Abstract
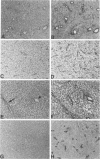
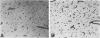
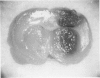
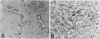
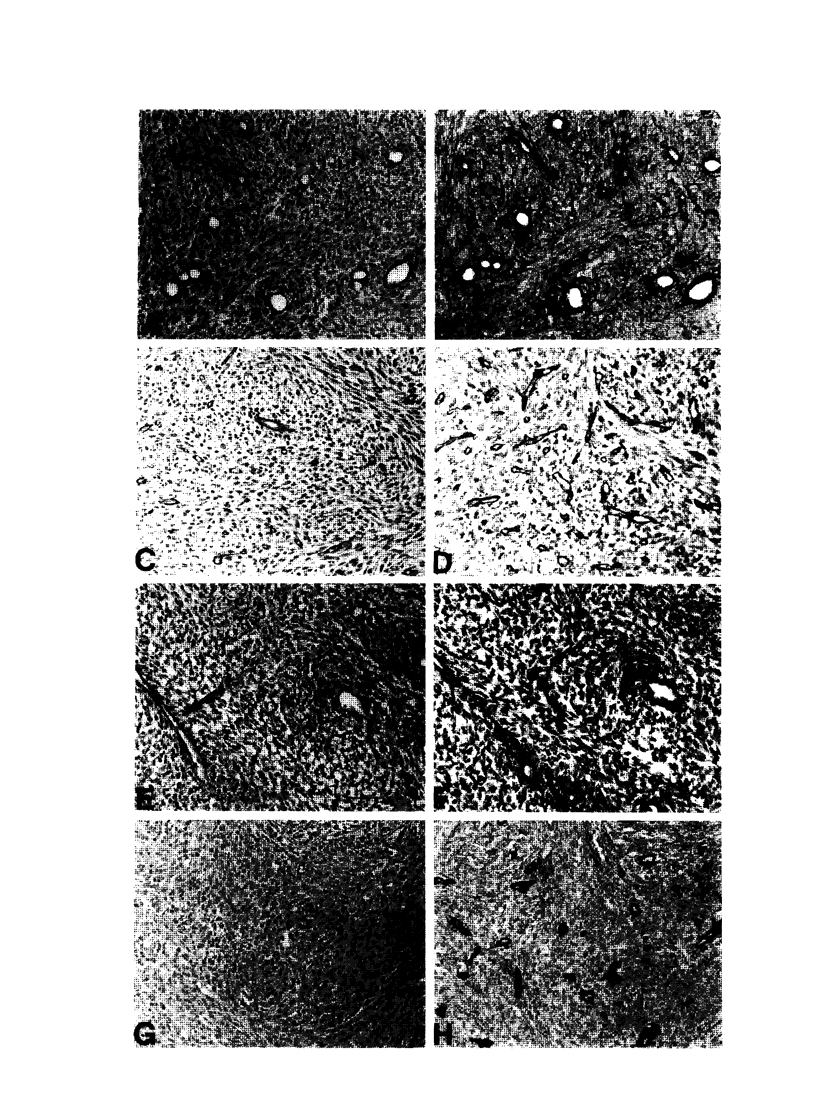
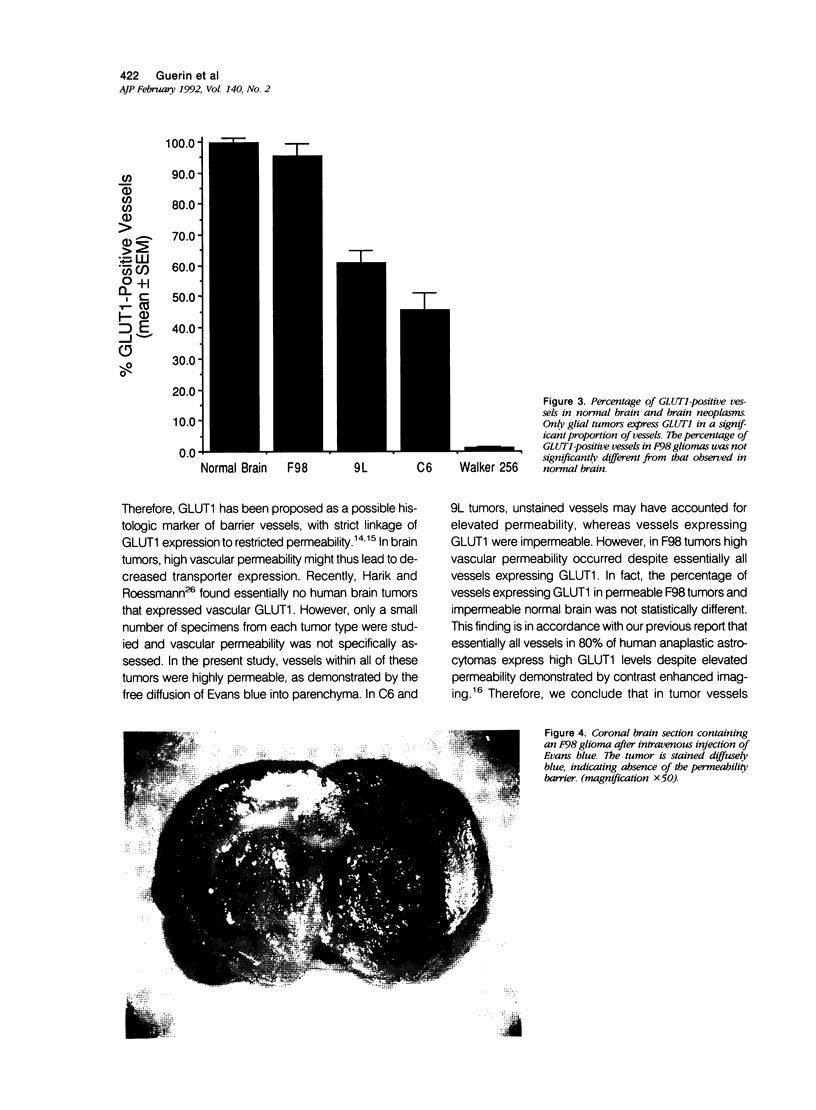
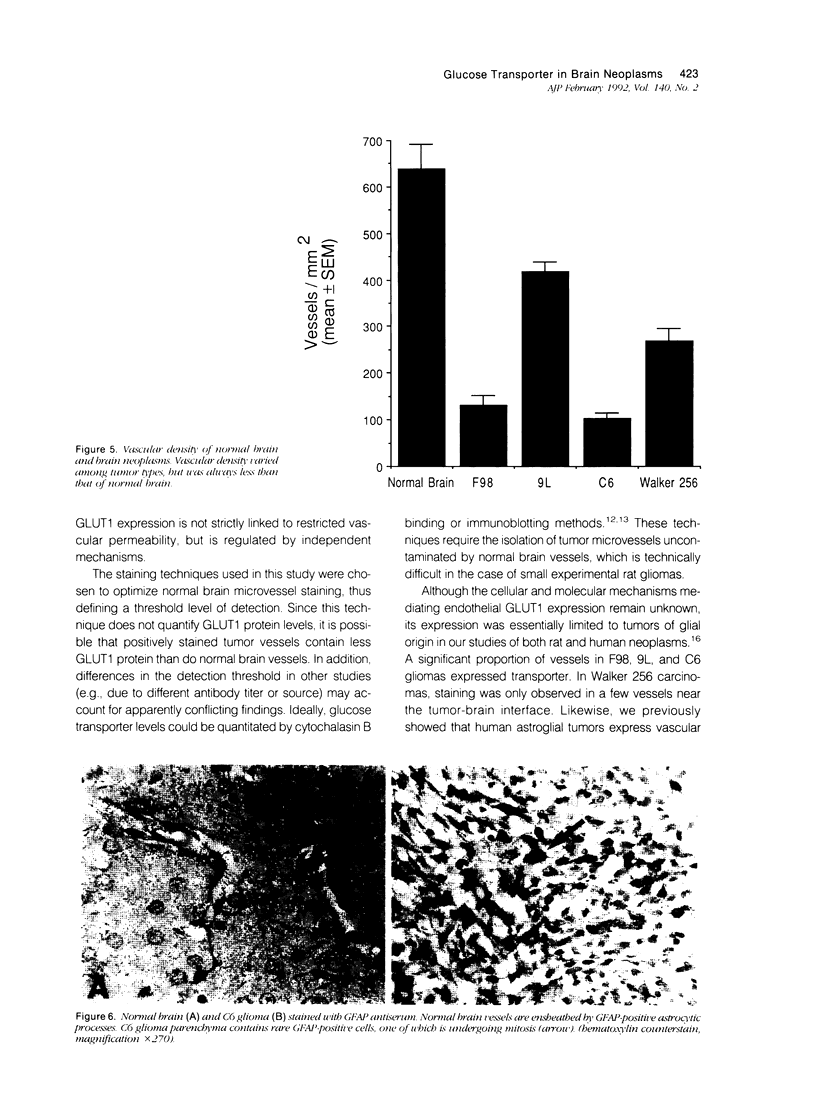
Vascular abnormalities in brain neoplasms are important to tumor biology and therapy. Glucose transporter (GLUT1) expression is a differentiated property of normal cerebral microvessels typically associated with expression of the blood-brain barrier. We investigated the relationship of GLUT1 expression to other vascular characteristics in F98, 9L, and C6 gliomas and Walker 256 carcinomas implanted into adult rat brains. The percentages of microvessels with immunohistochemically detectable GLUT1 were 95.5 +/- 3.9 in F98, 60.9 +/- 3.9 in 9L, 45.4 +/- 5.6 in C6, and 1.2 +/- 0.3 in Walker 256 (mean +/- SEM). The percentage of GLUT1-positive vessels in F98 was not statistically different from that in normal brain. GLUT1 expression was not dependent on restricted permeability as all tumors were highly permeable to Evans blue. GLUT1 expression was unrelated to vascular density, vascular morphology, and parenchymal GFAP expression. The expression of GLUT1, a marker of cerebral endothelial differentiation, is a newly described property of glial tumor vessels that may have diagnostic and prognostic significance.
