Abstract
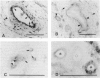
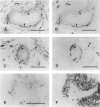
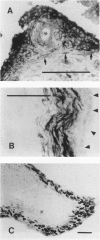
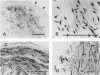
Regulatory peptides, including neuropeptides, are metabolized by membrane-bound peptidases. We have localized the membrane peptidases angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV), and aminopeptidase M (APM) in normal and inflamed human synovium by immunohistochemistry and enzyme histochemistry. ACE was localized to endothelial cells of all vessels, whereas endothelial DPPIV and APM were restricted to veins and capillaries of some cases. Perivascular spindle-shaped cells stained positively for APM, but rarely for ACE and DPPIV. Synovial lining cells were universally positive for APM but rarely for ACE or DPPIV, whereas a subintimal layer of spindle-shaped cells was frequently positive for all three enzymes, particularly APM. Staining for each enzyme was also observed on some stromal cells. Inflamed synovium displayed increased cellularity with corresponding increases in membrane peptidase staining. APM-positive, perivascular spindle-shaped cells and DPPIV-positive lymphocytes frequently bore HLA class II antigens. This distribution of membrane peptidases supports the hypothesis of a functional compartmentalization of vascular peptidergic systems, with the activities of vasoactive peptides localized to their sites of release. Furthermore, metabolic pathways for regulatory peptides may vary between different structures within human synovium, and these enzymes may be of different relative importance in normal and inflamed tissues. The implied regional control of regulatory peptide activity by membrane peptidases suggests novel potential approaches to the pharmacological manipulation of inflammation by specific enzyme inhibitors.
Full text
PDF

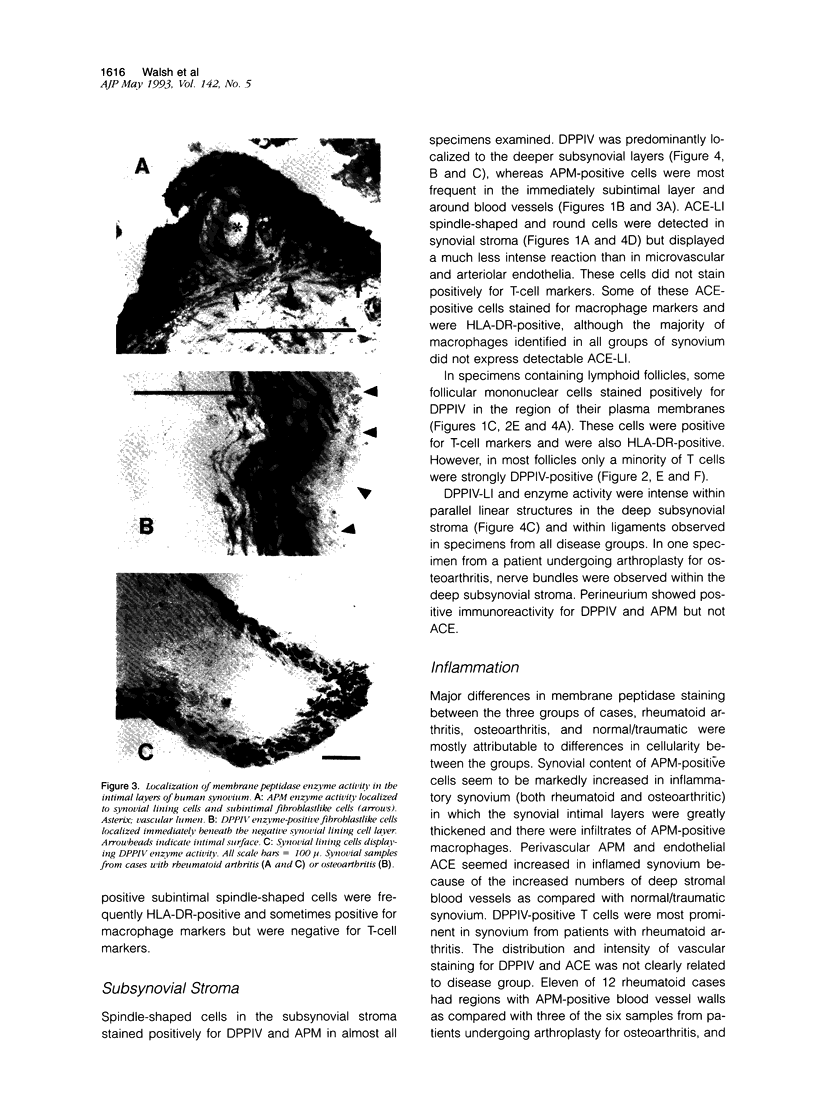
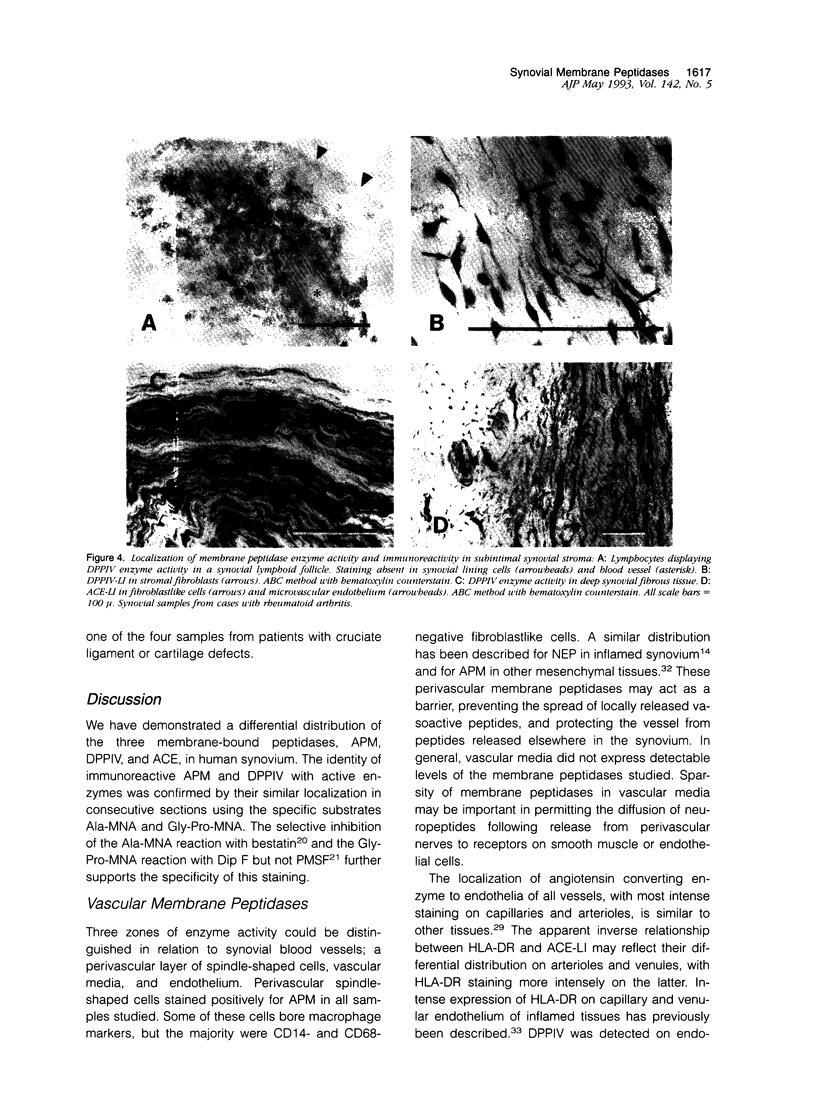




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad S., Wang L., Ward P. E. Dipeptidyl(amino)peptidase IV and aminopeptidase M metabolize circulating substance P in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Mar;260(3):1257–1261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURSTONE M. S. Histochemical demonstration of phosphatases in frozen sections with naphthol AS-phosphates. J Histochem Cytochem. 1961 Mar;9:146–153. doi: 10.1177/9.2.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes K., Bourne A., Cook P. A., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Membrane peptidases in the peripheral nervous system of the pig: their localization by immunohistochemistry at light and electron microscopic levels. Neuroscience. 1991;44(1):245–261. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90265-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell P. R., Seegal B. C., Hsu K. C., Das M., Soffer R. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme: vascular endothelial localization. Science. 1976 Mar 12;191(4231):1050–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.175444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusser D. J., Jacoby D. B., Djokic T. D., Rubinstein I., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Virus induces airway hyperresponsiveness to tachykinins: role of neutral endopeptidase. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Oct;67(4):1504–1511. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.4.1504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland J., Setton C., Silverstein E. Angiotensin converting enzyme: induction by steroids in rabbit alveolar macrophages in culture. Science. 