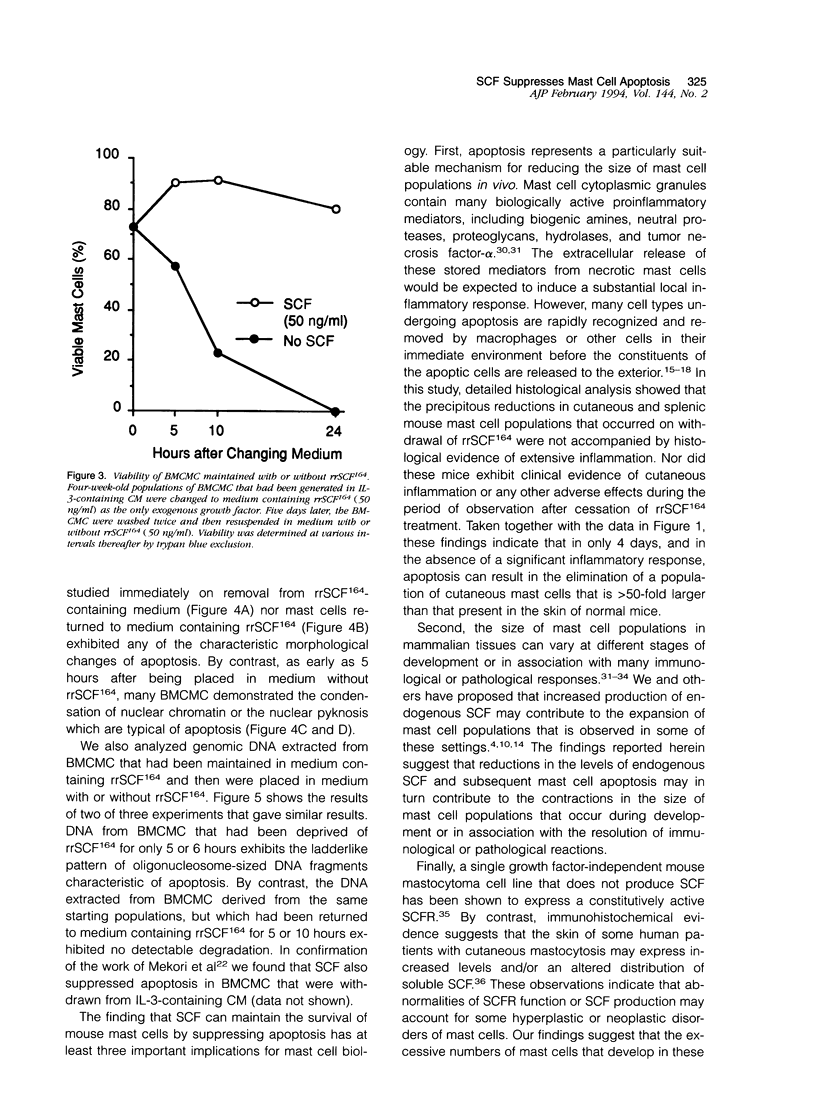
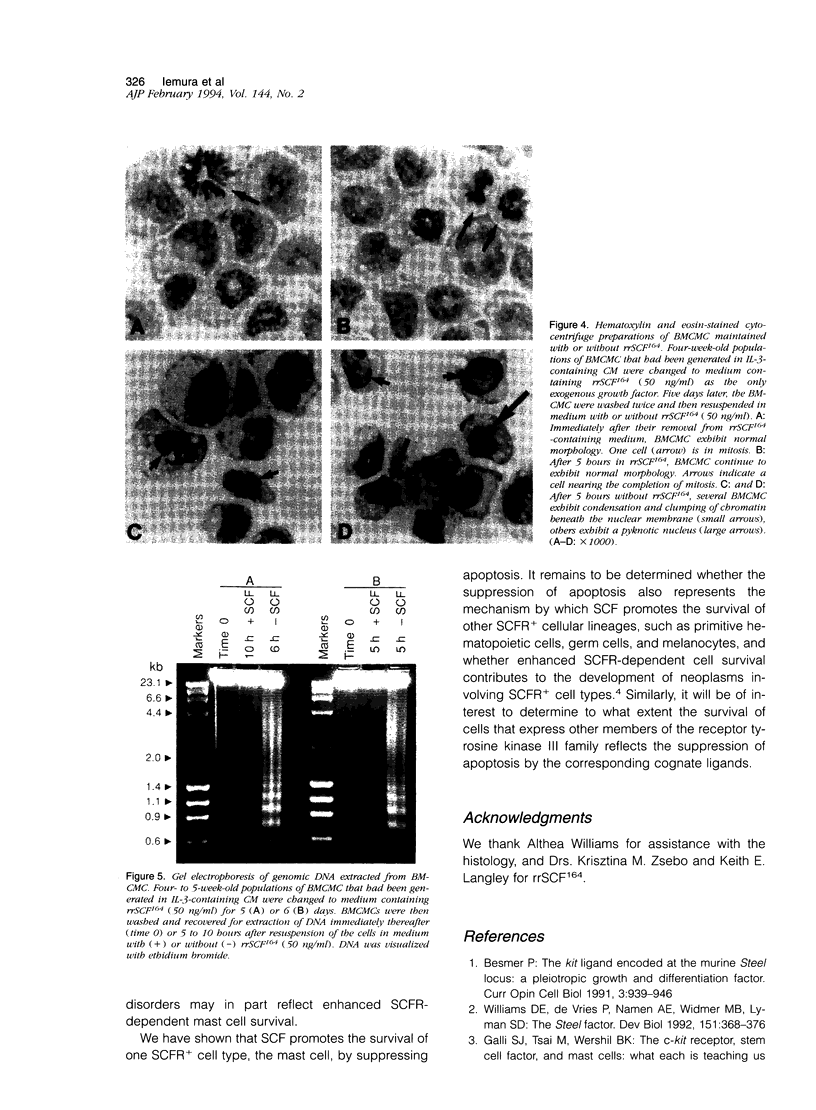
Abstract
Stem cell factor (SCF) and its receptor (SCFR), a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase III family that is encoded by the c-kit gene, critically regulate several complex biological programs including hematopoiesis, mast cell development, cutaneous pigmentation, and gametogenesis. We show herein that mouse mast cells die rapidly after the withdrawal of SCF in vivo or in vitro, and provide morphological evidence that such mast cells undergo programmed cell death or apoptosis. We also show that when in vitro-derived mouse mast cells maintained in SCF are removed from SCF-containing medium for only 5 or 6 hours, the cells' genomic DNA exhibits the ladder-like pattern of oligonucleosome-sized fragments typical of apoptosis. These findings demonstrate that SCF can regulate the survival of a cellular lineage which expresses the SCFR by suppressing apoptosis. They also identify a mechanism that can result in striking and rapid reductions in the size of tissue mast cell populations without histological evidence of the concomitant induction of a significant inflammatory response.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arizono N., Shiota T., Yamada M., Matsumoto Y., Yoshikawa H., Matsuda S., Tegoshi T. Bromodeoxyuridine labeling studies on the proliferation of intestinal mucosal mast cells in normal and athymic rats. APMIS. 1990 Apr;98(4):369–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1990.tb01046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besmer P. The kit ligand encoded at the murine Steel locus: a pleiotropic growth and differentiation factor. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):939–946. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90111-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannan C. I., Lyman S. D., Williams D. E., Eisenman J., Anderson D. M., Cosman D., Bedell M. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Steel-Dickie mutation encodes a c-kit ligand lacking transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4671–4674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J. Apoptosis. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):126–130. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Cho B. C., Donovan P. J., Jenkins N. A., Cosman D., Anderson D., Lyman S. D., Williams D. E. Mast cell growth factor maps near the steel locus on mouse chromosome 10 and is deleted in a number of steel alleles. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90298-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Cohen J. J. IL-2 addiction: withdrawal of growth factor activates a suicide program in dependent T cells. Lymphokine Res. 1986 Fall;5(4):289–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Mihm M. C., Jr, Dvorak A. M., Barnes B. A., Manseau E. J., Galli S. J. Rejection of first-set skin allografts in man. the microvasculature is the critical target of the immune response. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):322–337. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Chan D. C., Leder P. Transmembrane form of the kit ligand growth factor is determined by alternative splicing and is missing in the Sld mutant. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90326-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Arizono N., Murakami T., Dvorak A. M., Fox J. G. Development of large numbers of mast cells at sites of idiopathic chronic dermatitis in genetically mast cell-deficient WBB6F1-W/Wv mice. Blood. 1987 Jun;69(6):1661–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F. Basophils and mast cells: morphologic insights into their biology, secretory patterns, and function. Prog Allergy. 1984;34:1–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Marcum J. A., Ishizaka T., Nabel G., Der Simonian H., Pyne K., Goldin J. M., Rosenberg R. D., Cantor H. Mast cell clones: a model for the analysis of cellular maturation. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):435–444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Iemura A., Garlick D. S., Gamba-Vitalo C., Zsebo K. M., Andrews R. G. Reversible expansion of primate mast cell populations in vivo by stem cell factor. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):148–152. doi: 10.1172/JCI116164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J. New concepts about the mast cell. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jan 28;328(4):257–265. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199301283280408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Zsebo K. M., Geissler E. N. The kit ligand, stem cell factor. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:1–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Ryan M. A., Housman D. E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Kunisada T., Ogawa M., Yamaguchi K., Nishikawa S. Exon skipping by mutation of an authentic splice site of c-kit gene in W/W mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 25;19(6):1267–1271. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.6.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. J., Nocka K. H., Buck J., Besmer P. Differential expression and processing of two cell associated forms of the kit-ligand: KL-1 and KL-2. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Mar;3(3):349–362. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.3.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E., Nocka K., Beier D. R., Chu T. Y., Buck J., Lahm H. W., Wellner D., Leder P., Besmer P. The hematopoietic growth factor KL is encoded by the Sl locus and is the ligand of the c-kit receptor, the gene product of the W locus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90303-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y. Heterogeneity of mast cells and phenotypic change between subpopulations. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:59–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.000423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longley B. J., Jr, Morganroth G. S., Tyrrell L., Ding T. G., Anderson D. M., Williams D. E., Halaban R. Altered metabolism of mast-cell growth factor (c-kit ligand) in cutaneous mastocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 6;328(18):1302–1307. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305063281803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Tan J. C., Chiu E., Chu T. Y., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. Molecular bases of dominant negative and loss of function mutations at the murine c-kit/white spotting locus: W37, Wv, W41 and W. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1805–1813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottapel R., Reedijk M., Williams D. E., Lyman S. D., Anderson D. M., Pawson T., Bernstein A. The Steel/W transduction pathway: kit autophosphorylation and its association with a unique subset of cytoplasmic signaling proteins is induced by the Steel factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3043–3051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savill J., Fadok V., Henson P., Haslett C. Phagocyte recognition of cells undergoing apoptosis. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Austen K. F. Structure and function of the chemical mediators of mast cells. Prog Allergy. 1984;34:271–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M., Shih L. S., Newlands G. F., Takeishi T., Langley K. E., Zsebo K. M., Miller H. R., Geissler E. N., Galli S. J. The rat c-kit ligand, stem cell factor, induces the development of connective tissue-type and mucosal mast cells in vivo. Analysis by anatomical distribution, histochemistry, and protease phenotype. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):125–131. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M., Takeishi T., Thompson H., Langley K. E., Zsebo K. M., Metcalfe D. D., Geissler E. N., Galli S. J. Induction of mast cell proliferation, maturation, and heparin synthesis by the rat c-kit ligand, stem cell factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6382–6386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tushinski R. J., Oliver I. T., Guilbert L. J., Tynan P. W., Warner J. R., Stanley E. R. Survival of mononuclear phagocytes depends on a lineage-specific growth factor that the differentiated cells selectively destroy. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., de Vries P., Namen A. E., Widmer M. B., Lyman S. D. The Steel factor. Dev Biol. 1992 Jun;151(2):368–376. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90176-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T. Programmed cell death: apoptosis and oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1097–1098. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90002-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T., Smith C. A., Spooncer E., Dexter T. M., Taylor D. R. Haemopoietic colony stimulating factors promote cell survival by suppressing apoptosis. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):76–79. doi: 10.1038/343076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Williams D. A., Geissler E. N., Broudy V. C., Martin F. H., Atkins H. L., Hsu R. Y., Birkett N. C., Okino K. H., Murdock D. C. Stem cell factor is encoded at the Sl locus of the mouse and is the ligand for the c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90302-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





