Abstract
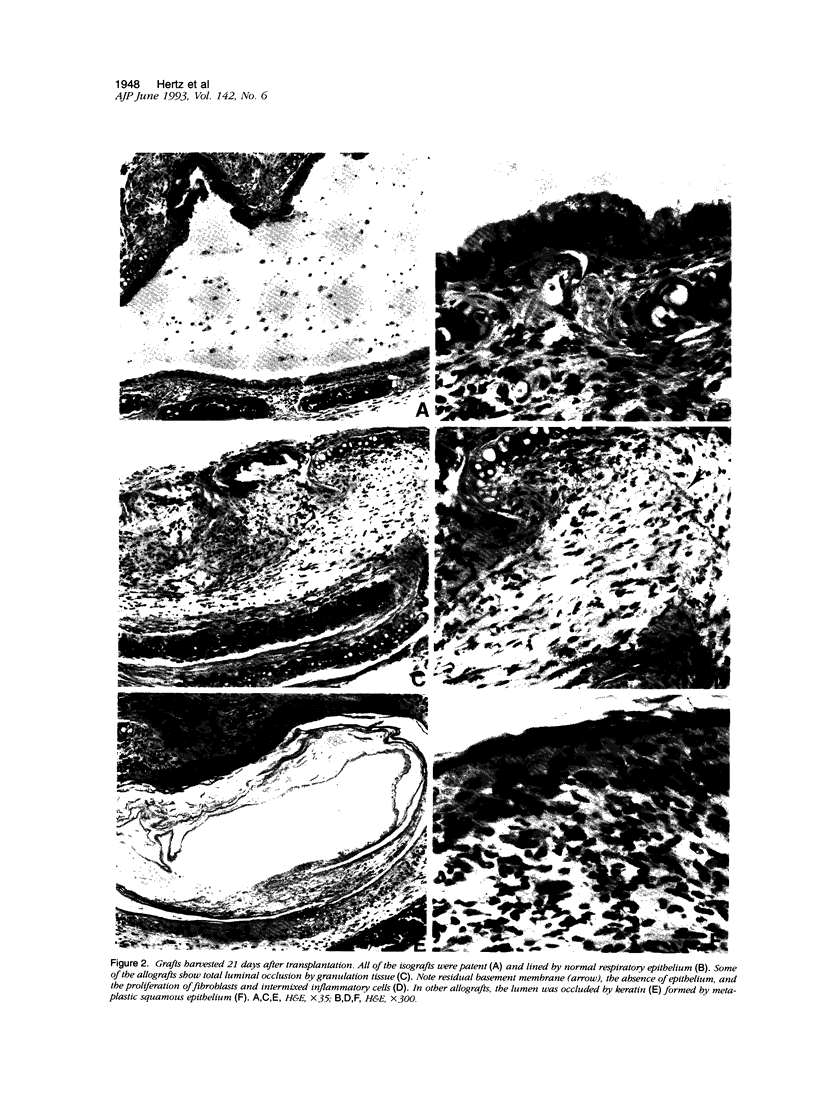
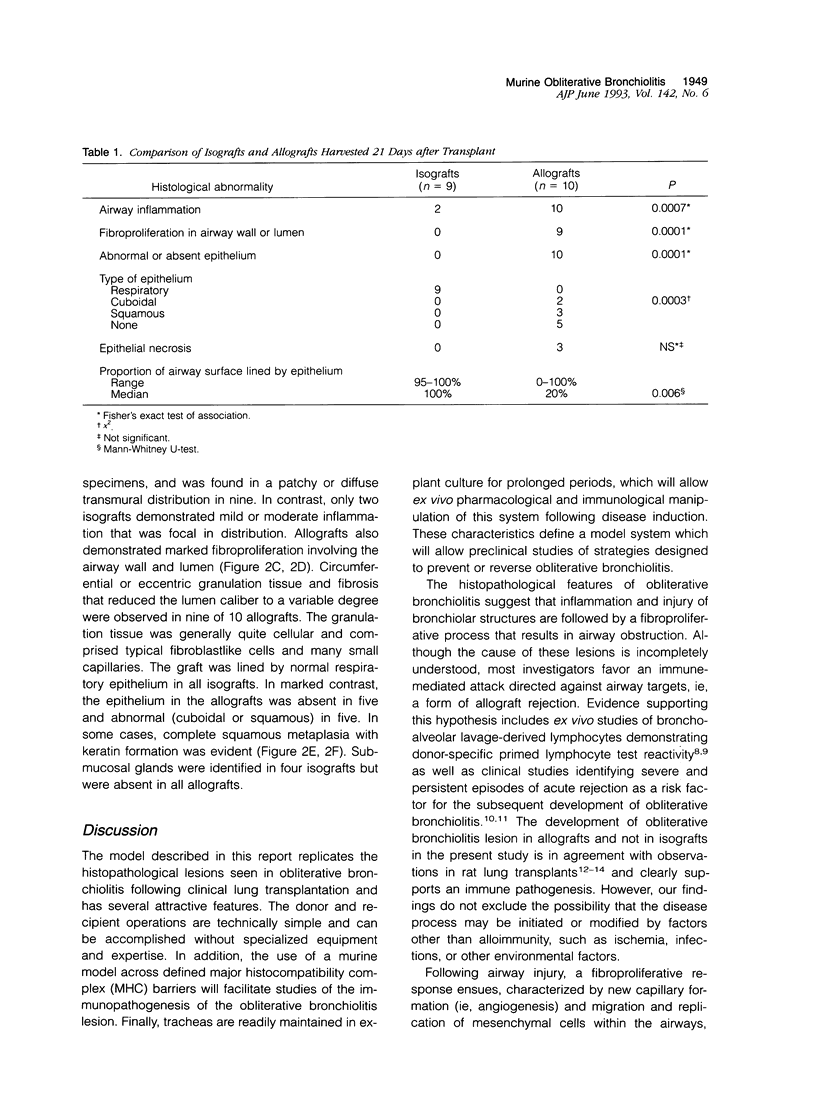
Obliterative bronchiolitis, characterized histopathologically by airway inflammation and occlusion of small airways by vascularized fibrous tissue, constitutes an important threat to the long-term survival of lung and heart-lung transplant recipients. The pathogenesis of obliterative bronchiolitis is poorly understood, and successful preventative or treatment strategies are not available. We sought to develop a preclinical model system of obliterative bronchiolitis by transplanting murine airway grafts, consisting of tracheas and main bronchi, into the subcutaneous tissue of allogeneically mismatched recipient animals. By 10 days after transplantation, allografts demonstrated subepithelial and/or peritracheal inflammation, epithelial necrosis, and early fibroproliferation. Grafts harvested 21 days after transplantation demonstrated fibroproliferation in the airway wall or lumen in nine of 10 allografts versus 0 of 10 isografts (P = 0.0001). In addition, abnormal epithelium (ie, nonciliated cuboidal, squamous, or absent) was seen in all allografts, while nine of nine isografts demonstrated normal respiratory epithelium (P = 0.0003). Although differences exist between this model and the chronic rejection process in human lung transplant recipients, these findings reproduce the characteristic features of obliterative bronchiolitis and demonstrate that this lesion can result from allograft rejection. This model will be useful for studying the pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment of obliterative bronchiolitis after lung transplantation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke C. M., Theodore J., Dawkins K. D., Yousem S. A., Blank N., Billingham M. E., Van Kessel A., Jamieson S. W., Oyer P. E., Baldwin J. C. Post-transplant obliterative bronchiolitis and other late lung sequelae in human heart-lung transplantation. Chest. 1984 Dec;86(6):824–829. doi: 10.1378/chest.86.6.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber S. A. The case for local immunosuppression. Transplantation. 1992 Jul;54(1):1–11. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199207000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz M. I., Henke C. A., Nakhleh R. E., Harmon K. R., Marinelli W. A., Fox J. M., Kubo S. H., Shumway S. J., Bolman R. M., 3rd, Bitterman P. B. Obliterative bronchiolitis after lung transplantation: a fibroproliferative disorder associated with platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10385–10389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura H., Tsubakihara M., Inayama Y., Ito T., Kanisawa M. Long-term maintenance of human distal airway epithelial cells in nude mice: a potentially useful model for the study of pulmonary carcinogenesis and lung cell biology. Lab Invest. 1990 Mar;62(3):383–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriett J. M., Kaye M. P. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: eighth official report--1991. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1991 Jul-Aug;10(4):491–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck K. W., Prop J., Wildevuur C. R., Nieuwenhuis P. Lung transplantation in the rat: histopathology of left lung iso- and allografts. J Heart Transplant. 