Full text
PDF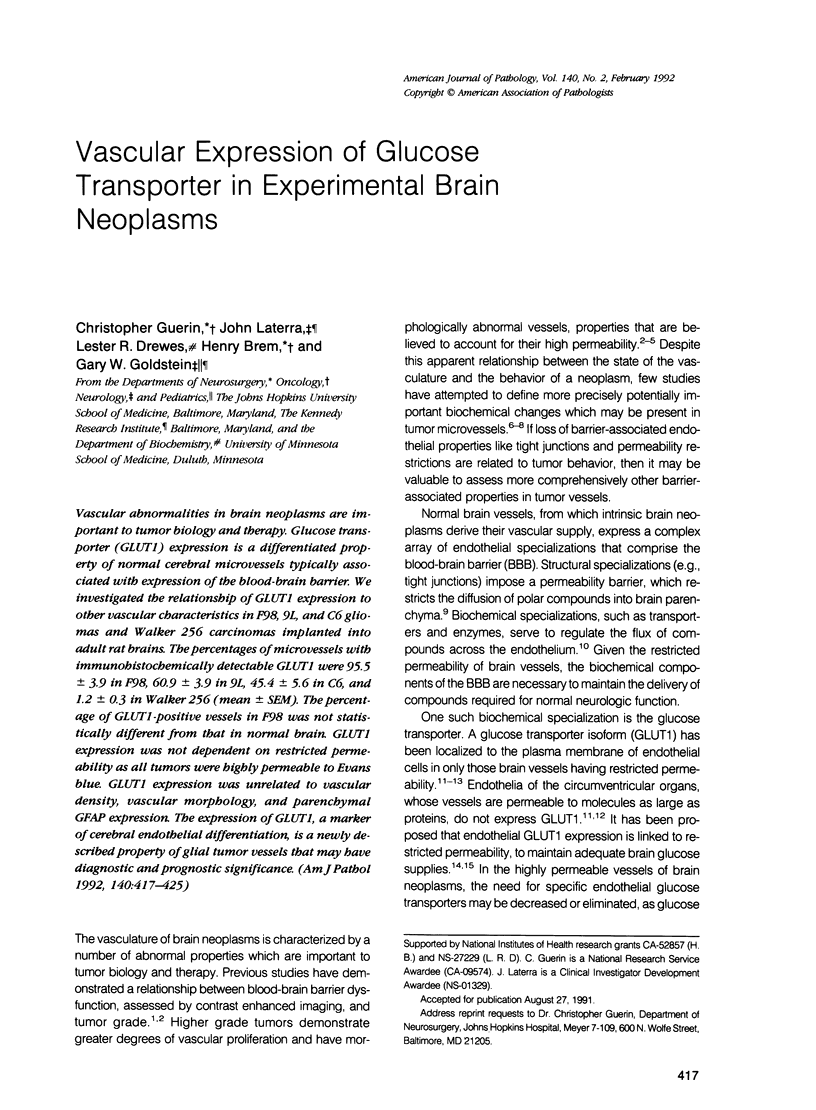





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benda P., Lightbody J., Sato G., Levine L., Sweet W. Differentiated rat glial cell strain in tissue culture. Science. 1968 Jul 26;161(3839):370–371. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3839.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell M. G., Rubinstein L. J., Bignami A., Herman M. M. Characteristics of the rat C-6 glioma maintained in organ culture systems. Production of glial fibrillary acidic protein in the absence of gliofibrillogenesis. Brain Res. 1974 Dec 20;82(1):77–89. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90894-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brem S., Cotran R., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: a quantitative method for histologic grading. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Feb;48(2):347–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A. R., Horii S. C., Kricheff I. I., Shannon M. B., Budzilovich G. N. Computed tomography in astrocytomas. A statistical analysis of the parameters of malignancy and the positive contrast-enhanced CT scan. Radiology. 1978 Nov;129(2):433–439. doi: 10.1148/129.2.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBault L. E., Cancilla P. A. gamma-Glutamyl transpeptidase in isolated brain endothelial cells: induction by glial cells in vitro. Science. 1980 Feb 8;207(4431):653–655. doi: 10.1126/science.6101511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debbage P. L., Gabius H. J., Bise K., Marguth F. Cellular glycoconjugates and their potential endogenous receptors in the cerebral microvasculature of man: a glycohistochemical study. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;46(3):425–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksdotter-Nilsson M., Björklund H., Olson L. Laminin immunohistochemistry: a simple method to visualize and quantitate vascular structures in the mammalian brain. J Neurosci Methods. 1986 Sep;17(4):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(86)90128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart D. Z., Drewes L. R. Glucose transporters at the blood-nerve barrier are associated with perineurial cells and endoneurial microvessels. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 29;508(1):46–50. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91115-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart D. Z., LeVasseur R. J., Broderius M. A., Drewes L. R. Glucose transporter localization in brain using light and electron immunocytochemistry. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Apr;22(4):464–472. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490220413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordana M. T., Germano I., Giaccone G., Mauro A., Migheli A., Schiffer D. The distribution of laminin in human brain tumors: an immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol. 1985;67(1-2):51–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00688123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G. W., Betz A. L. The blood-brain barrier. Sci Am. 1986 Sep;255(3):74–83. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0986-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerin C., Laterra J., Hruban R. H., Brem H., Drewes L. R., Goldstein G. W. The glucose transporter and blood-brain barrier of human brain tumors. Ann Neurol. 1990 Dec;28(6):758–765. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harik S. I., Kalaria R. N., Andersson L., Lundahl P., Perry G. Immunocytochemical localization of the erythroid glucose transporter: abundance in tissues with barrier functions. J Neurosci. 1990 Dec;10(12):3862–3872. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-12-03862.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harik S. I., Roessmann U. The erythrocyte-type glucose transporter in blood vessels of primary and metastatic brain tumors. Ann Neurol. 