Abstract
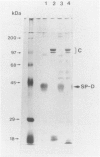
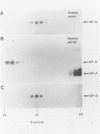
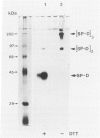
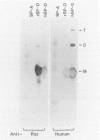
Surfactant protein D (SP-D) is a collagenous calcium-dependent carbohydrate-binding protein that is structurally related to the serum mannose-binding proteins and pulmonary surfactant protein A. SP-D was initially characterized as a biosynthetic product of freshly isolated rat type II cells and first purified in chemical amounts from bronchoalveolar lavage of rats with silica-induced alveolar lipoproteinosis. The present studies describe the characterization of human SP-D isolated from therapeutic bronchoalveolar lavage of patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Human proteinosis SP-D was extracted from the 10,000 x g pellet of bronchoalveolar lavage with 100 mmol/L glucose or ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, and specifically bound to and eluted from maltosyl-agarose. The protein cross-reacted with monospecific antibodies to rat SP-D by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunoblot and eluted near the position of rat SP-D on reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography. When chromatographed on 4% agarose (A-15M) in the presence of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, the solubilized human proteinosis SP-D eluted near the void volume and earlier than rat SP-D dodecamers or human SP-D multimers in the lavage supernatant. Two-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting of proteins in the lavage pellet with antibodies to the carbohydrate-binding domain of proteinosis human SP-D demonstrated covalently cross-linked multimers of SP-D monomers (43 kd, reduced) and multimers of trimeric components stabilized by disulfide and non-disulfide bonds. These studies describe the isolation and biochemical characterization of human SP-D and demonstrate the abnormal accumulation of this protein in the air spaces of patients with alveolar proteinosis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharyya S. N. Characterization of collagenous and non-collagenous peptides of a glycoprotein isolated from alveoli of patients with alveolar proteinosis. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):447–457. doi: 10.1042/bj1930447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya S. N., Lynn W. S. Structural studies on a collagen-like glycoprotein isolated from lung lavage of normal animal. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 16;626(2):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90141-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford S. W., Mecham R. P., Sage H. Structural characteristics and intermolecular organization of human pulmonary-surfactant-associated proteins. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):107–114. doi: 10.1042/bj2400107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch E., Parghi D., Kuan S. F., Persson A. Surfactant protein D: subcellular localization in nonciliated bronchiolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 1):L60–L66. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.263.1.L60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch E., Persson A., Chang D., Parghi D. Surfactant protein D. Increased accumulation in silica-induced pulmonary lipoproteinosis. Am J Pathol. 1991 Oct;139(4):765–776. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch E., Rust K., Marienchek W., Parghi D., Chang D., Persson A. Developmental expression of pulmonary surfactant protein D (SP-D). Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;5(1):13–18. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch E., Rust K., Persson A., Mariencheck W., Moxley M., Longmore W. Primary translation products of pulmonary surfactant protein D. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 1):L247–L253. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1991.260.4.L247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore L. B., Talley F. A., Hook G. E. Classification and morphometric quantitation of insoluble materials from the lungs of patients with alveolar proteinosis. Am J Pathol. 1988 Nov;133(2):252–264. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook G. E., Bell D. Y., Gilmore L. B., Nadeau D., Reasor M. J., Talley F. A. Composition of bronchoalveolar lavage effluents from patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Lab Invest. 1978 Oct;39(4):342–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook G. E., Gilmore L. B., Talley F. A. Dissolution and reassembly of tubular myelin-like multilamellated structures from the lungs of patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Lab Invest. 1986 Aug;55(2):194–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Chang D., Crouch E. Surfactant protein D is a divalent cation-dependent carbohydrate-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5755–5760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Chang D., Rust K., Moxley M., Longmore W., Crouch E. Purification and biochemical characterization of CP4 (SP-D), a collagenous surfactant-associated protein. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6361–6367. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Rust K., Chang D., Moxley M., Longmore W., Crouch E. CP4: a pneumocyte-derived collagenous surfactant-associated protein. Evidence for heterogeneity of collagenous surfactant proteins. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8576–8584. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. S., Taeusch H. W., Jr, Benson B., Hawgood S. An electrophoretic and immunochemical characterization of human surfactant-associated proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 7;791(2):226–238. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. F., Ohning B. L., Tannenbaum D., Whitsett J. A. Structural relationships of the major glycoproteins from human alveolar proteinosis surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 25;911(3):294–305. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rust K., Grosso L., Zhang V., Chang D., Persson A., Longmore W., Cai G. Z., Crouch E. Human surfactant protein D: SP-D contains a C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Oct;290(1):116–126. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90597-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Fisher J. H., Papst P., Benson B., Lau K., Mason R. J., Voelker D. R. Primary structure of rat pulmonary surfactant protein D. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1853–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh G., Katyal S. L., Bedrossian C. W., Rogers R. M. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Staining for surfactant apoprotein in alveolar proteinosis and in conditions simulating it. Chest. 1983 Jan;83(1):82–86. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura T., Fukuda Y., Harrison M., Ferrans V. J. Ultrastructural, histochemical, and freeze-fracture evaluation of multilamellated structures in human pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Anat. 1987 Jul;179(3):258–268. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001790307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]