Abstract
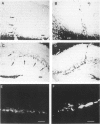
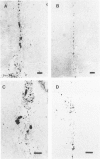
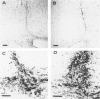
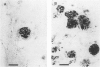
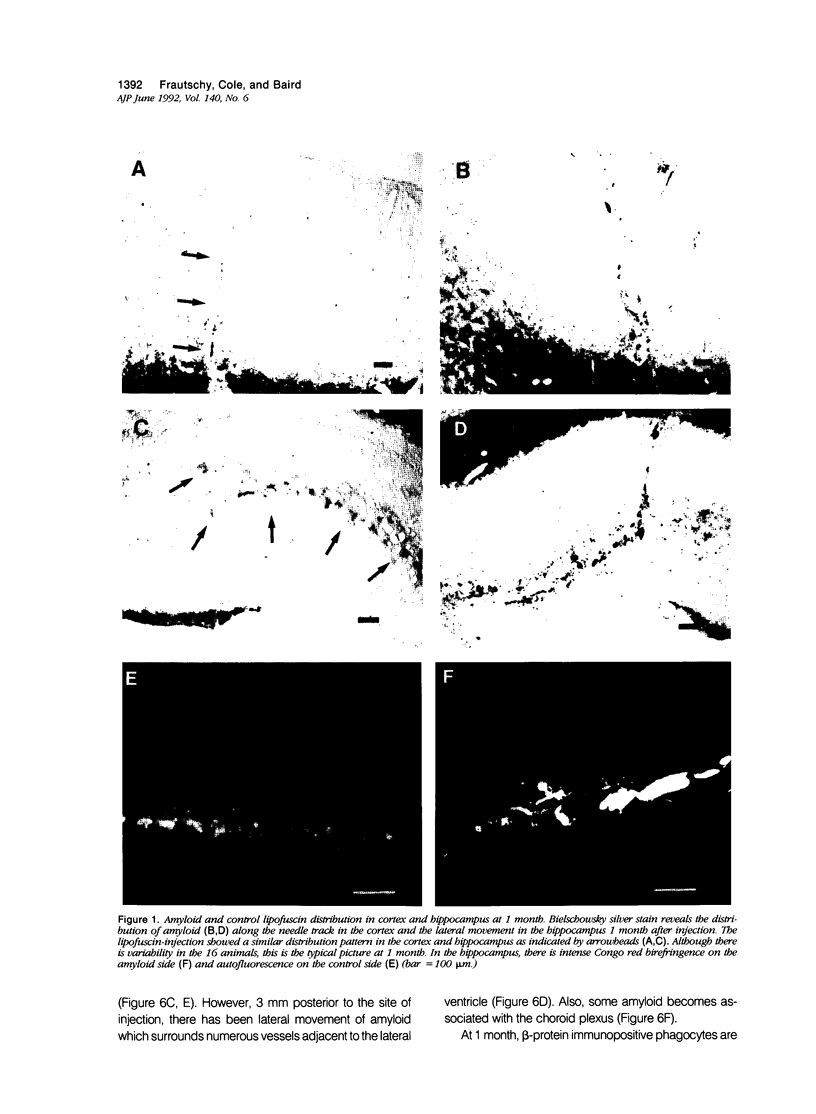
The presence of extracellular deposits of beta-amyloid protein in the brain is a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In an effort to determine the effect of amyloid in an animal model, the authors injected amyloid cores isolated from AD brains into the cortex and hippocampus of rats. Lipofuscin, a major contaminant of the plaque core preparation, was injected on the contralateral side and used as a control to induce an analogous phagocytic cell response. Rats were sacrificed 2 days, 7 days, and 1 month after injection and amyloid located by four histochemical techniques. Amyloid and lipofuscin move from the site of injection into otherwise undamaged neuropil, persist for at least 1 month and are both associated with increases in glial fibrillary acidic protein and microglia (OX-42) staining. By 1 week, many of the amyloid cores are ingested by phagocytes. Some of the beta-amyloid-containing phagocytes migrate to the vessels and to the ventricles, and by 1 month, a significant amount of the amyloid is directly associated with the vessels. This suggests that phagocytic cells can internalize exogenous amyloid and attempt to clear it from the central nervous system (CNS). Therefore, the observed distribution of amyloid is not necessarily the initial site of deposition.