1991 May;29(5):487–491. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janzer R. C., Raff M. C. Astrocytes induce blood-brain barrier properties in endothelial cells. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):253–257. doi: 10.1038/325253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalaria R. N., Gravina S. A., Schmidley J. W., Perry G., Harik S. I. The glucose transporter of the human brain and blood-brain barrier. Ann Neurol. 1988 Dec;24(6):757–764. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko L., Koestner A., Wechsler W. Morphological characterization of nitrosourea-induced glioma cell lines and clones. Acta Neuropathol. 1980;51(1):23–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00688846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long D. M. Capillary ultrastructure and the blood-brain barrier in human malignant brain tumors. J Neurosurg. 1970 Feb;32(2):127–144. doi: 10.3171/jns.1970.32.2.0127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor J. S., Laws E. R., Jr Changes in histochemical staining of brain tumor blood vessels associated with increasing malignancy. Acta Neuropathol. 1969;14(3):161–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00685296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Boado R. J., Farrell C. R. Brain-type glucose transporter (GLUT-1) is selectively localized to the blood-brain barrier. Studies with quantitative western blotting and in situ hybridization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):18035–18040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese T. S., Karnovsky M. J. Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):207–217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidek H. H., Nielsen S. L., Schiller A. L., Messer J. Morphological studies of rat brain tumors induced by N-nitrosomethylurea. J Neurosurg. 1971 Mar;34(3):335–340. doi: 10.3171/jns.1971.34.3.0335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz R. J., Deckert M., Wechsler W. Vascularization of syngenic intracerebral RG2 and F98 rat transplantation tumors. A histochemical and morphometric study by use of ricinus communis agglutinin I. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(6):599–605. doi: 10.1007/BF00689599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata S. Ultrastructure of capillary walls in human brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78(6):561–571. doi: 10.1007/BF00691283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman C., Marks J. E. Prognostic significance of contrast enhancement in low-grade astrocytomas of the adult cerebrum. Radiology. 1981 Apr;139(1):211–213. doi: 10.1148/radiology.139.1.7208924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. A., Wiley M. J. Developing nervous tissue induces formation of blood-brain barrier characteristics in invading endothelial cells: a study using quail--chick transplantation chimeras. Dev Biol. 1981 May;84(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svendgaard N. A., Björklund A., Hardebo J. E., Stenevi U. Axonal degeneration associated with a defective blood-brain barrier in cerebral implants. Nature. 1975 May 22;255(5506):334–336. doi: 10.1038/255334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata K., Kasahara T., Kasahara M., Ezaki O., Hirano H. Erythrocyte/HepG2-type glucose transporter is concentrated in cells of blood-tissue barriers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 30;173(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao-Cheng J. H., Brightman M. W. Development of membrane interactions between brain endothelial cells and astrocytes in vitro. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1988;6(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(88)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Semple J. P., Welch W. R., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 3;324(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]