Abstract
A novel cationic immune-complex-mediated arthritis (ICA) model was developed in mice. The highly cationic protein lysozyme was coupled to poly-L-lysine (PLL) and injected intra-articularly into the knee joint of the mouse, shortly after systemic administration of specific antibodies. A vehement joint inflammation developed, characterized by severe joint swelling and the influx of predominantly polymorphonuclear (PMN) leukocyte. Unique properties were combined in this protein. First, an excellent retention of the antigen in joint structures was found, facilitating sufficient IC formation in the synovial tissue and at the cartilage surface. Secondly, PLL.lysozyme appeared to be a potent inducer of interleukin-1 (IL-1). Similar IL-1 production was measured at 6 hours, in both immune or nonimmune mice. Neutralization with antibodies against either IL-1 alpha or IL-1 beta revealed that IL-1 alpha was the dominant cytokine. Resident cells were responsible for this IL-1 production since a comparable IL-1 signal was measured after intra-articular injection of PLL.lys in neutropenic mice. We further investigated whether IL-1 and complement factors were involved in the onset of this ICA. Neutralizing the IL-1 production with antibodies directed against IL-1 alpha and beta showed a significant decrease in joint swelling. Complement depletion by cobra venom factor also prevented the onset of arthritis for the greater part. Only a minor swelling remained at 6 hours after eliciting arthritis, which was similar to the swelling after injecting the antigen alone and probably reflects IL-1 mediated inflammation. In this study, the authors show a synergistic action of IL-1 and complement in the onset of cationic ICA. Unique properties of the antigen such as excellent retention and its ability to induce IL-1 are combined within one molecule and make this antigen arthritogenic in the presence of antibodies and complement activation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Massoni R. J. Effects of immune complexes on production by human monocytes of interleukin 1 or an interleukin 1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3868–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Wheeler M. E., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 acts on cultured human vascular endothelium to increase the adhesion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and related leukocyte cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):2003–2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI112200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjursten L. M., Bagge U., Ahlstedt S. Joint inflammation in rabbits induced by preformed immune complexes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;64(1):67–71. doi: 10.1159/000232675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockow B., Mannik M. Clearance and tissue uptake of immune complexes in complement-depleted and control mice. Immunology. 1981 Apr;42(4):497–504. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy R. M., Dahinden C. A., Hugli T. E. Arachidonate metabolism by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes stimulated by N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe or complement component C5a is independent of phospholipase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7200–7204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Hurd E. R., Ziff M., Jasin H. E. The pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental antigen-induced arthritis. II. Preferential localization of antigen-antibody complexes to collagenous tissues. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):323–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Sumi M., Maeda M. Nicolas Andry Award, 1984. Deleterious interactions of immune complexes in cartilage of experimental immune arthritis. I. The erosion of pannus-free hyaline cartilage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985 Mar;(193):235–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon D., Goldstein L., Marikovsky Y., Skutelsky E. Use of cationized ferritin as a label of negative charges on cell surfaces. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Mar;38(5):500–510. doi: 10.1016/0022-5320(72)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Waal R. M., Schrijver G., Bogman M. J., Assmann K. J., Koene R. A. An improved sensitive and simple microassay of mouse complement. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Apr 6;108(1-2):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeShazo C. V., Henson P. M., Cochrane C. G. Acute immunologic arthritis in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):50–57. doi: 10.1172/JCI106796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing A. J., Bird C. R., Bristow A., Poole S., Thorpe R. A simple sensitive bioassay for interleukin-1 which is unresponsive to 10(3) U/ml of interleukin-2. J Immunol Methods. 1987 May 4;99(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom J. T., Bendele A. M., Carlson D. G. In vivo administration with IL-1 accelerates the development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):834–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom J. T., Cole H., Bendele A. M. Interleukin 1 enhances the development of spontaneous arthritis in MRL/lpr mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Apr;55(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Smiley J. D., Ziff M. Electron microscopic demonstration of immunoglobulin deposition in rheumatoid cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(6):563–576. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A., Feinstein G., Malemud C. J., Elias J. M. Degradation of cartilage proteoglycan by human leukocyte granule neutral proteases--a model of joint injury. I. Penetration of enzyme into rabbit articular cartilage and release of 35SO4-labeled material from the tissue. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):615–624. doi: 10.1172/JCI108317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Phan S. H. Prostaglandins as endogenous mediators of interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
