Abstract
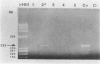
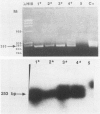
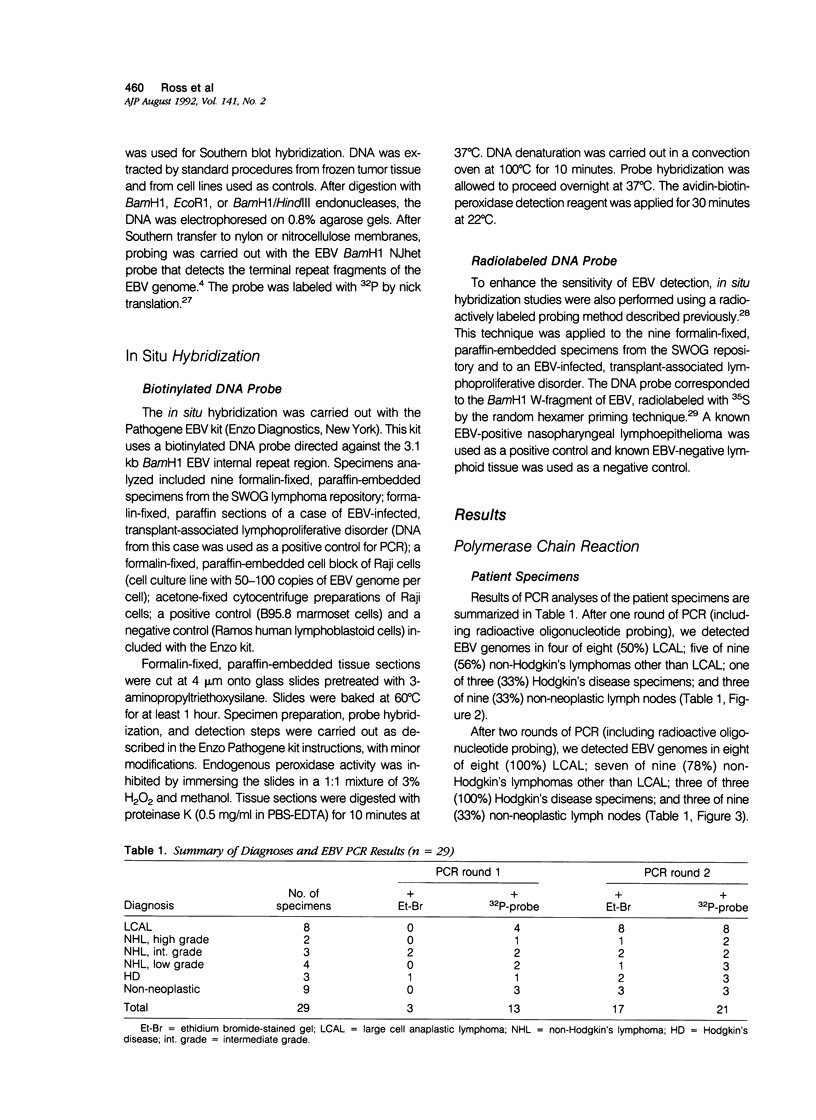
Ki-1 (CD30)-positive, large-cell anaplastic lymphoma (LCAL) is a distinctive subset of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; morphologically, the neoplastic cells of LCAL may closely resemble Reed-Sternberg cell variants of Hodgkin's disease. The neoplastic cells in Hodgkin's disease are often CD30-positive, as are some of the transformed lymphocytes in infectious mononucleosis. Recent evidence suggests an etiologic role for the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in Hodgkin's disease. Because of the phenotypic similarities between Hodgkin's disease and LCAL, we used the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to analyze eight specimens of LCAL for EBV genome. Diagnoses were established by paraffin section morphology and immunohistochemistry. For comparison, we also analyzed nine non-Hodgkin's lymphomas other than the LCAL type, three Hodgkin's disease specimens, and nine non-neoplastic lymph nodes. PCR was performed using DNA extracted from frozen tissue; DNA was amplified using two sets of oligonucleotide primers corresponding to the BamH1 W-fragment of the EBV genome. Amplified EBV genome was obtained from all specimens except for one mantle zone lymphoma, one diffuse mixed-cell lymphoma, and six non-neoplastic lymph nodes. EBV terminus region probing and in situ hybridization techniques, each less sensitive than PCR, were performed in selected cases in an attempt to corroborate our PCR results. Only 2 of 13 specimens contained EBV detectable by these other techniques, and neither specimen was a LCAL. In view of the high incidence of latent EBV infections in humans, the biologic significance of our PCR results is uncertain. Despite the detection of EBV genome by PCR in a high percentage of lymphomas, we were unable to substantiate an etiologic role for EBV in LCAL. The PCR technique may be too sensitive to provide meaningful data on the possible role of EBV in lymphomagenesis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbondanzo S. L., Sato N., Straus S. E., Jaffe E. S. Acute infectious mononucleosis. CD30 (Ki-1) antigen expression and histologic correlations. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 May;93(5):698–702. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/93.5.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnarsson B. A., Kadin M. E. Ki-1 positive large cell lymphoma. A morphologic and immunologic study of 19 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Apr;12(4):264–274. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198804000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos I., Herbst H., Niedobitek G., Stein H. Demonstration of monoclonal EBV genomes in Hodgkin's disease and Ki-1-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma by combined Southern blot and in situ hybridization. Blood. 1989 Aug 1;74(2):810–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth C. L., Hayashi H., Deegan M. J. Frozen RPMI 8402 cells: a reliable source of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase positive control material. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Feb 11;76(2):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90296-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisch-Chappuis B., Nezelof C., Müller H., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Different Epstein-Barr virus expression in lymphomas from immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients. Am J Pathol. 1990 Apr;136(4):751–758. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. K., Ng C. S., Hui P. K., Leung T. W., Lo E. S., Lau W. H., McGuire L. J. Anaplastic large cell Ki-1 lymphoma. Delineation of two morphological types. Histopathology. 