1985 Feb;4(2):263–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinsmoen N. L., Bolman R. M., Savik K., Butters K., Hertz M. Differentiation of class I- and class II-directed donor-specific alloreactivity in bronchoalveolar lavage lymphocytes from lung transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1992 Jan;53(1):181–189. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199201000-00036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk A., Prop J., Petersen A. H., Wildevuur C. R., Nieuwenhuis P. Expression of class II major histocompatibility complex antigens by bronchial epithelium in rat lung allografts. Transplantation. 1987 Aug;44(2):209–214. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198708000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. P., Higenbottam T. W., Sharples L., Clelland C. A., Smyth R. L., Stewart S., Wallwork J. Risk factors for obliterative bronchiolitis in heart-lung transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1991 Apr;51(4):813–817. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199104000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazelaar H. D., Prop J., Nieuwenhuis P., Billingham M. E., Wildevuur C. R. Airway pathology in the transplanted rat lung. Transplantation. 1988 May;45(5):864–869. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198805000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazelaar H. D., Yousem S. A. The pathology of combined heart-lung transplantation: an autopsy study. Hum Pathol. 1988 Dec;19(12):1403–1416. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyama T., Winter J. B., Groen G., Wildevuur C. R., Monden Y., Prop J. Late airway changes caused by chronic rejection in rat lung allografts. Transplantation. 1992 Nov;54(5):809–812. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199211000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. L., Cagle P., Churg A., Colby T. V., Myers J. Diseases of the small airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jul;146(1):240–262. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.1.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousem S. A., Burke C. M., Billingham M. E. Pathologic pulmonary alterations in long-term human heart-lung transplantation. Hum Pathol. 1985 Sep;16(9):911–923. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousem S. A., Dauber J. A., Keenan R., Paradis I. L., Zeevi A., Griffith B. P. Does histologic acute rejection in lung allografts predict the development of bronchiolitis obliterans? Transplantation. 1991 Aug;52(2):306–309. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199108000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousem S. A., Dauber J. H., Griffith B. P. Bronchial cartilage alterations in lung transplantation. Chest. 1990 Nov;98(5):1121–1124. doi: 10.1378/chest.98.5.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousem S. A., Paradis I. L., Dauber J. A., Zeevi A., Rabinowich H., Duquesnoy R., Hardesty R., Griffith B. P. Large airway inflammation in heart-lung transplant recipients--its significance and prognostic implications. Transplantation. 1990 Mar;49(3):654–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]