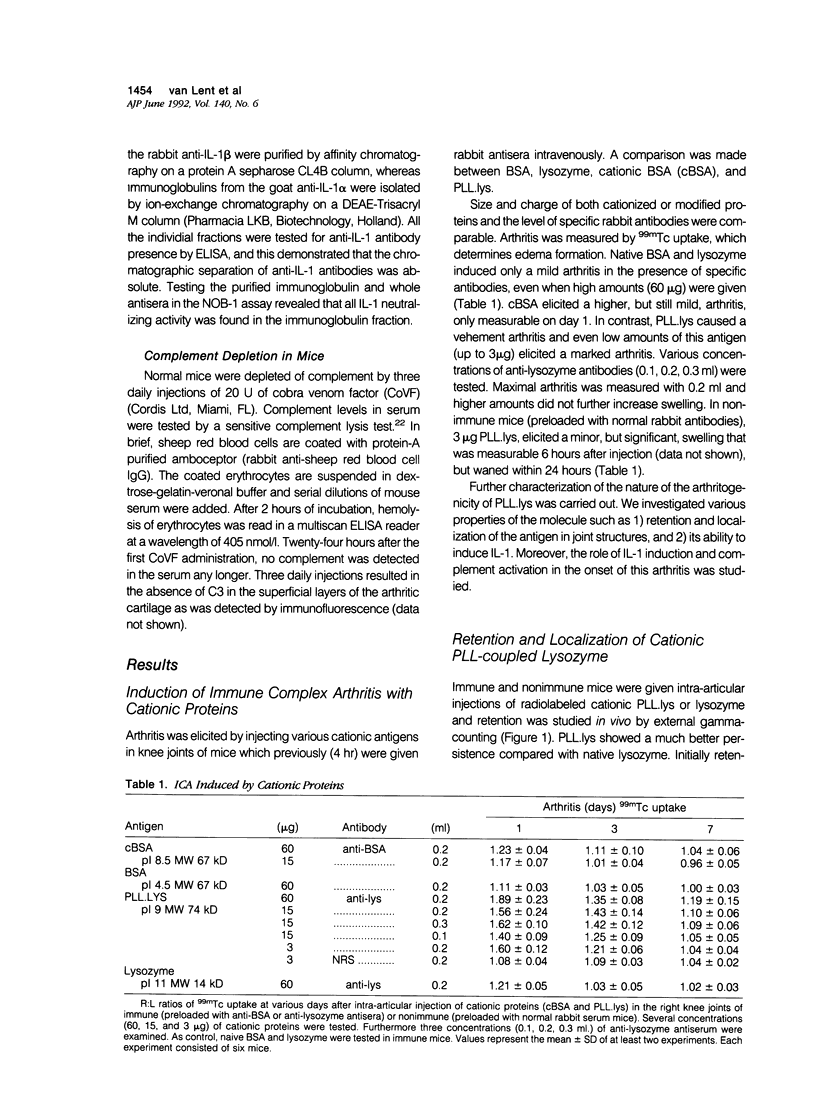
- Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Quantitation of arthritis by 99mTc-uptake measurements in the mouse knee-joint: correlation with histological joint inflammation scores. Agents Actions. 1984 Jun;14(5-6):723–728. doi: 10.1007/BF01978915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
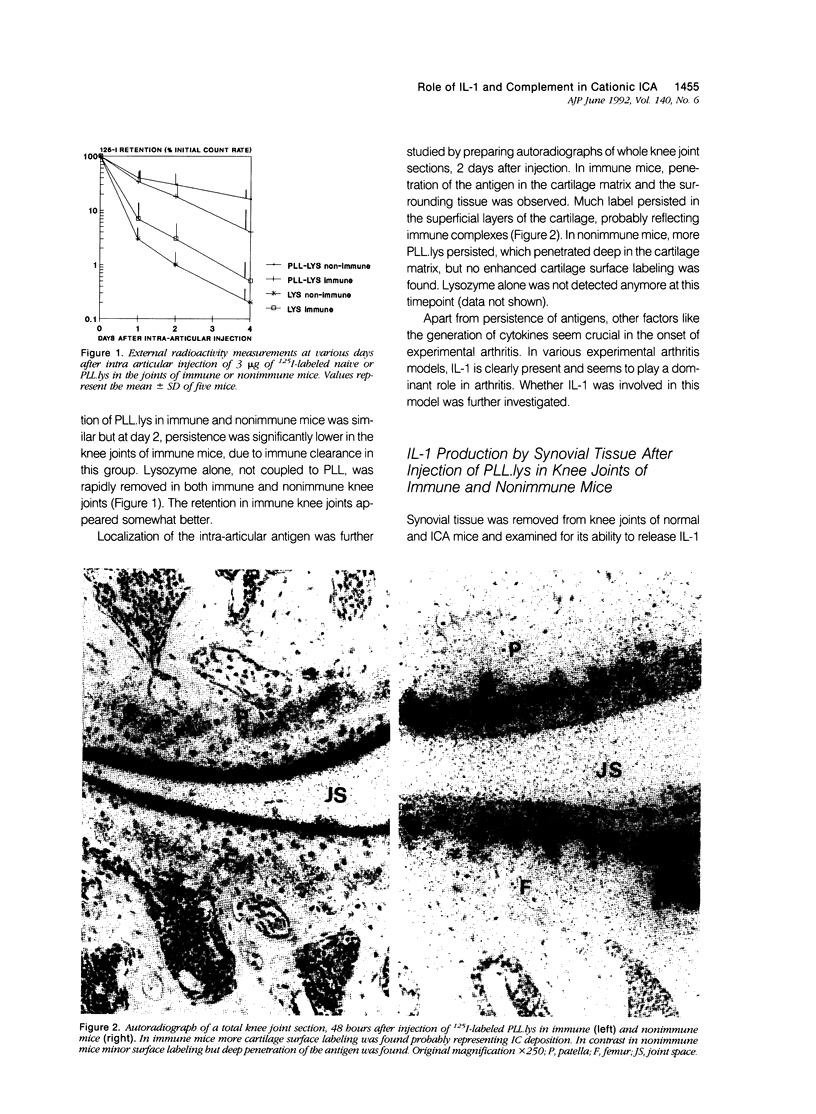
- Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 8 and MCAF: novel inflammatory cytokines inducible by IL 1 and TNF. Cytokine. 1989 Nov;1(1):2–13. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(89)91043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Dinarello C. A., Yancey K. B., Endres S., Lawley T. J., Frank M. M., Burke J. F., Gelfand J. A. C5a induction of human interleukin 1. Synergistic effect with endotoxin or interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2635–2640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
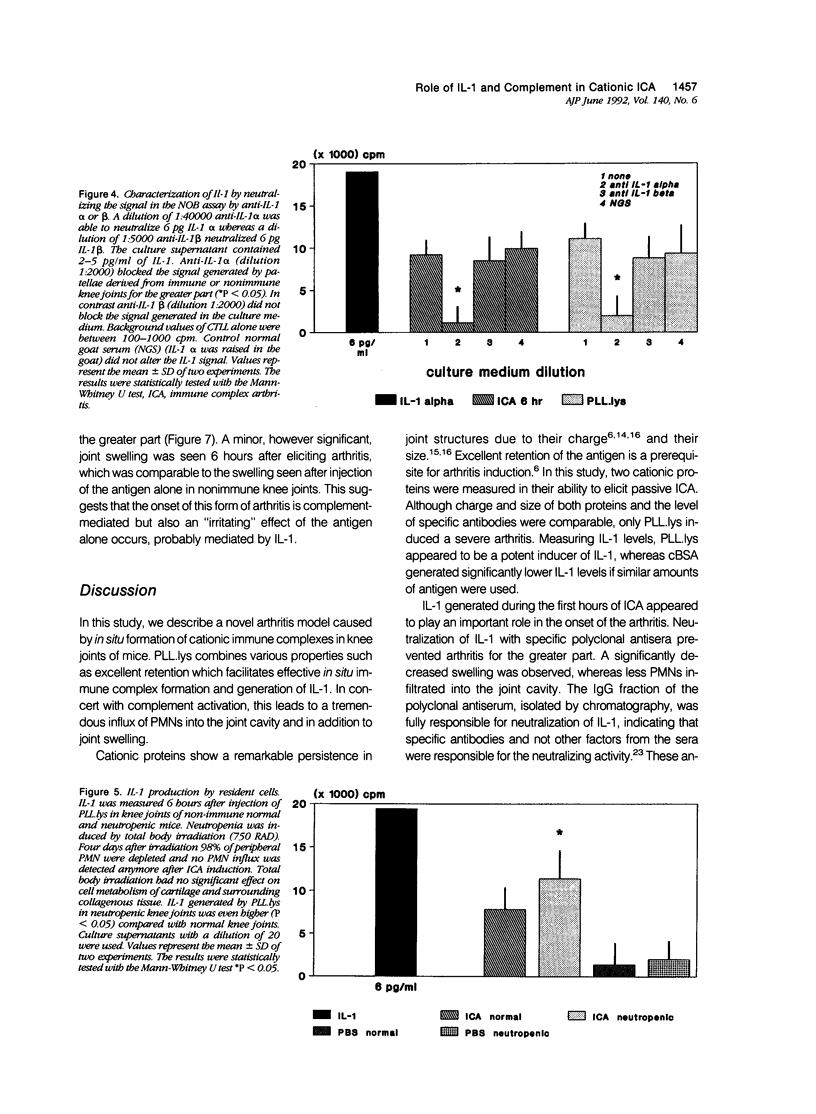
- Saxne T., Palladino M. A., Jr, Heinegård D., Talal N., Wollheim F. A. Detection of tumor necrosis factor alpha but not tumor necrosis factor beta in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid and serum. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Aug;31(8):1041–1045. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. B., Gamble J. R., Clark-Lewis I., Vadas M. A. Interleukin-8 induces neutrophil transendothelial migration. Immunology. 1991 Jan;72(1):65–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staite N. D., Richard K. A., Aspar D. G., Franz K. A., Galinet L. A., Dunn C. J. Induction of an acute erosive monarticular arthritis in mice by interleukin-1 and methylated bovine serum albumin. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Feb;33(2):253–260. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenseth K., Hedin U., Thyberg J. Endocytosis, intracellular transport, and turnover of anionic and cationic proteins in cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;31(1):15–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimpson S. A., Dalldorf F. G., Otterness I. G., Schwab J. H. Exacerbation of arthritis by IL-1 in rat joints previously injured by peptidoglycan-polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):2964–2969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Vogt A. Mitogenic activity of extracellular cationic products produced by group A streptococci; analysis of the lymphocyte response. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Oct;66(1):132–138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen P., Bjursten L. M., Ahlstedt S., Bagge U., Ericson L. E. Proliferative synovitis in rabbit knee joints induced by antigen and preformed immune complexes. Scand J Rheumatol. 