1989 Jul;15(1):11–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1989.tb03038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A., Kieff E. Long internal direct repeat in Epstein-Barr virus DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):286–294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.286-294.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chott A., Kaserer K., Augustin I., Vesely M., Heinz R., Oehlinger W., Hanak H., Radaszkiewicz T. Ki-1-positive large cell lymphoma. A clinicopathologic study of 41 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990 May;14(5):439–448. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199005000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN M. A., ACHONG B. G., BARR Y. M. VIRUS PARTICLES IN CULTURED LYMPHOBLASTS FROM BURKITT'S LYMPHOMA. Lancet. 1964 Mar 28;1(7335):702–703. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91524-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. M., Quertermous T., Seidman J. G., Kersey J. H. Human T cell gamma-chain gene rearrangements in acute lymphoid and nonlymphoid leukemia: comparison with the T cell receptor beta-chain gene. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):2043–2049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., d'Ardenne A. J., Stansfeld A. G. Paraffin section immunohistochemistry. II. Hodgkin's disease and large cell anaplastic (Ki1) lymphoma. Histopathology. 1988 Aug;13(2):161–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1988.tb02021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. Evidence for an oncogenic potential of the Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Res. 1973 Jun;33(6):1419–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst H., Dallenbach F., Hummel M., Niedobitek G., Pileri S., Müller-Lantzsch N., Stein H. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein expression in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4766–4770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst H., Niedobitek G., Kneba M., Hummel M., Finn T., Anagnostopoulos I., Bergholz M., Krieger G., Stein H. High incidence of Epstein-Barr virus genomes in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jul;137(1):13–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. F., Shurin S., Abramowsky C., Tubbs R. R., Sciotto C. G., Wahl R., Sands J., Gottman D., Katz B. Z., Sklar J. T-cell lymphomas containing Epstein-Barr viral DNA in patients with chronic Epstein-Barr virus infections. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 24;318(12):733–741. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803243181203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht H., Odermatt B. F., Bachmann E., Teixeira S., Sahli R., Hayoz D., Heitz P., Bachmann F. Frequent detection of Epstein-Barr virus DNA by the polymerase chain reaction in lymph node biopsies from patients with Hodgkin's disease without genomic evidence of B- or T-cell clonality. Blood. 1991 Aug 1;78(3):760–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libetta C. M., Pringle J. H., Angel C. A., Craft A. W., Malcolm A. J., Lauder I. Demonstration of Epstein-Barr viral DNA in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples of Hodgkin's disease. J Pathol. 1990 Jul;161(3):255–260. doi: 10.1002/path.1711610313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masih A., Weisenburger D., Duggan M., Armitage J., Bashir R., Mitchell D., Wickert R., Purtilo D. T. Epstein-Barr viral genome in lymph nodes from patients with Hodgkin's disease may not be specific to Reed-Sternberg cells. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jul;139(1):37–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G., Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Rowe M., Young L. S. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene products in tumour cells of Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1991 Feb 9;337(8737):320–322. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90943-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G. The diagnostic significance of the CD30 (Ki-1) antigen. Histopathology. 1990 Apr;16(4):409–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1990.tb01151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton D. F., Wilkowski C. W., Hanson C. A., Shapiro R., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Filipovich A. H., McClain K. L. Epstein-Barr virus--determined clonality in posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease. Transplantation. 1990 Jun;49(6):1080–1084. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199006000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett R., Pendersen M., Kieff E. Complexity of EBV homologous DNA in continous lymphoblastoid cell lines. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):227–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N., Flynn K. The structure of the termini of the Epstein-Barr virus as a marker of clonal cellular proliferation. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):883–889. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90803-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer B., Roth M. S., Hyder D. M., Ginsburg D. Ki-1 lymphomas in children. Cancer. 1988 Mar 15;61(6):1213–1221. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880315)61:6<1213::aid-cncr2820610626>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D., Weiss L. M., Nathwani B. N., Brynes R. K., Levine A. M. Epstein-Barr virus in benign lymph node biopsies from individuals infected with the human immunodeficiency virus is associated with concurrent or subsequent development of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Blood. 1991 Apr 1;77(7):1527–1533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Mason D. Y., Gerdes J., O'Connor N., Wainscoat J., Pallesen G., Gatter K., Falini B., Delsol G., Lemke H. The expression of the Hodgkin's disease associated antigen Ki-1 in reactive and neoplastic lymphoid tissue: evidence that Reed-Sternberg cells and histiocytic malignancies are derived from activated lymphoid cells. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):848–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su I. J., Hsieh H. C., Lin K. H., Uen W. C., Kao C. L., Chen C. J., Cheng A. L., Kadin M. E., Chen J. Y. Aggressive peripheral T-cell lymphomas containing Epstein-Barr viral DNA: a clinicopathologic and molecular analysis. Blood. 1991 Feb 15;77(4):799–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su I. J., Lin K. H., Chen C. J., Tien H. F., Hsieh H. C., Lin D. T., Chen J. Y. Epstein-Barr virus-associated peripheral T-cell lymphoma of activated CD8 phenotype. Cancer. 1990 Dec 15;66(12):2557–2562. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19901215)66:12<2557::aid-cncr2820661218>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Movahed L. A. In situ demonstration of Epstein-Barr viral genomes in viral-associated B cell lymphoproliferations. Am J Pathol. 1989 Mar;134(3):651–659. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Movahed L. A., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. Detection of Epstein-Barr viral genomes in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 23;320(8):502–506. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902233200806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Strickler J. G., Warnke R. A., Purtilo D. T., Sklar J. Epstein-Barr viral DNA in tissues of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1987 Oct;129(1):86–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]