Full text
PDF


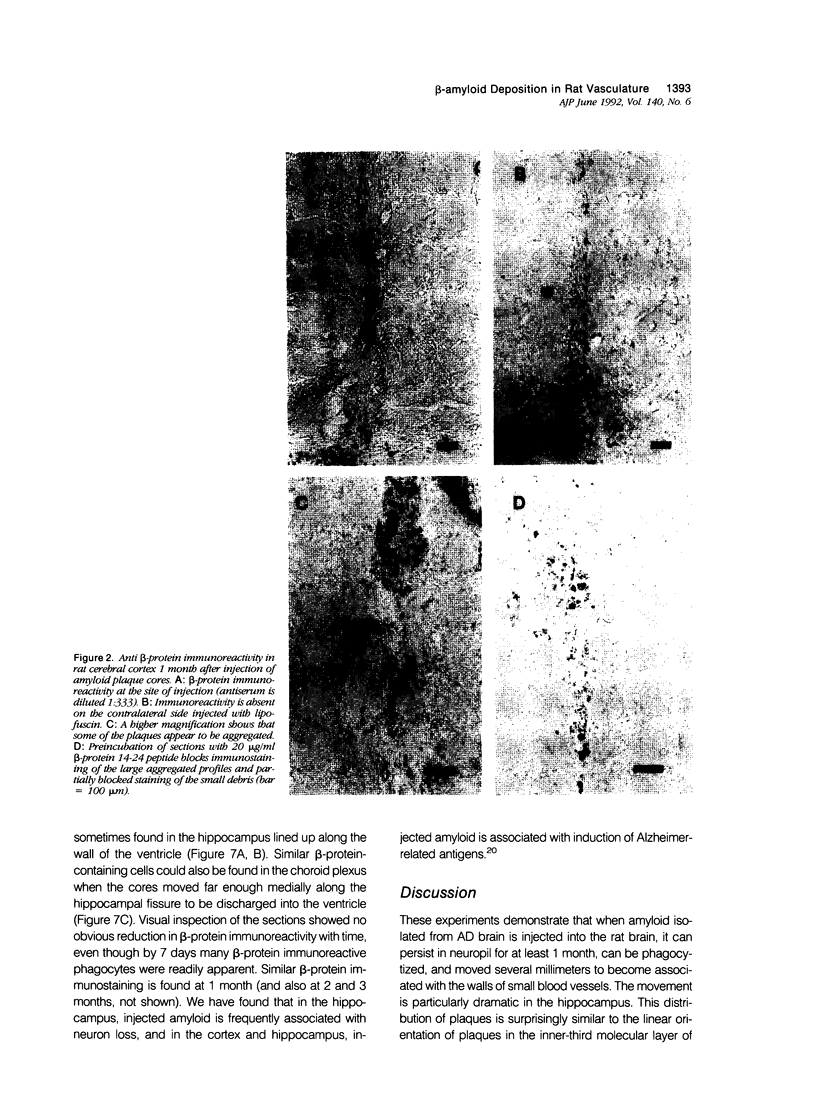
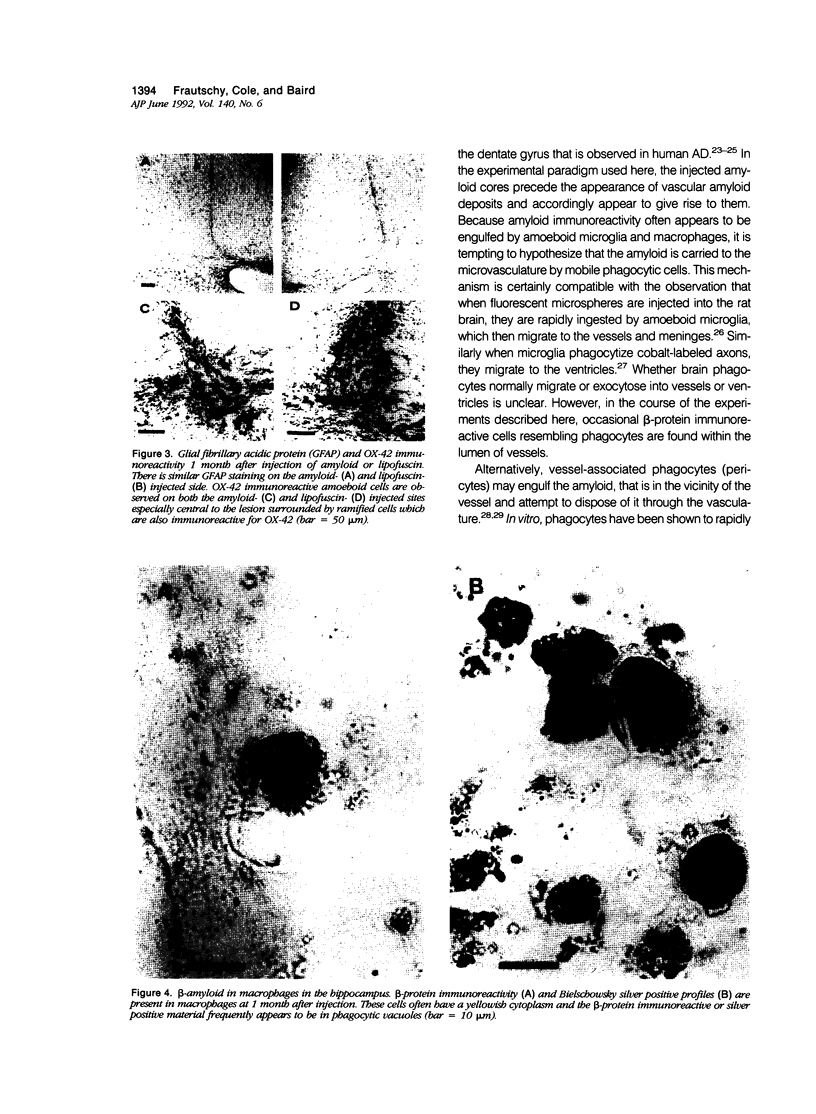
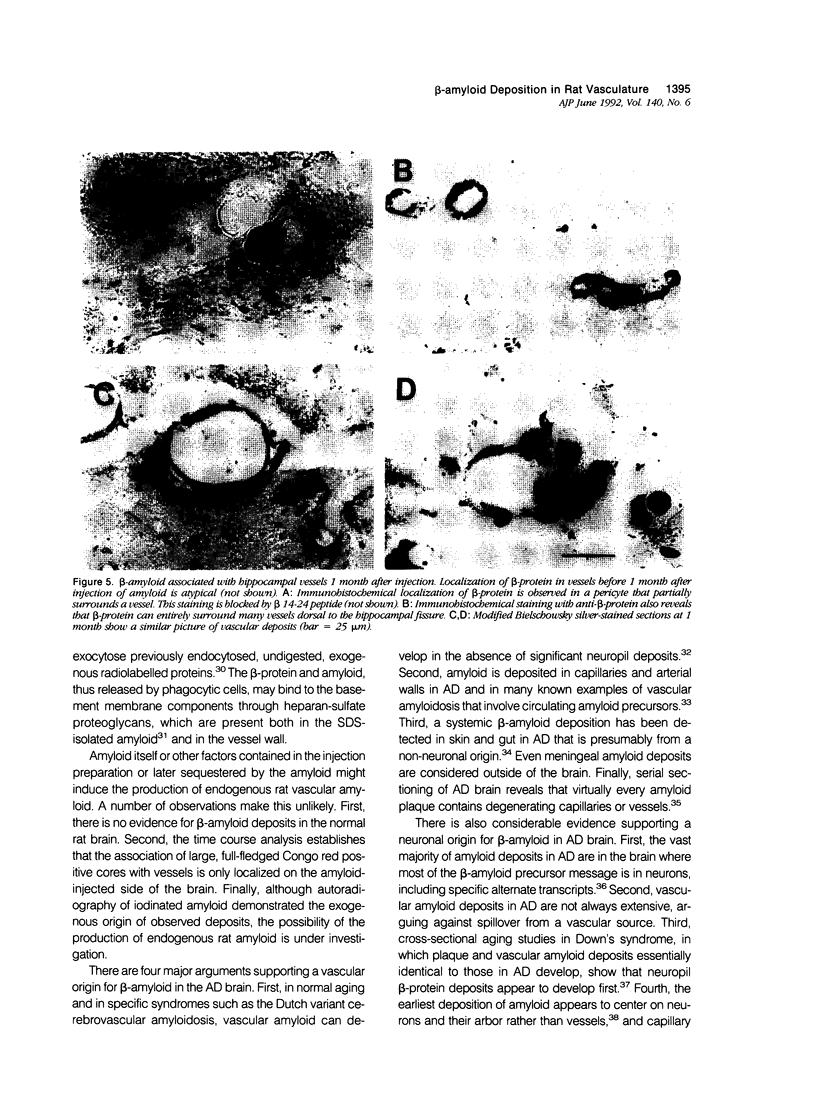
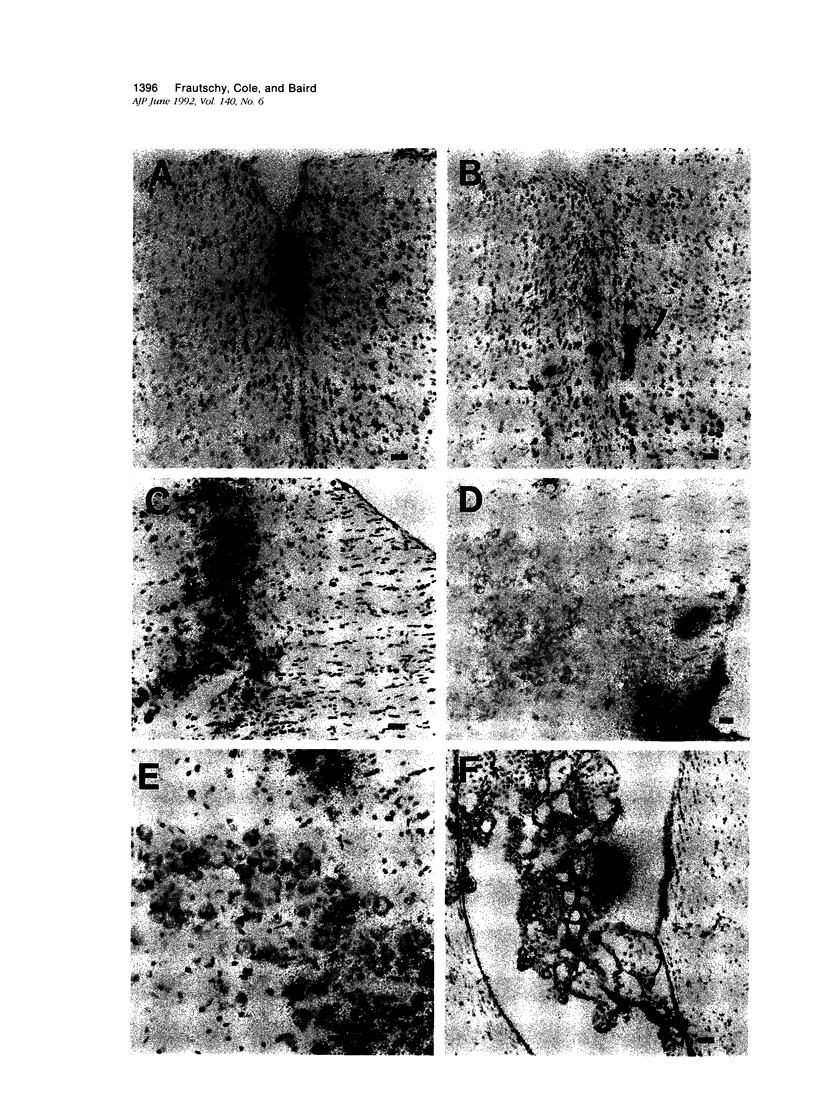



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsop D., Haga S. I., Haga C., Ikeda S. I., Mann D. M., Ishii T. Early senile plaques in Down's syndrome brains show a close relationship with cell bodies of neurons. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1989 Nov-Dec;15(6):531–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1989.tb01252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahmanyar S., Higgins G. A., Goldgaber D., Lewis D. A., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C., Shankar S. K., Gajdusek D. C. Localization of amyloid beta protein messenger RNA in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Jul 3;237(4810):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3299701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buktenica S., Olenick S. J., Salgia R., Frankfater A. Degradation and regurgitation of extracellular proteins by cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages and baby hamster kidney fibroblasts. Kinetic evidence that the transfer of proteins to lysosomes is not irreversible. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9469–9476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G., Masliah E., Huynh T. V., DeTeresa R., Terry R. D., Okuda C., Saitoh T. An antiserum against amyloid beta-protein precursor detects a unique peptide in Alzheimer brain. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 22;100(1-3):340–346. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90710-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crain B. J., Burger P. C. Neuritic plaques in the human fascia dentata: a model system for the study of plaque formation in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;317:523–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frautschy S. A., Baird A., Cole G. M. Effects of injected Alzheimer beta-amyloid cores in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8362–8366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaccone G., Tagliavini F., Linoli G., Bouras C., Frigerio L., Frangione B., Bugiani O. Down patients: extracellular preamyloid deposits precede neuritic degeneration and senile plaques. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Feb 13;97(1-2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Chen J., Ingeman J. E., George J. K., Noponen M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in wound healing after traumatic injury to adult mammalian brain. J Neurosci. 