1985;14(3):239–251. doi: 10.3109/03009748509100401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugai K., Ishikawa H., Hirohata K., Shirane H. Interaction of polymorphonuclear leukocytes with immune complexes trapped in rheumatoid articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Dec;26(12):1434–1441. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt A., Batsford S., Rodríguez-Iturbe B., García R. Cationic antigens in poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1983 Dec;20(6):271–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Georgescu H. I., Kuhns D. B., Evans C. H. Chondrocyte activation by a putative interleukin-1 derived from lapine polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Apr;270(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Gamma globulin complexes in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Partial characterization and relationship to lowered complement levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):689–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Luthra H. S., Krco C. J., Stuart J. M., David C. S. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. II. Passive transfer and suppression by intravenous injection of anti-type II collagen antibody or free native type II collagen. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Sep;27(9):1010–1017. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lent P. L., Dekker C., Mosterd J., van den Bersselaar L., van den Berg W. B. Allergic arthritis induced by cationic proteins: role of molecular weight. Immunology. 1989 Aug;67(4):447–452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lent P. L., van den Berg W. B., Schalkwijk J., van de Putte L. B., van den Bersselaar L. Allergic arthritis induced by cationic antigens: relationship of chronicity with antigen retention and T-cell reactivity. Immunology. 1987 Oct;62(2):265–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lent P. L., van den Berg W. B., Schalkwijk J., van de Putte L. B., van den Bersselaar L. The impact of protein size and charge on its retention in articular cartilage. J Rheumatol. 1987 Aug;14(4):798–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lent P. L., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., van den Bersselaar L. Electrical charge of a protein determines penetration and localization in hyaline articular cartilage. Quantitative and autoradiographic studies on cartilage of different species, including man. Rheumatol Int. 1988;8(4):145–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00270452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Loo A. A., Arntz O. J., van den Berg W. B. Flare-up of experimental arthritis in mice with murine recombinant IL-1. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Feb;87(2):196–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb02974.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A., Joosten L. A. Electrical charge of the antigen determines intraarticular antigen handling and chronicity of arthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1850–1859. doi: 10.1172/JCI111604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]