Abstract
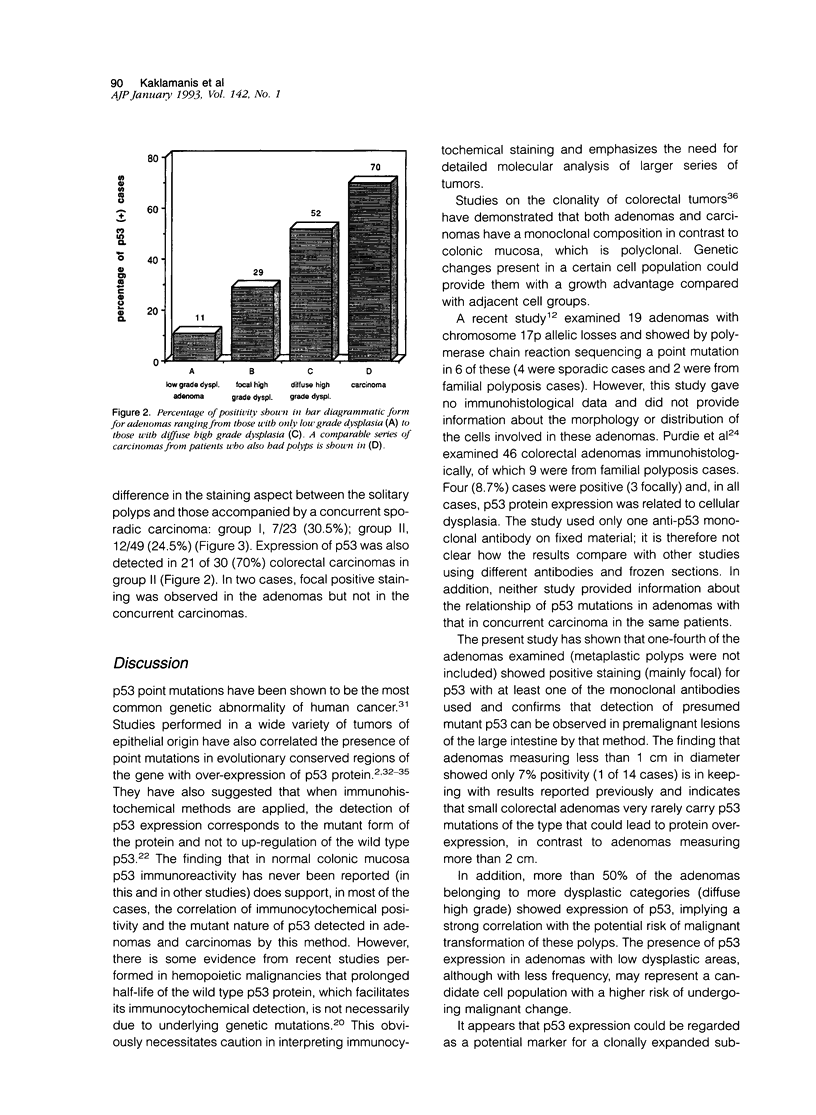
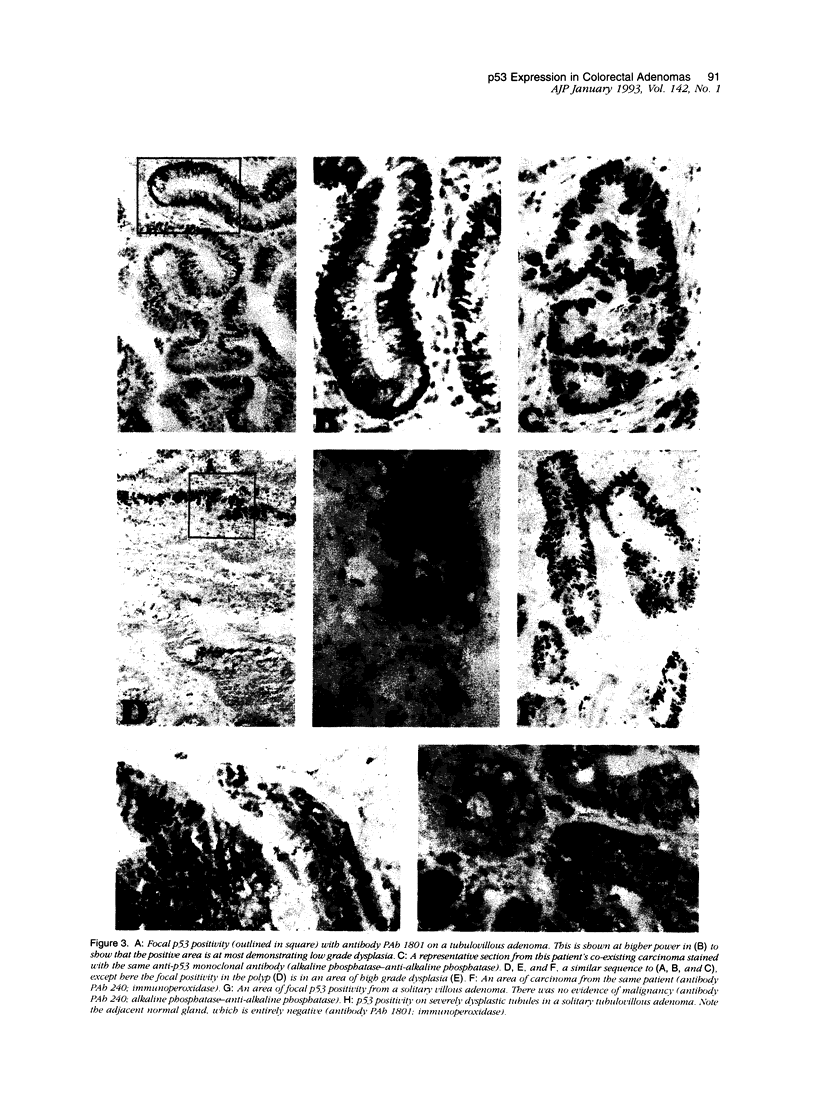
To assess the expression of p53 in premalignant lesions, we examined by immunohistochemistry benign colorectal adenomas (n = 72, measuring more than 6 mm and less than 95 mm in diameter) from patients without (group I, n = 23) or with (group II, n = 49) concurrent sporadic colorectal carcinomas. Using a panel of three monoclonal antibodies (PAb 240, PAb 421, PAb 1801) and two polyclonal antibodies (CM1, C19) immunohistological staining was demonstrated in 26% of the cases (19 of 72 adenomas, 7 of 23 from group I and 12 of 49 from group II). In the majority of the cases, p53 positive foci in the adenomas occurred in the most dysplastic areas, although focal positivity was detected in glands that were histologically normal. Expression of p53 protein was also detected in 21 of 30 (70%) colorectal carcinomas of group II. In two cases focal positive staining was observed in the polyps but not in the concurrent carcinomas. Non-neoplastic colonic mucosa and stromal lymphoid cells were negative in all cases examined. Over-expression of p53 in neoplastic tissues detected by immunocytochemistry is generally believed to correlate with the presence of mutation in the gene. This may not be an absolute rule, because in some hemopoietic malignancies, there is evidence that p53 protein may be detectable in the absence of an underlying mutation. These findings therefore represent the highest incidence in colorectal adenomas of abnormalities in the p53 protein expression, probably largely due to underlying mutations. This study also suggests that immunocytochemical demonstration of p53 protein may be a suitable method for the routine detection of subpopulations of cells which, by clonal expansion, could acquire a growth advantage within an adenoma during the neoplastic process.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Paraskeva C., Markowitz S., Willson J. K., Hamilton S., Vogelstein B. p53 gene mutations occur in combination with 17p allelic deletions as late events in colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 1;50(23):7717–7722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Matlashewski G., Crawford L. Isolation of human-p53-specific monoclonal antibodies and their use in the studies of human p53 expression. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressac B., Kew M., Wands J., Ozturk M. Selective G to T mutations of p53 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma from southern Africa. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):429–431. doi: 10.1038/350429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Rilke F., Andreola S., D'Amato L., Delia D. P53 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1988 Feb 15;41(2):178–183. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba I., Takahashi T., Nau M. M., D'Amico D., Curiel D. T., Mitsudomi T., Buchhagen D. L., Carbone D., Piantadosi S., Koga H. Mutations in the p53 gene are frequent in primary, resected non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer Study Group. Oncogene. 