Abstract
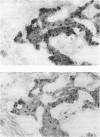
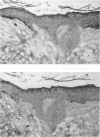
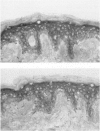
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) of the skin is the most common human cancer, but its molecular-genetic pathogenesis is unclear. In many other types of cancer, mutations of the tumor-suppressor gene p53 occur frequently and may lead to overexpression of a long-lived mutant form of p53 protein. In this study, overexpression of p53 protein was detected immunohistochemically in 30 (83%) of 36 specimens of BCC of the head and neck. The same regions of tumor typically were reactive both with a monoclonal antibody (PAb240) specific for the mutant protein and with one (PAb1801) directed against an epitope common to both wild-type and mutant p53 protein. Keratinocytes of chronically sun-exposed epidermis adjacent to BCCs also focally overexpressed p53 protein in the majority of cases, whereas those of sun-protected buttock skin did not. Mutation of p53 may form an important part of the pathogenetic sequence in a majority of cases of BCC.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ananthaswamy H. N., Price J. E., Goldberg L. H., Bales E. S. Detection and identification of activated oncogenes in human skin cancers occurring on sun-exposed body sites. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 15;48(12):3341–3346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Matlashewski G., Crawford L. Isolation of human-p53-specific monoclonal antibodies and their use in the studies of human p53 expression. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boring C. C., Squires T. S., Tong T. Cancer statistics, 1991. CA Cancer J Clin. 1991 Jan-Feb;41(1):19–36. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.41.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden G. T., Jaffe D., Andrews K. Biological and molecular aspects of radiation carcinogenesis in mouse skin. Radiat Res. 1990 Mar;121(3):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash D. E., Rudolph J. A., Simon J. A., Lin A., McKenna G. J., Baden H. P., Halperin A. J., Pontén J. A role for sunlight in skin cancer: UV-induced p53 mutations in squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10124–10128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Rilke F., Andreola S., D'Amato L., Delia D. P53 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1988 Feb 15;41(2):178–183. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., O'Connell J., Patskan G., Conti C., Ariza A., Slaga T. J. Malignant progression of papilloma-derived keratinocytes: differential effects of the ras, neu, and p53 oncogenes. Mol Carcinog. 1988;1(3):171–179. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy O., Michalovitz D., Oren M. Different tumor-derived p53 mutants exhibit distinct biological activities. Science. 1990 Oct 5;250(4977):113–116. doi: 10.1126/science.2218501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L. Mutant p53--the commonest genetic abnormality in human cancer? J Pathol. 1990 Sep;162(1):5–6. doi: 10.1002/path.1711620103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo R., Gatter K., Bartek J., Lane D., Harris A. L. Increased expression of mutant forms of p53 oncogene in primary lung cancer. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):675–679. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90801-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe M., Emanuel B. S., Givol D., Oren M., Croce C. M. Localization of gene for human p53 tumour antigen to band 17p13. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):84–85. doi: 10.1038/320084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Chumakov P., Currie G. A. The cellular oncogene p53 can be activated by mutagenesis. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):816–818. doi: 10.1038/317816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb P., Crawford L. Characterization of the human p53 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1379–1385. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigueur A., Maltby V., Mock D., Rossant J., Pawson T., Bernstein A. High incidence of lung, bone, and lymphoid tumors in transgenic mice overexpressing mutant alleles of the p53 oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3982–3991. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Merry D., Givol D. The gene for human p53 cellular tumor antigen is located on chromosome 17 short arm (17p13). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):130–134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Shields M. T., Amin M., Sauve G. J., Appella E., Romano J. W., Ullrich S. J. Negative growth regulation in a glioblastoma tumor cell line that conditionally expresses human wild-type p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6166–6170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens F., Heim S., Mandahl N., Johansson B., Mertens O., Persson B., Salemark L., Wennerberg J., Jonsson N., Mitelman F. Cytogenetic analysis of 33 basal cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1991 Feb 1;51(3):954–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90113-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogiso Y., Oikawa T., Kondo N., Kuzumaki N., Sugihara T., Ohura T. Expression of proto-oncogenes in normal and tumor tissues of human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Jun;90(6):841–844. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12462078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Michalovitz D., Ben-Zeev A., Oren M. Specific interaction between the p53 cellular tumour antigen and major heat shock proteins. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):182–184. doi: 10.1038/320182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdie C. A., O'Grady J., Piris J., Wyllie A. H., Bird C. C. p53 expression in colorectal tumors. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):807–813. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Oren M., Levine A. J. Two distinct mechanisms regulate the levels of a cellular tumor antigen, p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2143–2150. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovinski B., Benchimol S. Immortalization of rat embryo fibroblasts by the cellular p53 oncogene. Oncogene. 1988 May;2(5):445–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. E., Carroll R. J., Day C. L., Jr Long-term recurrence rates in previously untreated (primary) basal cell carcinoma: implications for patient follow-up. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1989 Mar;15(3):315–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.1989.tb03166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safai B., Good R. A. Basal cell carcinoma with metastasis. Review of literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1977 Jun;101(6):327–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R. Tumor suppressor genes: the puzzle and the promise. Science. 1989 Dec 15;246(4936):1406–1412. doi: 10.1126/science.2574499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sober A. J. Diagnosis and management of skin cancer. Cancer. 1983 Jun 15;51(12 Suppl):2448–2452. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830615)51:12+<2448::aid-cncr2820511311>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretch J. R., Gatter K. C., Ralfkiaer E., Lane D. P., Harris A. L. Expression of mutant p53 in melanoma. Cancer Res. 1991 Nov 1;51(21):5976–5979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkenandt M., Schlegel U., Nanus D. M., Albino A. P. Mutational analysis of the human p53 gene in malignant melanoma. Pigment Cell Res. 1991 Feb;4(1):35–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.1991.tb00311.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Tumor suppressor genes. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1138–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.1659741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock M. A., Bogaars H. A., Ashley M., Litle V., Bilodeau E., Kimmel S. Nonmelanoma skin cancer mortality. A population-based study. Arch Dermatol. 1991 Aug;127(8):1194–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Schroeff J. G., Evers L. M., Boot A. J., Bos J. L. Ras oncogene mutations in basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas of human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Apr;94(4):423–425. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]