1989 Dec;9(12):4416–4429. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-12-04416.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Murphy M. A. Amyloidosis of the nervous system. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Dec;94(1-3):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(89)90214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeber M. B., Streit W. J., Kreutzberg G. W. Identity of ED2-positive perivascular cells in rat brain. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Jan;22(1):103–106. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490220114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin W. S., Stanley L. C., Ling C., White L., MacLeod V., Perrot L. J., White C. L., 3rd, Araoz C. Brain interleukin 1 and S-100 immunoreactivity are elevated in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7611–7615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Damasio A. R., Barnes C. L. Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1168–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.6474172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itagaki S., McGeer P. L., Akiyama H., Zhu S., Selkoe D. Relationship of microglia and astrocytes to amyloid deposits of Alzheimer disease. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Oct;24(3):173–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joachim C. L., Mori H., Selkoe D. J. Amyloid beta-protein deposition in tissues other than brain in Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):226–230. doi: 10.1038/341226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Carman M. D., Fernandez-Madrid I. J., Power M. D., Lieberburg I., van Duinen S. G., Bots G. T., Luyendijk W., Frangione B. Mutation of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid gene in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage, Dutch type. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1124–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.2111584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Jones D., Prinja D., Purkiss M. S. The prevalence of amyloid (A4) protein deposits within the cerebral and cerebellar cortex in Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(3):318–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00294651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Simms G., Pottgiesser J., Martins R. N., Beyreuther K. Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E., Rogers J., Sibley J. Anti-inflammatory drugs and Alzheimer disease. Lancet. 