1990 Oct;5(10):1603–1610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. F., Cheng K., Frey A. B., Stein R., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. Purification of complexes of nuclear oncogene p53 with rat and Escherichia coli heat shock proteins: in vitro dissociation of hsc70 and dnaK from murine p53 by ATP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1206–1215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham J., Lust J. A., Schaid D. J., Bren G. D., Carpenter H. A., Rizza E., Kovach J. S., Thibodeau S. N. Expression of p53 and 17p allelic loss in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7):1974–1980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Goldfinger N., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Shaulsky G., Skurnik Y., Arai N., Rotter V., Oren M. Meth A fibrosarcoma cells express two transforming mutant p53 species. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Cho K. R., Nigro J. M., Kern S. E., Simons J. W., Ruppert J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Thomas G., Kinzler K. W. Identification of a chromosome 18q gene that is altered in colorectal cancers. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):49–56. doi: 10.1126/science.2294591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B. Clonal analysis of human colorectal tumors. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):193–197. doi: 10.1126/science.2889267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L. Mutant p53--the commonest genetic abnormality in human cancer? J Pathol. 1990 Sep;162(1):5–6. doi: 10.1002/path.1711620103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Functional inactivation of genes by dominant negative mutations. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):219–222. doi: 10.1038/329219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Mutation is required to activate the p53 gene for cooperation with the ras oncogene and transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.739-746.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu I. C., Metcalf R. A., Sun T., Welsh J. A., Wang N. J., Harris C. C. Mutational hotspot in the p53 gene in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):427–428. doi: 10.1038/350427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo R., Gatter K., Bartek J., Lane D., Harris A. L. Increased expression of mutant forms of p53 oncogene in primary lung cancer. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):675–679. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90801-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe M., Emanuel B. S., Givol D., Oren M., Croce C. M. Localization of gene for human p53 tumour antigen to band 17p13. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):84–85. doi: 10.1038/320084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hamilton S. R., Hedge P., Markham A. Identification of a gene located at chromosome 5q21 that is mutated in colorectal cancers. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1366–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.1848370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. R., Davidoff A. M., Kerns B. J., Humphrey P. A., Pence J. C., Dodge R. K., Clarke-Pearson D. L., Iglehart J. D., Bast R. C., Jr, Berchuck A. Overexpression and mutation of p53 in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Jun 1;51(11):2979–2984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Merry D., Givol D. The gene for human p53 cellular tumor antigen is located on chromosome 17 short arm (17p13). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):130–134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. W., Aslo A., Tsay C., Slamon D., Ishizaki K., Toguchida J., Yamamuro T., Lampkin B., Koeffler H. P. Frequency and structure of p53 rearrangements in human osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 15;50(24):7950–7954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Medcalf E. A. Cotranslation of activated mutant p53 with wild type drives the wild-type p53 protein into the mutant conformation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90384-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser J., Thompson A. M., Cranston G., Evans H. J. Evidence that p53 behaves as a tumour suppressor gene in sporadic breast tumours. Oncogene. 1990 Oct;5(10):1573–1579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdie C. A., O'Grady J., Piris J., Wyllie A. H., Bird C. C. p53 expression in colorectal tumors. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):807–813. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Rowan A., Smith M. E., Kerr I. B., Bodmer W. F., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 mutations in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7555–7559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogel A., Popliker M., Webb C. G., Oren M. p53 cellular tumor antigen: analysis of mRNA levels in normal adult tissues, embryos, and tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2851–2855. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slingerland J. M., Minden M. D., Benchimol S. Mutation of the p53 gene in human acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1991 Apr 1;77(7):1500–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Chumakov P., Welch W. J., Jenkins J. R. Mutant p53 proteins bind hsp 72/73 cellular heat shock-related proteins in SV40-transformed monkey cells. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):201–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade-Evans A., Jenkins J. R. Precise epitope mapping of the murine transformation-associated protein, p53. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):699–706. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg F. M., Tigges A. J., Schipper M. E., den Hartog-Jager F. C., Kroes W. G., Walboomers J. M. Expression of the nuclear oncogene p53 in colon tumours. J Pathol. 1989 Mar;157(3):193–199. doi: 10.1002/path.1711570304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]