Abstract
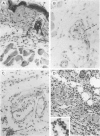
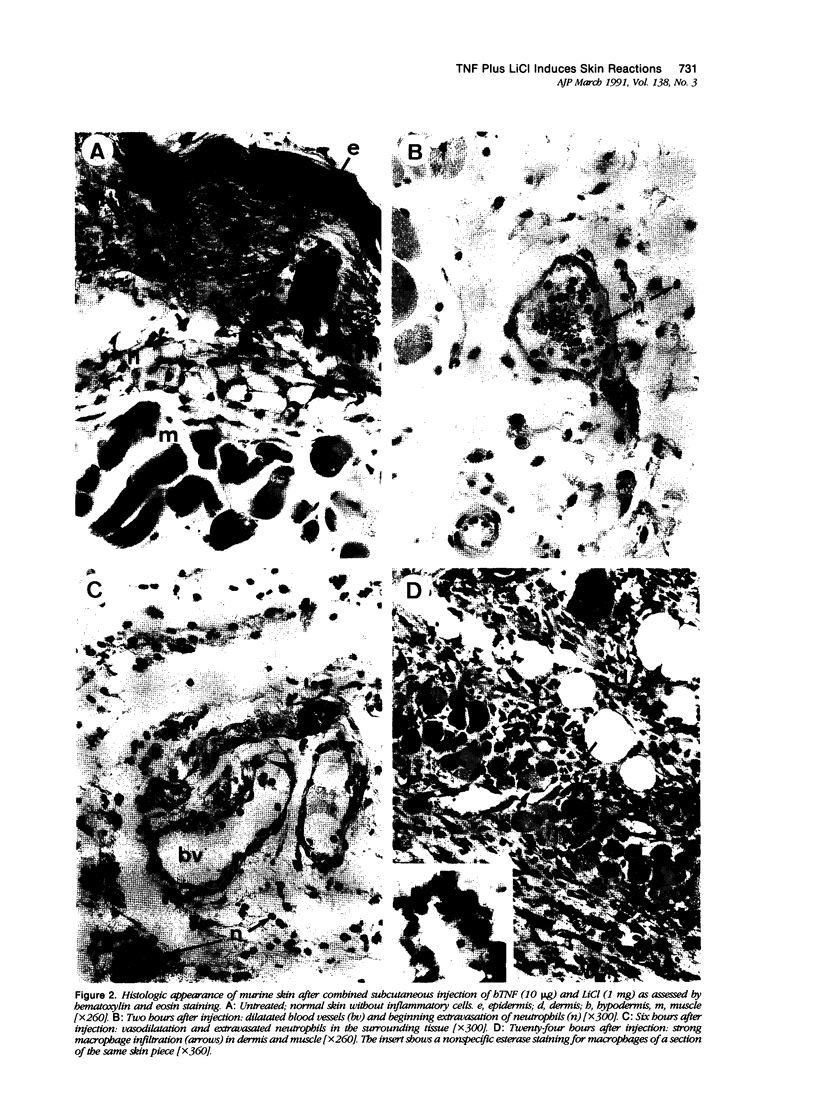
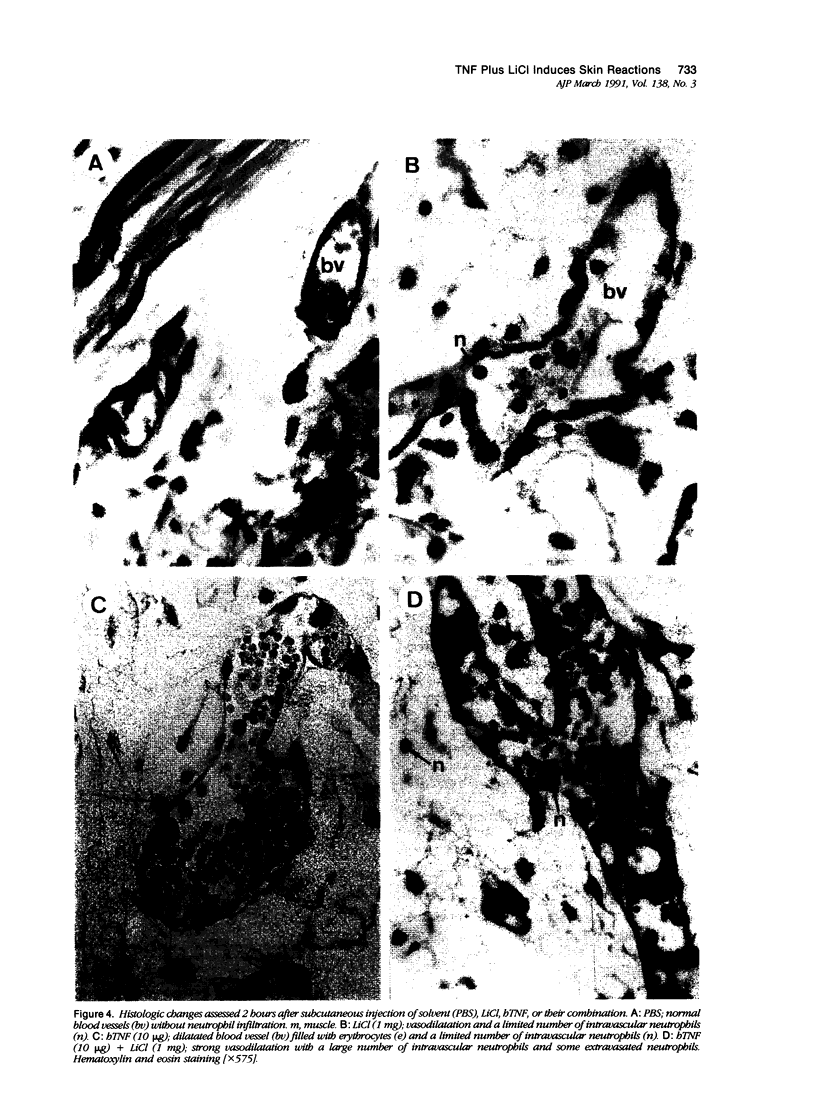
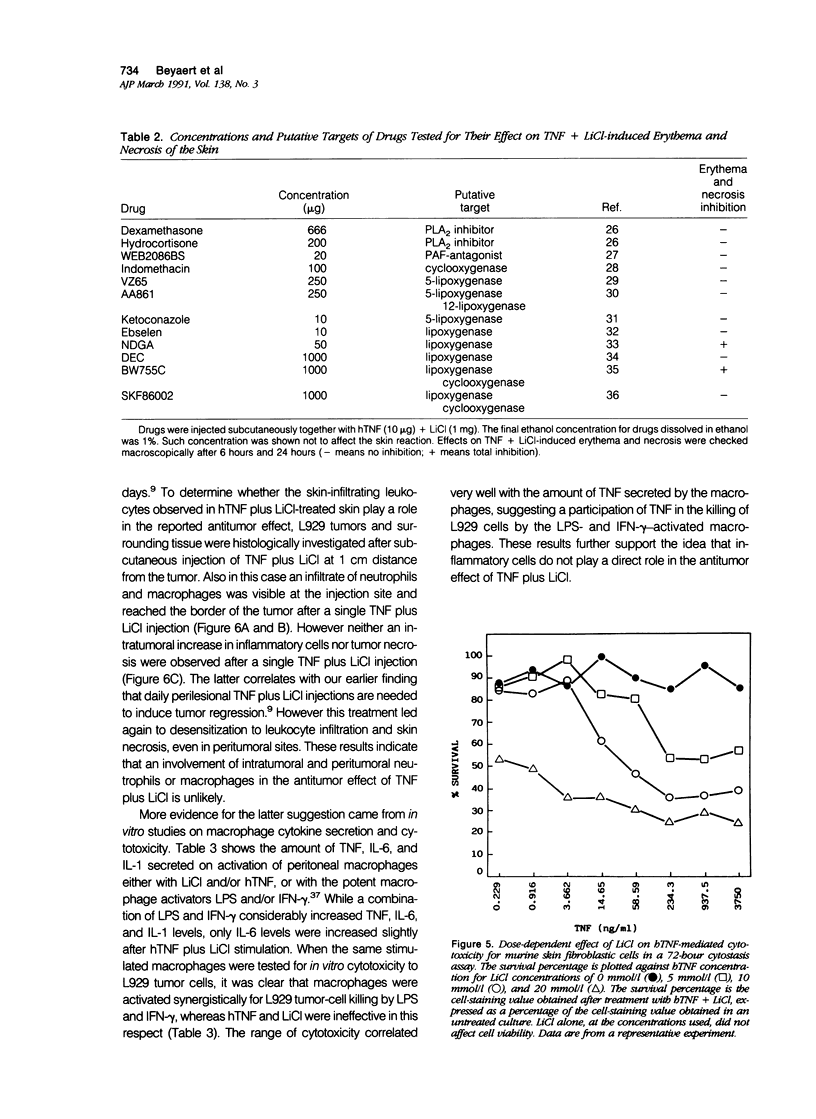
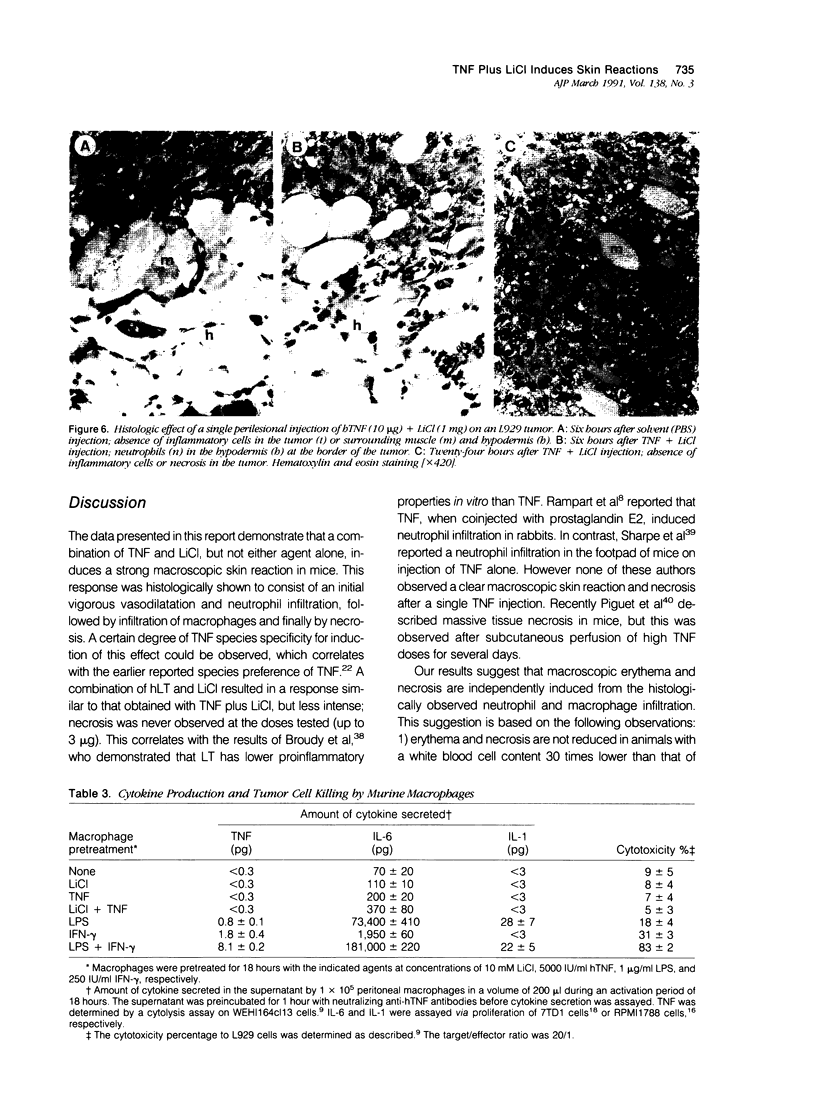
Previously we reported that lithium chloride (LiCl) potentiates tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Here, using a murine normal skin model, it is shown that a subcutaneous injection of TNF plus LiCl induces acute dermal and subcutaneous inflammation and necrosis. Histology showed a marked initial dermal and subcutaneous neutrophil infiltrate by approximately 2 hours, followed by a predominantly mononuclear infiltrate by 24 hours, which remained present for several days. Tumor necrosis factor or LiCl alone induced negligible inflammation, disappearing after 6 hours; furthermore there was never necrosis or ulceration of the overlying skin in case of single-agent application. In vitro studies showed that the combination of TNF and LiCl, but not either agent alone, was directly cytotoxic to fibroblastic cells of murine skin. No inflammatory infiltration was visible in tumors treated intratumorally or perilesionally with TNF plus LiCl, although the latter treatment resulted in a perilesional leukocyte infiltration. Furthermore the combination of TNF and LiCl had no effect on macrophage cytotoxicity to L929 tumors.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R. Studies with inhibitors of sulfidopeptide leukotriene synthesis. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;199:85–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beetens J. R., Loots W., Somers Y., Coene M. C., De Clerck F. Ketoconazole inhibits the biosynthesis of leukotrienes in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Mar 15;35(6):883–891. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. A., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: production, distribution, and metabolic fate in vivo. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3972–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Mahoney J., Le Trang N., Pekala P., Cerami A. Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):984–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyaert R., Vanhaesebroeck B., Suffys P., Van Roy F., Fiers W. Lithium chloride potentiates tumor necrosis factor-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9494–9498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Flower R. J., Langham C. S., Parente L., Persico P., Russel-Smith N. C., Stone D. Glucocorticoids induce the formation and release of anti-inflammatory and anti-phospholipase proteins into the peritoneal cavity of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 May;76(1):185–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09205.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield F. J., Young M. M. Enhanced release of inflammatory mediators from lithium-stimulated neutrophils in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1983 Jul;109(1):9–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1983.tb03985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouckaert P., Spriggs D. R., Demetri G., Kufe D. W., Fiers W. Circulating interleukin 6 during a continuous infusion of tumor necrosis factor and interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2257–2262. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broudy V. C., Harlan J. M., Adamson J. W. Disparate effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha/cachectin and tumor necrosis factor-beta/lymphotoxin on hematopoietic growth factor production and neutrophil adhesion molecule expression by cultured human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4298–4302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Tetta C., Bussolino F., Baglioni C. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates human neutrophils to release leukotriene B4 and platelet-activating factor. Induction of phospholipase A2 and acetyl-CoA:1-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine O2-acetyltransferase activity and inhibition by antiproteinase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jul 1;182(3):661–666. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casals-Stenzel J., Muacevic G., Weber K. H. Pharmacological actions of WEB 2086, a new specific antagonist of platelet activating factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jun;241(3):974–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Suzuki Y., Wheelock E. F. Interferon-gamma synergizes with tumor necrosis factor and with interleukin 1 and requires the presence of both monokines to induce antitumor cytotoxic activity in macrophages. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4096–4101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2163–2168. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLamarter J. F., Mermod J. J., Liang C. M., Eliason J. F., Thatcher D. R. Recombinant murine GM-CSF from E. coli has biological activity and is neutralized by a specific antiserum. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2575–2581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03973.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deandrea D., Walker N., Mehlmauer M., White K. Dermatological reactions to lithium: a critical review of the literature. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1982 Jun;2(3):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Opsomer C., Scahill S. J., Van der Heyden J., Fiers W. Purification of recombinant glycosylated human gamma interferon expressed in transformed Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Interferon Res. 1984 Fall;4(4):461–468. doi: 10.1089/jir.1984.4.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M., Christanthou A., Fletcher A., Veroni M., Woodman P., Larkins R. Effects of inhibitors of eicosanoid synthesis on insulin release by neonatal pancreatic islets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 7;801(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90206-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza I., Männel D., Ruppel A., Falk W., Krammer P. H. Interferon gamma and lymphotoxin or tumor necrosis factor act synergistically to induce macrophage killing of tumor cells and schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):589–594. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen L., Müller R., Marmenout A., Tavernier J., Van der Heyden J., Kawashima E., Chollet A., Tizard R., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Vliet A. Molecular cloning of mouse tumour necrosis factor cDNA and its eukaryotic expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4417–4429. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen L., Van der Heyden J., Ruysschaert R., Fiers W. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor: its effect and its synergism with interferon-gamma on a variety of normal and transformed human cell lines. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1986 Apr;22(4):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(86)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing A. J., Fincham N. J., Bird C. R., Wadhwa M., Meager A., Cartwright J. E., Camp R. D. Cytokines in skin lesions of psoriasis. Cytokine. 1990 Jan;2(1):68–75. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90045-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griswold D. E., Marshall P. J., Webb E. F., Godfrey R., Newton J., Jr, DiMartino M. J., Sarau H. M., Gleason J. G., Poste G., Hanna N. SK&F 86002: a structurally novel anti-inflammatory agent that inhibits lipoxygenase- and cyclooxygenase-mediated metabolism of arachidonic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 15;36(20):3463–3470. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90327-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. A., Groenewoud Y., Chamberland S. Characterization of lithium-induced enzyme release from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;64(9):880–885. doi: 10.1139/o86-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Flower R. J., Vane J. R. A new approach to anti-inflammatory drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jun 15;28(12):1959–1961. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90651-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Inamitsu T., Hashimoto T., Koga T. An inhibitor of lipoxygenase, nordihydroguaiaretic acid, shortens actin filaments. J Biochem. 1984 Mar;95(3):891–894. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinerman E. S., Knowles R. D., Blick M. B., Zwelling L. A. Lithium chloride stimulates human monocytes to secrete tumor necrosis factor/cachectin. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Nov;46(5):484–492. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.5.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer S. M., Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., McCabe S. M., Ferraiolo B. L., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Characterization of the in vitro and in vivo species preference of human and murine tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):920–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl F. A., Jr, Egan R. W. Prostaglandins, arachidonic acid, and inflammation. Science. 1980 Nov 28;210(4473):978–984. doi: 10.1126/science.6254151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. Y., Lam K. W., Yam L. T. Esterases in human leukocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):1–12. doi: 10.1177/21.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: characterization of priming and trigger signals during lymphokine activation. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke V., Bauman J. G., Sticherling M., Ibs T., Zomershoe A. G., Seligmann K., Henneicke H. H., Schröder J. M., Sterry W., Christophers E. Detection of neutrophil-activating peptide NAP/IL-8 and NAP/IL-8 mRNA in human recombinant IL-1 alpha- and human recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated human dermal fibroblasts. An immunocytochemical and fluorescent in situ hybridization study. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):153–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming W. J., Bersani L., Mantovani A. Tumor necrosis factor is chemotactic for monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1469–1474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrove J. M., Gifford G. E. Stimulation of RNA synthesis in L-929 cells by rabbit tumor necrosis factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Mar;160(3):354–358. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palombella V. J., Vilcek J. Mitogenic and cytotoxic actions of tumor necrosis factor in BALB/c 3T3 cells. Role of phospholipase activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18128–18136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez H. D., Kaplan H. B., Goldstein I. M., Shenkman L., Borkowsky W. Reversal of an abnormality of polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemotaxis with lithium. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Jul;16(3):308–315. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R., Epstein L. B. Tumour necrosis factor as immunomodulator and mediator of monocyte cytotoxicity induced by itself, gamma-interferon and interleukin-1. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):86–89. doi: 10.1038/323086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Grau G. E., Vassalli P. Subcutaneous perfusion of tumor necrosis factor induces local proliferation of fibroblasts, capillaries, and epidermal cells, or massive tissue necrosis. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):103–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S. Effects of tumour necrosis factor and related cytokines on vascular endothelial cells. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;131:170–184. doi: 10.1002/9780470513521.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampart M., De Smet W., Fiers W., Herman A. G. Inflammatory properties of recombinant tumor necrosis factor in rabbit skin in vivo. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2227–2232. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. L., Lint T. F., Schreiber H. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin. Induction of hemorrhagic necrosis in normal tissue requires the fifth component of complement (C5). J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2007–2021. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. L., Schreiber H. Synergy between tumor necrosis factor and bacterial products causes hemorrhagic necrosis and lethal shock in normal mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):607–611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safayhi H., Tiegs G., Wendel A. A novel biologically active seleno-organic compound--V. Inhibition by ebselen (PZ 51) of rat peritoneal neutrophil lipoxygenase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Aug 1;34(15):2691–2694. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90569-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scahill S. J., Devos R., Van der Heyden J., Fiers W. Expression and characterization of the product of a human immune interferon cDNA gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4654–4658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade U. F., Ernst M., Reinke M., Wolter D. T. Lipoxygenase inhibitors suppress formation of tumor necrosis factor in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):748–754. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe R. J., Margolis R. J., Askari M., Amento E. P., Granstein R. D. Induction of dermal and subcutaneous inflammation by recombinant cachectin/tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha) in the mouse. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Oct;91(4):353–357. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12475754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suffys P., Beyaert R., Van Roy F., Fiers W. TNF in combination with interferon-gamma is cytotoxic to normal, untransformed mouse and rat embryo fibroblast-like cells. Anticancer Res. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):167–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington F. W. Lymphotoxin, tumor necrosis factor, and gamma interferon are cytostatic for normal human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Jun;92(6):798–805. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12696816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAPPEL A. L., LUNDBERG W. O., BOYER P. D. Effect of temperature and antioxidants upon the lipoxidase-catalyzed oxidation of sodium linoleate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Feb;42(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada H., Shiho O., Kuroshima K., Koyama M., Tsukamoto K. An improved colorimetric assay for interleukin 2. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 6;93(2):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenabeele P., Declercq W., Libert C., Fiers W. Development of a simple, sensitive and specific bioassay for interleukin-1 based on the proliferation of RPMI 1788 cells. Comparison with other bioassays for IL-1. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Dec 31;135(1-2):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90252-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Peck M. J. Role of prostaglandin-mediated vasodilatation in inflammation. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):530–532. doi: 10.1038/270530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Yokoyama C., Ochi K., Yamamoto S., Maki Y., Ashida Y., Terao S., Shiraishi M. 2,3,5-Trimethyl-6-(12-hydroxy-5,10-dodecadiynyl)-1,4-benzoquinone (AA861), a selective inhibitor of the 5-lipoxygenase reaction and the biosynthesis of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 12;713(2):470–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]