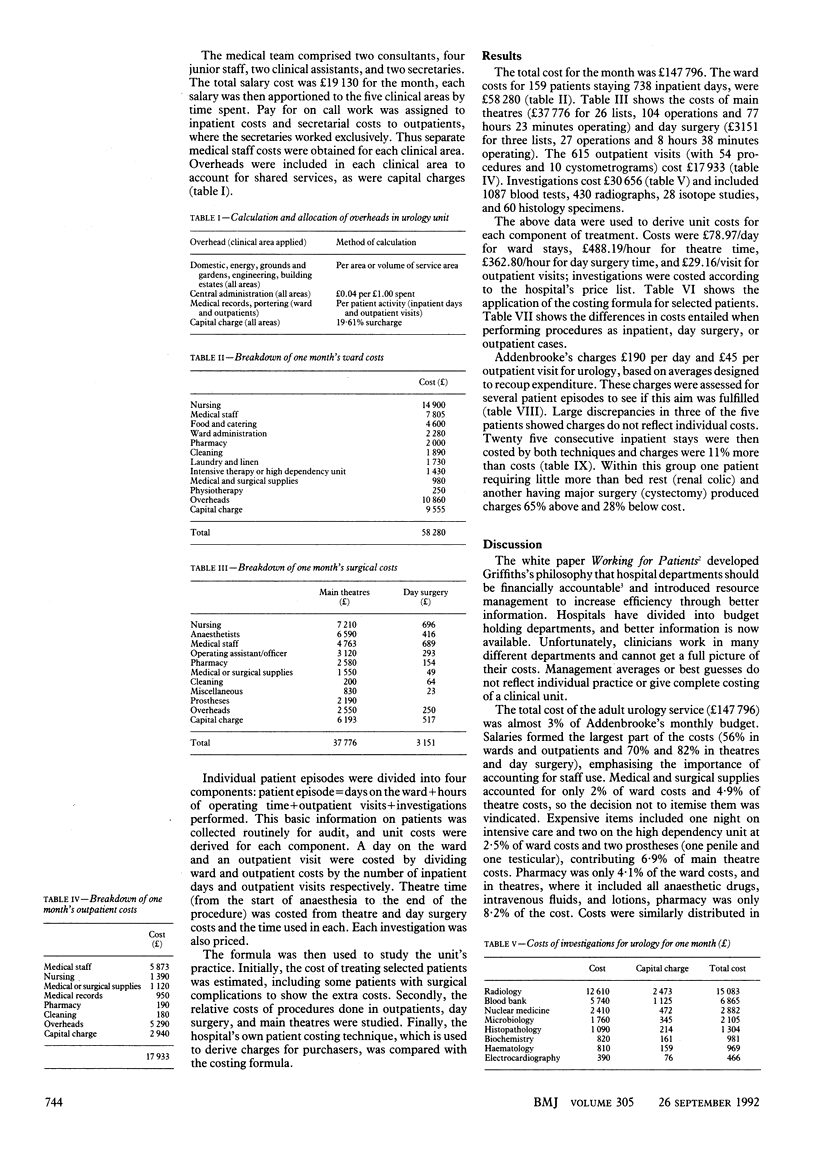
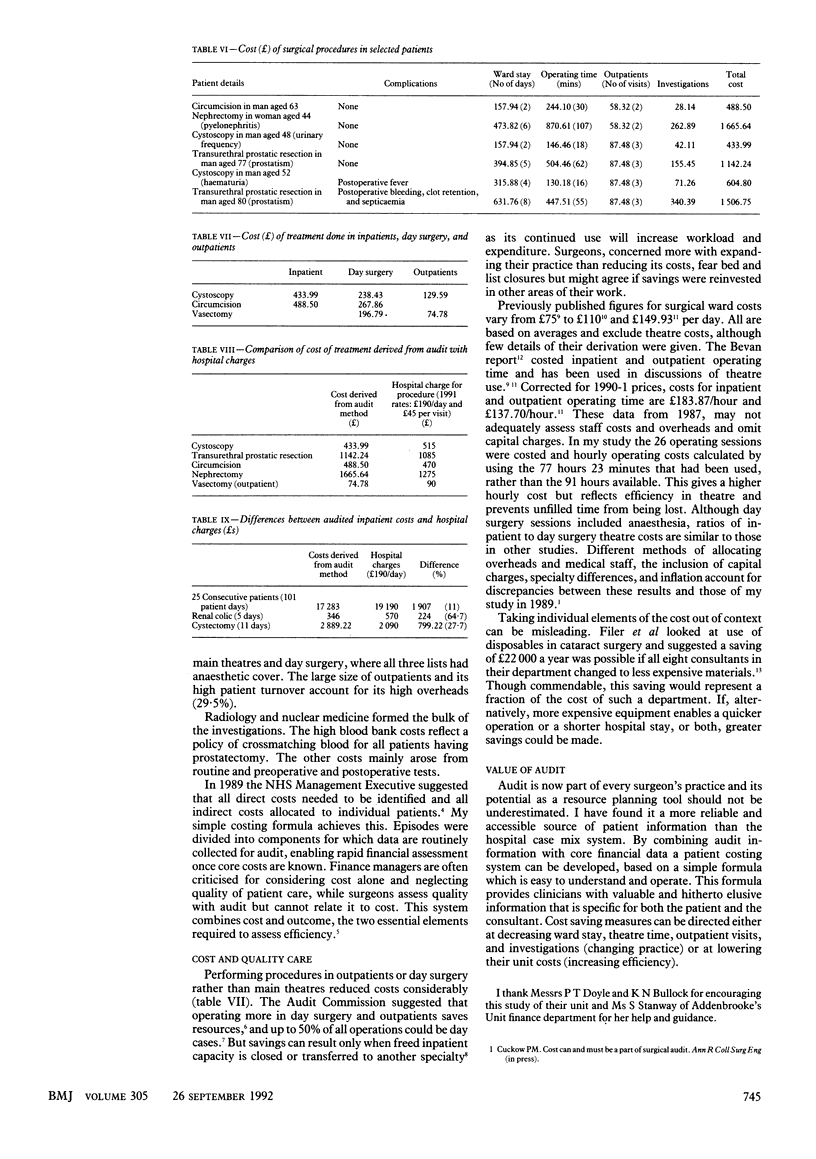
OBJECTIVES--To cost a clinical unit over one month in 1991, to cost treatment of individual patients from audit data, and to compare this costing method with the hospital charging system. DESIGN--A financial breakdown was obtained for one month's work. Ward stay, operating time, investigations, and outpatient visits were costed and a formula (episode = days on ward+hours of operating+investigations+outpatient visits) was used to cost patient episodes from audit data. SETTING--The adult urology unit in a teaching hospital. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Costs for each part of patients' treatment. RESULTS--Total cost was 147,796 pounds for 159 admissions, 738 inpatient days, 131 operations in 29 operating lists, and 615 outpatient visits. An uncomplicated transurethral prostatectomy cost 1140 pounds but complications increased this to 1500 pounds in another patient. The costs of diagnostic cystoscopy were 130 pounds in outpatients, 240 pounds in day surgery, and 430 pounds in inpatients. Hospital charges do not reflect the individual costs of treatment, charges being greater than costs for some patients and lower than costs for others. CONCLUSIONS--Clinicians can produce a financial analysis of their work and cost their patients' treatment. Audit is strongly advocated as a resource planning tool.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry M. G., Briggs T. P., Parker C., Miller R. A. Beds or day case unit: your choice? Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1991 Nov;73(6 Suppl):114–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn J. M. Responsible use of resources: day surgery. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Feb 5;286(6363):492–493. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6363.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis B. W., Rivett R. C., Dudley H. A. Extending the use of clinical audit data: a resource planning model. BMJ. 1990 Jul 21;301(6744):159–162. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6744.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filer J., Roberts-Harry T. J., Jagger J. D. Cutting the cost of cataract surgery--a financial audit. Br J Ophthalmol. 1991 Apr;75(4):227–228. doi: 10.1136/bjo.75.4.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J., Mooney G. What every doctor should know about economics. Part 1. The benefits of costing. Med J Aust. 1990 Jan 1;152(1):29–31. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1990.tb124425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opit L. J., Collins R. E., Campbell G. Use of operating theatres: the effects of case-mix and training in general surgery. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1991 Nov;73(6):389–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


