Abstract
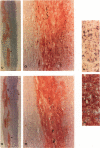
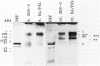
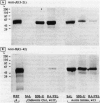
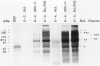
Cadaveric aortic intimas with uncomplicated atherosclerosis were examined to determine the distribution and polypeptide chain composition of fibrinogen-related protein. Immunohistochemical staining showed deposits rich in fibrinopeptides A and B. The deposits were usually disseminated throughout intimas of moderate thickness < 0.7 mm, but were distributed focally in elongate patches bounded both lumenally and medially by deposit-free tissue in thick atheromas. Saline extracts generally showed undegraded monomers and dimers by electrophoresis. The residual protein contained A alpha and gamma-chains that were cross-linked predominantly (>80%) into unresolved high M(r) (>200 kd) derivatives, whereas B beta-chains were left non-cross-linked, as occurs in late stages of cross-linking by transglutaminases. The resolved components had electrophoretic mobilities corresponding to characteristic products of both factor XIIIa and tissue-transglutaminase. A greater incorporation of alpha- rather than gamma-chains into cross-linked products implicated tissue-transglutaminase as contributing heavily. By contrast, vascular graft pseudo-intimas and a cadaveric clot were rich in degraded fibrin devoid of fibrinopeptide A, and cross-linked in patterns typical of XIIIa with gamma 2 dimers constituting the principal product. The findings indicate that the fibrinogen in the aortic intima is comparatively well protected from thrombin and plasmin, and that much of it is deposited through direct cross-linking by tissue-transglutaminase without being converted to fibrin.
Full text
PDF



















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsigian C., Fellin F. M., Jain A., Martinez J. Dissociation of fibrinogen and fibronectin binding from transglutaminase-mediated cross-linking at the hepatocyte surface. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14015–14022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell F. P., Gallus A. S., Schwartz C. J. Focal and regional patterns of uptake and the transmural distribution of 131-I-fibrinogen in the pig aorta in vivo. Exp Mol Pathol. 1974 Apr;20(2):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(74)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bini A., Fenoglio J. J., Jr, Mesa-Tejada R., Kudryk B., Kaplan K. L. Identification and distribution of fibrinogen, fibrin, and fibrin(ogen) degradation products in atherosclerosis. Use of monoclonal antibodies. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):109–121. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bini A., Fenoglio J., Jr, Sobel J., Owen J., Fejgl M., Kaplan K. L. Immunochemical characterization of fibrinogen, fibrin I, and fibrin II in human thrombi and atherosclerotic lesions. Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1038–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Blombäck M., Henschen A., Hessel B., Iwanaga S., Woods K. R. N-terminal disulphide knot of human fibrinogen. Nature. 1968 Apr 13;218(5137):130–134. doi: 10.1038/218130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowness J. M., Tarr A. H., Wiebe R. I. Transglutaminase-catalysed cross-linking: a potential mechanism for the interaction of fibrinogen, low density lipoprotein and arterial type III procollagen. Thromb Res. 1989 May 15;54(4):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardinali M., Uchino R., Chung S. I. Interaction of fibrinogen with murine melanoma cells: covalent association with cell membranes and protection against recognition by lymphokine-activated killer cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 15;50(24):8010–8016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. I. Comparative studies on tissue transglutaminase and factor XIII. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:240–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Angelo V., Villa S., Mysliwiec M., Donati M. B., de Gaetano G. Defective fibrinolytic and prostacyclin-like activity in human atheromatous plaques. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Apr 30;39(2):535–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. B. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1949 Nov 19;2(6586):925–927. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(49)91503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Senger D. R., Dvorak A. M., Harvey V. S., McDonagh J. Regulation of extravascular coagulation by microvascular permeability. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):1059–1061. doi: 10.1126/science.3975602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Cole P. W. Mechanism of action of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme: identification of a functional cysteine essential for activity. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5518–5525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. W., Connaghan D. G., Scott W. L., Marder V. J. Increased plasma concentration of cross-linked fibrin polymers in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1987 Jun;75(6):1170–1177. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.6.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda S. R., Shainoff J. R. Adsorptive endocytosis of fibrin monomer by macrophages: evidence of a receptor for the amino terminus of the fibrin alpha chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4565–4569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D., Reidy M. A., Benditt E. P., Schwartz S. M. Cell proliferation in human coronary arteries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4600–4604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg C. S., Achyuthan K. E., Borowitz M. J., Shuman M. A. The transglutaminase in vascular cells and tissues could provide an alternate pathway for fibrin stabilization. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):702–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøn B., Bennick A., Nieuwenhuizen W., Brosstad F. Normal and fibrinaemic patient plasma contain high-molecular weight crosslinked fibrin(ogen) derivatives with intact fibrinopeptide A. Thromb Res. 1990 Jan 15;57(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90325-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegt V. N. Relations between activation and inhibition of fibrinolysis in the walls of human arteries and veins. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Aug 31;38(2):407–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henschen A., Edman P. Large scale preparation of S-carboxymethylated chains of human fibrin and fibrinogen and the occurrence of -chain variants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 15;263(2):351–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui K. Y., Haber E., Matsueda G. R. Monoclonal antibodies to a synthetic fibrin-like peptide bind to human fibrin but not fibrinogen. Science. 1983 Dec 9;222(4628):1129–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.6648524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juprelle-Soret M., Wattiaux-De Coninck S., Wattiaux R. Subcellular localization of transglutaminase. Effect of collagen. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):421–427. doi: 10.1042/bj2500421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaide H., Shainoff J. R. Cross-linking of fibrinogen and fibrin by fibrin-stablizing factor (factor XIIIa). J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Apr;85(4):574–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao V. C., Wissler R. W. A study of the immunohistochemical localization of serum lipoproteins and other plasma proteins in human atherosclerotic lesions. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Oct;4(5):465–479. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao V. C., Wissler R. W. A study of the immunohistochemical localization of serum lipoproteins and other plasma proteins in human atherosclerotic lesions. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Oct;4(5):465–479. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaubert W., Schönbauer R., Gilg T., Gollwitzer R., Hafter R., Graeff H., Spann W., Wilmanns W. The role of coagulation, fibrinogenolysis and fibrinolysis in the development of fluid and clotted cadaver plasma. Thromb Res. 1988 Apr 1;50(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudryk B., Rohoza A., Ahadi M., Chin J., Wiebe M. E. A monoclonal antibody with ability to distinguish between NH2-terminal fragments derived from fibrinogen and fibrin. Mol Immunol. 1983 Nov;20(11):1191–1200. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laki K., Benkö A., Farrell J. Clot stabilization and atherosclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:235–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Kasamatsu H. On the electrotransfer of polypeptides from gels to nitrocellulose membranes. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;128(2):302–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90379-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissilour S., Godinot C. Influence of SDS and methanol on protein electrotransfer to Immobilon P membranes in semidry blot systems. Biotechniques. 1990 Oct;9(4):397-8, 400-1. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Mussoni L. Interactions between fibrin and the plasminogen activators produced by cultured endothelial cells. Blood. 1983 Jul;62(1):62–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao S. J., Rechtin A. E., Krstenansky J. L., Jackson R. L. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific to the amino terminus of the alpha-chain of human fibrin. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Jun 28;63(3):445–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Rich E., Barsigian C. Transglutaminase-mediated cross-linking of fibrinogen by human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20502–20508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. A., Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L. Cross-linking of fibrin by fibrin=stabilizing factor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:127–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirshahi M., Azzarone B., Soria J., Mirshahi F., Soria C. The role of fibroblasts in organization and degradation of a fibrin clot. J Lab Clin Med. 1991 Apr;117(4):274–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Siebenlist K. R., Amrani D. L., DiOrio J. P. Identification of covalently linked trimeric and tetrameric D domains in crosslinked fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1113–1117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Schad P. E. Cross-linking of fibronectin to collagen by blood coagulation Factor XIIIa. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):781–787. doi: 10.1172/JCI109524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy S. N., Lorand L. Cross-linked A alpha.gamma chain hybrids serve as unique markers for fibrinogen polymerized by tissue transglutaminase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9679–9682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Aoki N. Significance of cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin in inhibition of fibrinolysis and in hemostasis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):536–542. doi: 10.1172/JCI110479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Page I. H. Deposition of modified fibrinogen within the aortic intima. Atherosclerosis. 1972 Nov-Dec;16(3):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(72)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Stearns D. J., DiBello P. M., Hishikawa-Itoh Y. Characterization of a mode of specific binding of fibrin monomer through its amino-terminal domain by macrophages and macrophage cell-lines. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Apr 12;63(2):193–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Urbanic D. A., DiBello P. M. Immunoelectrophoretic characterizations of the cross-linking of fibrinogen and fibrin by factor XIIIa and tissue transglutaminase. Identification of a rapid mode of hybrid alpha-/gamma-chain cross-linking that is promoted by the gamma-chain cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6429–6437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Urbanic D. A. Multicolour immuno-staining of fibrinogen polypeptide chains for identification of their derivatives in electrophoregrams. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1990 Oct;1(4-5):479–484. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199010000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Valenzuela R., Urbanic D. A., DiBello P. M., Lucas F. V., Graor R. Fibrinogen A alpha and gamma-chain dimers as potential differential indicators of atherosclerotic and thrombotic vascular disease. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1990 Oct;1(4-5):499–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R. Zonal immobilization of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 31;95(2):690–695. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90840-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. B., Alexander K. M., Massie I. B. Insoluble "fibrin" in human aortic intima. Quantitative studies on the relationship between insoluble "fibrin", soluble fibrinogen and low density lipoprotein. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Jan-Feb;23(1):19–39. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. B., Keen G. A., Grant A., Stirk C. Fate of fibrinogen in human arterial intima. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Mar-Apr;10(2):263–275. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. B., Massie I. B., Alexander K. M. The release of an immobilized lipoprotein fraction from atherosclerotic lesions by incubation with plasmin. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Oct;25(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. B. Plasma macromolecules in interstitial fluid from normal and atherosclerotic human aorta. Monogr Atheroscler. 1986;14:179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. B., Staples E. M. Distribution of plasma proteins across the human aortic wall--barrier functions of endothelium and internal elastic lamina. Atherosclerosis. 1980 Dec;37(4):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(80)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. B., Staples E. M. Haemostatic factors in human aortic intima. Lancet. 1981 May 30;1(8231):1171–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD A. S. The histological localisation of fibrinolysin activator. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78:281–283. doi: 10.1002/path.1700780131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox J. N., Smith K. M., Schwartz S. M., Gordon D. Localization of tissue factor in the normal vessel wall and in the atherosclerotic plaque. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. S., Warnke R. Suppression of endogenous avidin-binding activity in tissues and its relevance to biotin-avidin detection systems. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Oct;29(10):1196–1204. doi: 10.1177/29.10.7028859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf N., Carstairs K. C. Infiltration and thrombosis in atherogenesis. A study using immunofluorescent techniques. Am J Pathol. 1967 Sep;51(3):373–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Chung A. E. Potential role of entactin in hemostasis. Specific interaction of entactin with fibrinogen A alpha and B beta chains. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18802–18807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]