1977 Jul 1;197(4298):64–65. doi: 10.1126/science.194311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B., Aboukhair N., Watson S. Immunohistochemical localization of aminopeptidase M in rat brain and periphery: relationship of enzyme localization and enkephalin metabolism. Peptides. 1987 May-Jun;8(3):523–532. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(87)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., MacDonald S., Slusarenko M., Beverley P. C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for human monocytes, granulocytes and endothelium. Immunology. 1984 Dec;53(4):753–767. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi T., Kurosaka M., Ziff M. Electron microscopic study of HLA-DR and monocyte/macrophage staining cells in the rheumatoid synovial membrane. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 May;29(5):600–613. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R., Ashton J., Schulz W. W., Erdös E. G. Neutral metalloendopeptidase in human lung tissue and cultured cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):564–568. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karchuk O. A., Gariaev P. P., Pustovoit V. I., Poglazov B. F. Issledovanie struktury belka virusa ogurechnoi mozaiki-3,4 metodom dispersii opticheskogo vrashcheniia. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1973 Jul-Aug;211(1):245–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Booth A. G., George S. G., Ingram J., Kershaw D., Wood E. J., Young A. R. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, a kidney brush-border serine peptidase. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):169–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1570169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd B. L., Mapp P. I., Gibson S. J., Polak J. M., O'Higgins F., Buckland-Wright J. C., Blake D. R. A neurogenic mechanism for symmetrical arthritis. Lancet. 1989 Nov 11;2(8672):1128–1130. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91491-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Burrows J. C., Skoutelis A., Marder R., Domer P. H., Anderson B., Leibovich S. J. Monoclonal antibodies detect monocyte/macrophage activation and differentiation antigens and identify functionally distinct subpopulations of human rheumatoid synovial tissue macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):165–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson J., Ekblom A., Henriksson K., Lundeberg T., Theodorsson E. Immunoreactive tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and neuropeptide Y in human synovial fluid from inflamed knee joints. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 22;100(1-3):326–330. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90707-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Holzer P., Schweditsch M., Gamse R. Elimination of substance P from the circulation of the rat and its inhibition by bacitracin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;305(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00497000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Look A. T., Ashmun R. A., Shapiro L. H., Peiper S. C. Human myeloid plasma membrane glycoprotein CD13 (gp150) is identical to aminopeptidase N. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1299–1307. doi: 10.1172/JCI114015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Carson D. A., Vaughan J. H. Substance P activation of rheumatoid synoviocytes: neural pathway in pathogenesis of arthritis. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):893–895. doi: 10.1126/science.2433770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapp P. I., Kidd B. L., Gibson S. J., Terry J. M., Revell P. A., Ibrahim N. B., Blake D. R., Polak J. M. Substance P-, calcitonin gene-related peptide- and C-flanking peptide of neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive fibres are present in normal synovium but depleted in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Neuroscience. 