Abstract
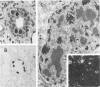
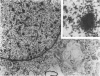
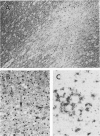
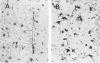
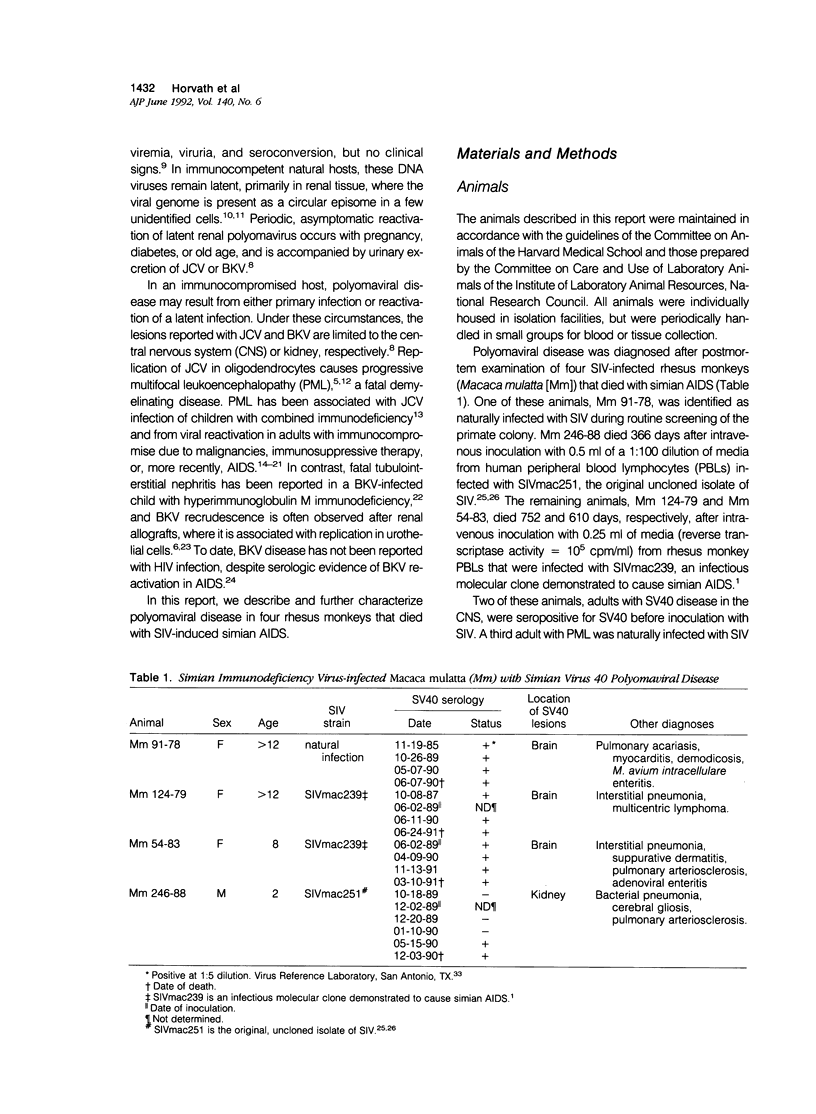
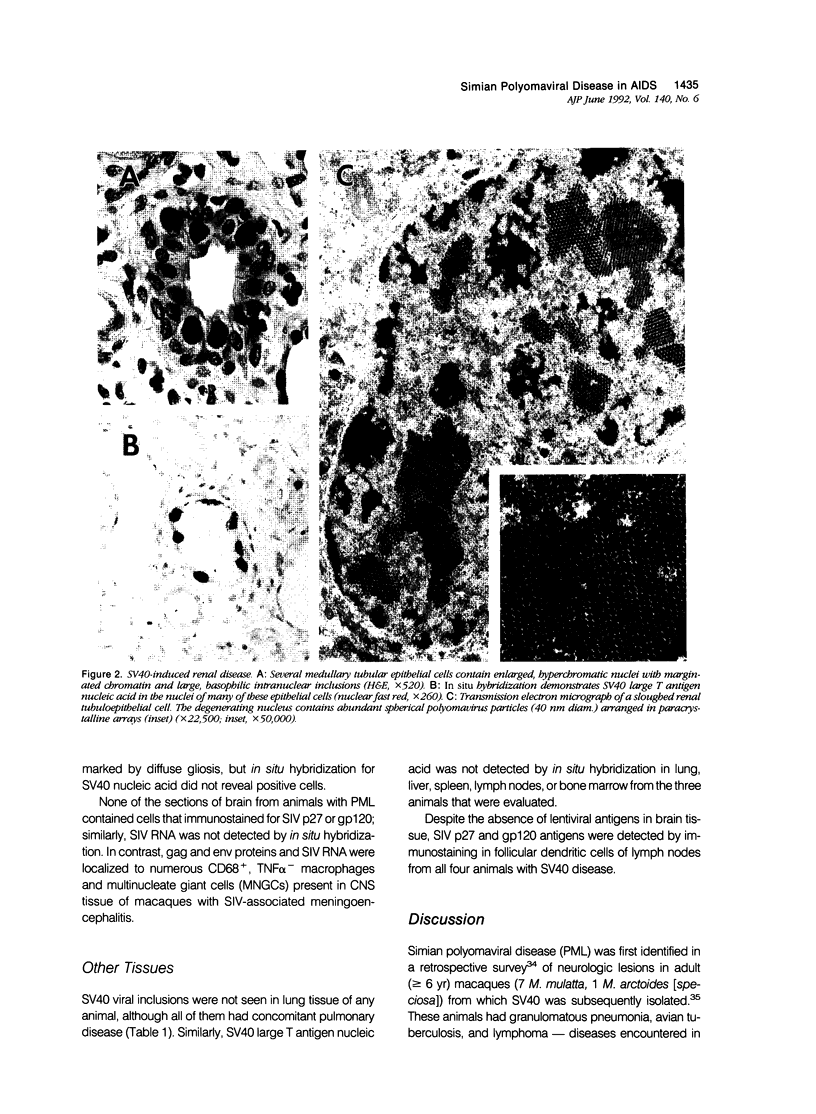
Simian virus 40 (SV40) disease was diagnosed in four rhesus monkeys that died with SIV-induced acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). One juvenile monkey seroconverted for SV40 6 months after inoculation with SIV and developed severe bilateral tubulointerstitial nephritis. In contrast, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) occurred in two adult monkeys that were seropositive for SV40 before SIV inoculation, as well as a third adult that was naturally infected with SIV and seropositive for SV40 5 years before death. Large intranuclear inclusions containing abundant polyomavirus particles were limited to either renal tubular epithelial cells or oligodendrocytes. In situ DNA hybridization for SV40 large T antigen further demonstrated that SV40 nucleic acid was localized to either kidney or brain tissue. By immunohistochemical analysis, areas of central nervous system inflammation and demyelination were shown to contain CD68+ macrophages (gitter cells), aggregates of CD8+ T lymphocytes, and numerous gemistocytic astrocytes that labeled for glial fibrillary acidic protein. These observations indicate that rhesus monkeys with SIV-induced AIDS are predisposed to polyomaviral disease, in which SV40 nucleic acid is observed in renal tissue in primary infections and brain tissue after viral reactivation. Furthermore, this organ-specific replication suggests that tissue-tropic strains of SV40 may develop in immunodeficient monkeys.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger J. R., Kaszovitz B., Post M. J., Dickinson G. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. A review of the literature with a report of sixteen cases. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Jul;107(1):78–87. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-1-78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesters P. M., Heritage J., McCance D. J. Persistence of DNA sequences of BK virus and JC virus in normal human tissues and in diseased tissues. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):676–684. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Letvin N. L., King N. W., Kannagi M., Sehgal P. K., Hunt R. D., Kanki P. J., Essex M., Desrosiers R. C. Isolation of T-cell tropic HTLV-III-like retrovirus from macaques. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1201–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.3159089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Fromental C., Augereau P., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Cell-type specific protein binding to the enhancer of simian virus 40 in nuclear extracts. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):544–548. doi: 10.1038/323544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Hansen-Moosa A., Mori K., Bouvier D. P., King N. W., Daniel M. D., Ringler D. J. Macrophage-tropic variants of SIV are associated with specific AIDS-related lesions but are not essential for the development of AIDS. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jul;139(1):29–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaegstad T., Permin H., Husebekk A., Husby G., Traavik T. BK virus infection in patients with AIDS. Scand J Infect Dis. 1988;20(2):145–150. doi: 10.3109/00365548809032431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner S. D., Field A. M., Coleman D. V., Hulme B. New human papovavirus (B.K.) isolated from urine after renal transplantation. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1253–1257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91776-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Phelps W., Feigenbaum L., Ostrove J. M., Adachi A., Howley P. M., Khoury G., Ginsberg H. S., Martin M. A. Trans-activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat sequence by DNA viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9759–9763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribble D. H., Haden C. C., Schwartz L. W., Henrickson R. V. Spontaneous progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) in macaques. Nature. 1975 Apr 17;254(5501):602–604. doi: 10.1038/254602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell B. W., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Distribution of nonintegrated DNA from JC papovavirus in organs of patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):669–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haring J. I., Van Dis M. L. Odontogenic keratocysts: a clinical, radiographic, and histopathologic study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1988 Jul;66(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(88)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberling R. L., Kalter S. S. Rapid dot-immunobinding assay on nitrocellulose for viral antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):109–113. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.109-113.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heritage J., Chesters P. M., McCance D. J. The persistence of papovavirus BK DNA sequences in normal human renal tissue. J Med Virol. 1981;8(2):143–150. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs T. W., Moore N. J., Badawi D. Y., Taub F. E. Type-specific human papillomavirus detection in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections using nonradioactive deoxyribonucleic acid probes. Lab Invest. 1990 Oct;63(4):557–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan T. F., Borden E. C., McBain J. A., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Human polyomavirus infections with JC virus and BK virus in renal transplant patients. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Mar;92(3):373–378. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-3-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg C. A., Gribble D. H., Takemoto K. K., Howley P. M., Espana C., Osburn B. I. Isolation of simian virus 40 from rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) with spontaneous progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):593–596. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg C. A., Henrickson R., Anderson J., Osburn B. I. Malignant lymphoma in a colony of Macaca arctoides. Vet Pathol. 1985 Jan;22(1):42–45. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houff S. A., Major E. O., Katz D. A., Kufta C. V., Sever J. L., Pittaluga S., Roberts J. R., Gitt J., Saini N., Lux W. Involvement of JC virus-infected mononuclear cells from the bone marrow and spleen in the pathogenesis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 1988 Feb 4;318(5):301–305. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198802043180507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiung G. D. Latent virus infections in primate tissues with special reference to simian viruses. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Sep;32(3):185–205. doi: 10.1128/br.32.3.185-205.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ironside J. W., Lewis F. A., Blythe D., Wakefield E. A. The identification of cells containing JC papovavirus DNA in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy by combined in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. J Pathol. 1989 Apr;157(4):291–297. doi: 10.1002/path.1711570405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoyama Y., Webster H. D., Sternberger N. H., Richardson E. P., Jr, Walker D. L., Quarles R. H., Padgett B. L. Distribution of papovavirus, myelin-associated glycoprotein, and myelin basic protein in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy lesions. Ann Neurol. 1982 Apr;11(4):396–407. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Natarajan V., Strike D., Khoury G., Salzman N. P. JC virus enhancer-promoter active in human brain cells. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6095453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler H., Kodama T., Ringler D., Marthas M., Pedersen N., Lackner A., Regier D., Sehgal P., Daniel M., King N. Induction of AIDS in rhesus monkeys by molecularly cloned simian immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1109–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.2160735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King N. W., Hunt R. D., Letvin N. L. Histopathologic changes in macaques with an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Am J Pathol. 1983 Dec;113(3):382–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp L. B., Lipton R. B., Swerdlow M. L., Leeds N. E., Llena J. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: clinical and radiographic features. Ann Neurol. 1985 Apr;17(4):344–349. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner A. A., Smith M. O., Munn R. J., Martfeld D. J., Gardner M. B., Marx P. A., Dandekar S. Localization of simian immunodeficiency virus in the central nervous system of rhesus monkeys. Am J Pathol. 1991 Sep;139(3):609–621. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence J. Molecular interactions among herpesviruses and human immunodeficiency viruses. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):338–346. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Daniel M. D., Sehgal P. K., Desrosiers R. C., Hunt R. D., Waldron L. M., MacKey J. J., Schmidt D. K., Chalifoux L. V., King N. W. Induction of AIDS-like disease in macaque monkeys with T-cell tropic retrovirus STLV-III. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2412295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeber G., Dörries K. DNA rearrangements in organ-specific variants of polyomavirus JC strain GS. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1730–1735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1730-1735.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Goverman J., Mirell C., Calame K. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer requires one or more tissue-specific factors. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):266–270. doi: 10.1126/science.3917575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Penney J. B., Jr, Johnson R. T., Herndon R. M., Weiner L. P. Etiology of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Identification of papovavirus. N Engl J Med. 1973 Dec 13;289(24):1278–1282. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197312132892405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Ghazal P., Wiley C. A. Role of opportunistic viral infections in AIDS. AIDS. 1990 Jan;4(1):1–10. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199001000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein J. M., Jannotta F. Human immunodeficiency virus and papovavirus infections in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: an ultrastructural study of three cases. Hum Pathol. 1988 Mar;19(3):350–361. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80531-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Eckroade R. J., Dessel B. H. Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1257–1260. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Hodach A. E., Chou S. M. JC Papovavirus in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133(6):686–690. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.6.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M. Mutations near the carboxyl terminus of the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen alter viral host range. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):569–575. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.569-575.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes R. H., Ward J. M., Walker D. L., Ross A. A. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and retroviral encephalitis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Dec;112(12):1207–1213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringler D. J., Hunt R. D., Desrosiers R. C., Daniel M. D., Chalifoux L. V., King N. W. Simian immunodeficiency virus-induced meningoencephalitis: natural history and retrospective study. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S101–S107. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringler D. J., Walsh D. G., Chalifoux L. V., MacKey J. J., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., King N. W., Hancock W. W. Soluble and membrane-associated interleukin 2 receptor-alpha expression in rhesus monkeys infected with simian immunodeficiency virus. Lab Invest. 1990 Apr;62(4):435–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringler D. J., Wyand M. S., Walsh D. G., MacKey J. J., Chalifoux L. V., Popovic M., Minassian A. A., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Cellular localization of simian immunodeficiency virus in lymphoid tissues. I. Immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy. Am J Pathol. 1989 Feb;134(2):373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S., Harmon W., Krensky A. M., Edelson P. J., Padgett B. L., Grinnell B. W., Rubino M. J., Walker D. L. Tubulo-interstitial nephritis associated with polyomavirus (BK type) infection. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 19;308(20):1192–1196. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198305193082004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaravilli F., Ellis D. S., Tovey G., Harcourt-Webster J. N., Guiloff R. J., Sinclair E. Unusual development of polyoma virus in the brains of two patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1989 Sep-Oct;15(5):407–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1989.tb01242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidbauer M., Budka H., Shah K. V. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) in AIDS and in the pre-AIDS era. A neuropathological comparison using immunocytochemistry and in situ DNA hybridization for virus detection. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(4):375–380. doi: 10.1007/BF00307690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah K. V., Willard S., Myers R. E., Hess D. M., DiGiacomo R. Experimental infection of rhesus with simian virus 40 (SV40). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jan;130(1):196–203. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield W. D., Strandberg J. D., Braun L., Shah K., Kalter S. S. Simian virus 40-associated fatal interstitial pneumonia and renal tubular necrosis in a rhesus monkey. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):618–622. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. L., Ryschkewitsch C. F., Walker D. L., Webster H. D. JC papovavirus large tumor (T)-antigen expression in brain tissue of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and non-AIDS patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2271–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada H., Rappaport J., Lashgari M., Amini S., Wong-Staal F., Khalili K. Trans-activation of the JC virus late promoter by the tat protein of type 1 human immunodeficiency virus in glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3479–3483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Grafe M., Kennedy C., Nelson J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and JC virus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(4):338–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00686970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyand M. S., Ringler D. J., Naidu Y. M., Mattmuller M., Chalifoux L. V., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., King N. W. Cellular localization of simian immunodeficiency virus in lymphoid tissues. II. In situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1989 Feb;134(2):385–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]