1990 Apr 28;335(8696):1037–1037. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91101-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa T., Shimoji A., Kuramoto R., Higuchi Y. The relationship between senile plaques and cerebral blood vessels in Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia. Morphological mechanism of senile plaque production. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982 Aug;40(2):121–129. doi: 10.1007/BF02932857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motte J., Williams R. S. Age-related changes in the density and morphology of plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in Down syndrome brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;77(5):535–546. doi: 10.1007/BF00687256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelli F., Castaño E., Glenner G. G., Frangione B. Differences between vascular and plaque core amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):648–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Luber-Narod J., Styren S. D., Civin W. H. Expression of immune system-associated antigens by cells of the human central nervous system: relationship to the pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(4):339–349. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(88)80079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roher A., Gray E. G., Paula-Barbosa M. Alzheimer's disease: coated vesicles, coated pits and the amyloid-related cell. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jan 22;232(1269):367–373. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozemuller J. M., Eikelenboom P., Stam F. C., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. A4 protein in Alzheimer's disease: primary and secondary cellular events in extracellular amyloid deposition. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1989 Nov;48(6):674–691. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198911000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Abraham C. R. Isolation of paired helical filaments and amyloid fibers from human brain. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:388–404. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. Molecular pathology of amyloidogenic proteins and the role of vascular amyloidosis in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):387–395. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer A. D., Wilson B. R. Light microscopic study of degenerating cobalt-filled optic axons in goldfish: role of microglia and radial glia in debris removal. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Apr 1;282(1):119–132. doi: 10.1002/cne.902820109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suenaga T., Hirano A., Llena J. F., Yen S. H., Dickson D. W. Modified Bielschowsky stain and immunohistochemical studies on striatal plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(3):280–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00294646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY R. D., GONATAS N. K., WEISS M. ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDIES IN ALZHEIMER'S PRESENILE DEMENTIA. Am J Pathol. 1964 Feb;44:269–297. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Giaccone G., Frangione B., Bugiani O. Preamyloid deposits in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease and nondemented individuals. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 11;93(2-3):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan D. W., Peters A. The structure of neuritic plaque in the cerebral cortex of aged rats. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 Jul;40(4):472–487. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198107000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walicke P., Cowan W. M., Ueno N., Baird A., Guillemin R. Fibroblast growth factor promotes survival of dissociated hippocampal neurons and enhances neurite extension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3012–3016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Barcikowska M., Kida E. Phagocytosis of beta/A4 amyloid fibrils of the neuritic neocortical plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;81(5):588–590. doi: 10.1007/BF00310142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Wegiel J., Wang K. C., Kujawa M., Lach B. Ultrastructural studies of the cells forming amyloid fibers in classical plaques. Can J Neurol Sci. 1989 Nov;16(4 Suppl):535–542. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100029887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H. M., Ghetti B., Terry R. D. Neuritic (senile) plaques and filamentous changes in aged rhesus monkeys. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1973 Oct;32(4):566–584. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197310000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Johnson A. B., Raine C. S., Kay W. J., Terry R. D. Senile plaques and cerebral amyloidosis in aged dogs. A histochemical and ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1970 Sep;23(3):287–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]