1990;37(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90199-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapp P. I., Walsh D. A., Kidd B. L., Cruwys S. C., Polak J. M., Blake D. R. Localization of the enzyme neutral endopeptidase to the human synovium. J Rheumatol. 1992 Dec;19(12):1838–1844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. W., Chiu B., Inman R. D. Substance P and arthritis: analysis of plasma and synovial fluid levels. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jan;33(1):87–90. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. F., Surrall K. E., McKenna F., Dixon J. S., Bird H. A., Wright V. Captopril: a new treatment for rheumatoid arthritis? Lancet. 1984 Jun 16;1(8390):1325–1328. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91821-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaughan G. W., Wickson J. E., Creswick P. F., Gorrell M. D. Identification of the bile canalicular cell surface molecule GP110 as the ectopeptidase dipeptidyl peptidase IV: an analysis by tissue distribution, purification and N-terminal amino acid sequence. Hepatology. 1990 Apr;11(4):534–544. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechtersheimer G., Möller P. Expression of aminopeptidase N (CD13) in mesenchymal tumors. Am J Pathol. 1990 Nov;137(5):1215–1222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R., Lacefield W. Specific inhibitors of aminopeptidase M--relationship to anti-inflammatory activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 1;28(5):673–675. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow B. Substance P. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Jun;35(2):85–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piazza G. A., Callanan H. M., Mowery J., Hixson D. C. Evidence for a role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in fibronectin-mediated interactions of hepatocytes with extracellular matrix. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):327–334. doi: 10.1042/bj2620327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Duke O., Hobbs S., Janossy G., Panayi G. Histochemical discrimination of HLA-DR positive cell populations in the normal and arthritic synovial lining. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 May;48(2):381–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulford K. A., Rigney E. M., Micklem K. J., Jones M., Stross W. P., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. KP1: a new monoclonal antibody that detects a monocyte/macrophage associated antigen in routinely processed tissue sections. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Apr;42(4):414–421. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.4.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. H., Moon B. J., Harbeson S. Inhibition of aminopeptidases by amastatin and bestatin derivatives. Effect of inhibitor structure on slow-binding processes. J Med Chem. 1984 Apr;27(4):417–422. doi: 10.1021/jm00370a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. A., Fernandez N., Kurpisz M., Okoye R., Ogilvie J., Awad J., Labeta M., Festenstein H. Serological biochemical and functional characterisation of three different HLA-DR monoclonal antibodies derived from C57BL6 mice. Tissue Antigens. 1986 Oct;28(4):199–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1986.tb00483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Ansorge S. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV in the immune system. Cytofluorometric evidence for induction of the enzyme on activated T lymphocytes. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 Aug;371(8):699–705. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1990.371.2.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Jahn S., Kiessig S. T., Demuth H. U., Neubert K., Barth A., Von Baehr R., Ansorge S. The role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human T lymphocyte activation. Inhibitors and antibodies against dipeptidyl peptidase IV suppress lymphocyte proliferation and immunoglobulin synthesis in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1821–1826. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. H., Brown M. H., Rowe D., Callard R. E., Beverley P. C. Functional subsets of human helper-inducer cells defined by a new monoclonal antibody, UCHL1. Immunology. 1986 May;58(1):63–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S. P., Goetzl E. J., Malfroy B. Elevated synovial tissue concentration of the common acute lymphoblastic leukaemia antigen (CALLA)-associated neutral endopeptidase (3.4.24.11) in human chronic arthritis. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):142–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisz A., Scicchitano R., Stead R., Matsuda H., Tomioka M., Denburg J., Bienenstock J. Neuropeptides and immunity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Dec;136(6 Pt 2):S48–S51. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.6_Pt_2.S48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson S. L., Kenny A. J. Metabolism of neuropeptides. Hydrolysis of the angiotensins, bradykinin, substance P and oxytocin by pig kidney microvillar membranes. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj2410237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. R., Beckstead J. H., Warnke R. A., Wood G. S. Endothelial cell phenotypic diversity. In situ demonstration of immunologic and enzymatic heterogeneity that correlates with specific morphologic subtypes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 May;87(5):569–575. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.5.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer A. J., Mattern T., Feller A. C., Heymann E., Flad H. D. CD26 antigen is a surface dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV) as characterized by monoclonal antibodies clone TII-19-4-7 and 4EL1C7. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Apr;31(4):429–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbi W., Greaves M. F., Schneider C., Koubek K., Janossy G., Stein H., Kung P., Goldstein G. Monoclonal antibodies OKT 11 and OKT 11A have pan-T reactivity and block sheep erythrocyte "receptors". Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jan;12(1):81–86. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Mapp P. I., Wharton J., Rutherford R. A., Kidd B. L., Revell P. A., Blake D. R., Polak J. M. Localisation and characterisation of substance P binding to human synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Mar;51(3):313–317. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.3.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Wharton J., Blake D. R., Polak J. M. Neural and endothelial regulatory peptides, their possible involvement in inflammation. Int J Tissue React. 1992;14(3):101–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock J. V. The significance of angiotensin I converting enzyme in granulomatous inflammation. Functions of ACE in granulomas. Sarcoidosis. 1986 Mar;3(1):19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Rutherford R. A., Walsh D. A., Mapp P. I., Knock G. A., Blake D. R., Polak J. M. Autoradiographic localization and analysis of endothelin-1 binding sites in human synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Aug;35(8):894–899. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]