Abstract
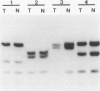
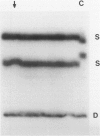
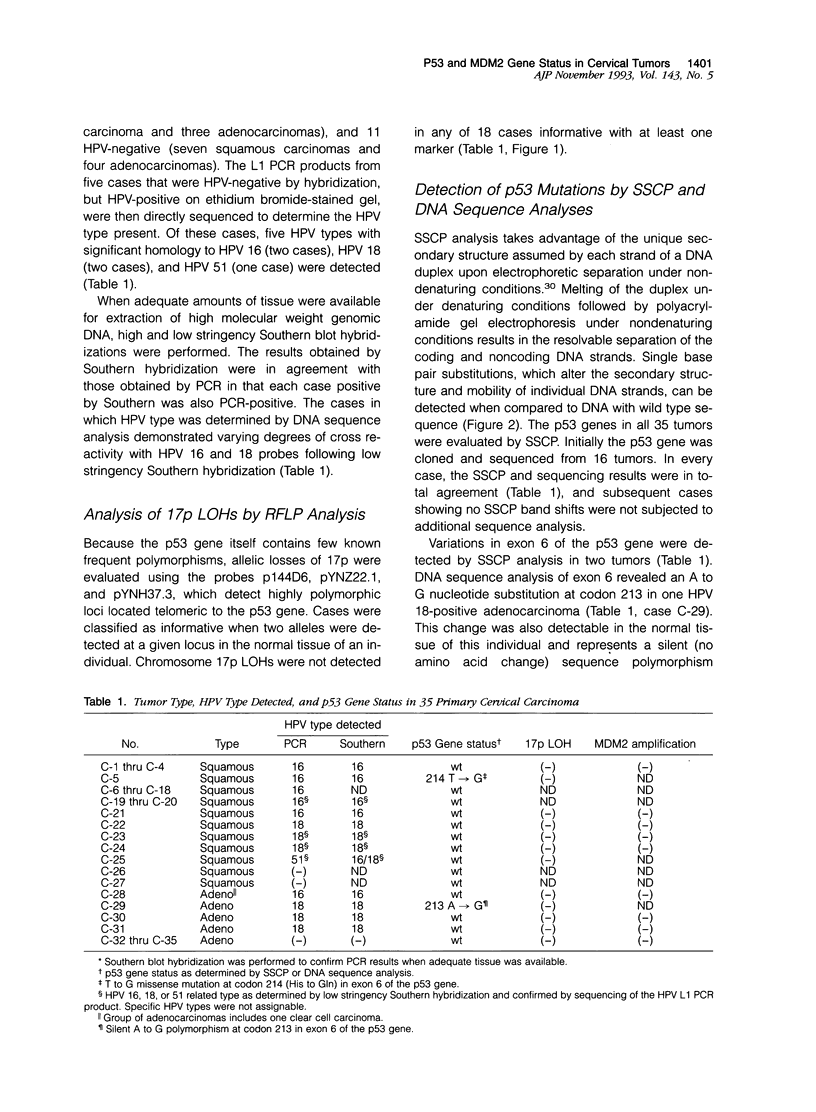
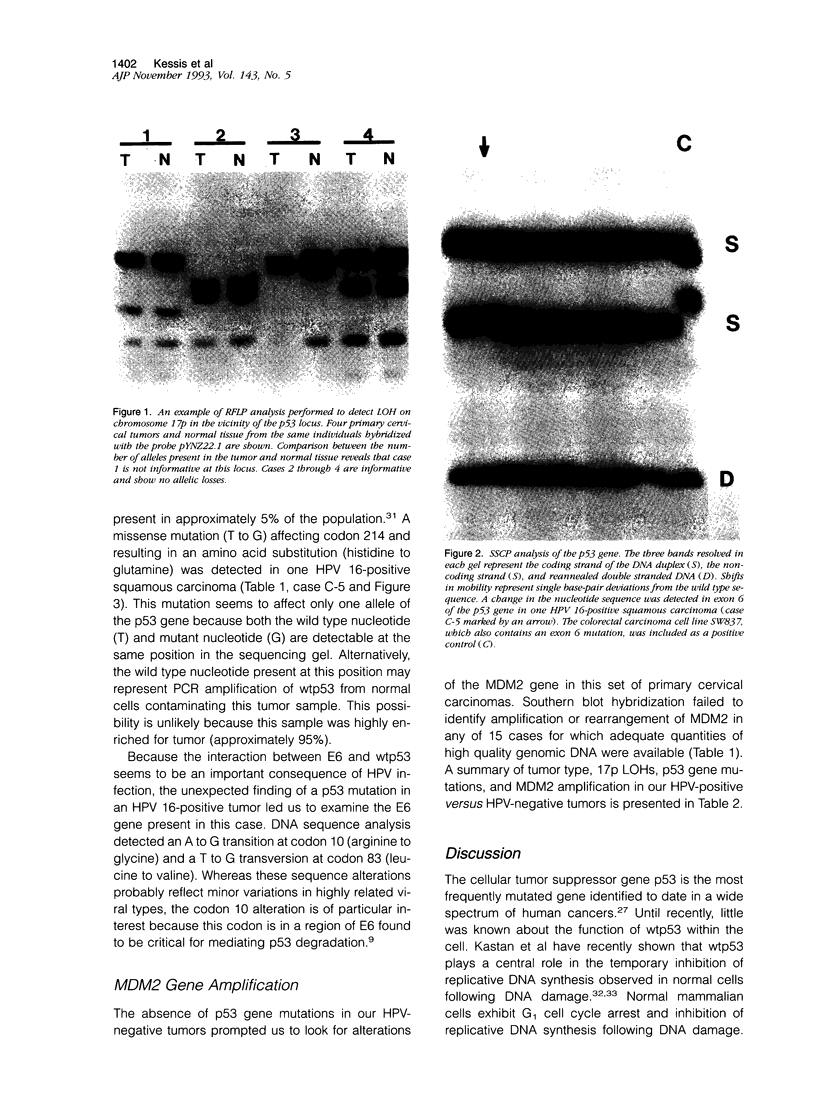
The p53 gene is the most frequently altered gene known thus far in a wide variety of human cancers. Inactivation of p53, either through mutation or through interaction with the human papillomavirus (HPV) E6 oncoprotein, is a characteristic feature of all cervical carcinoma cell lines that have been studied. These findings suggest that p53 inactivation is required for cervical carcinoma development and that HPV infection and p53 mutation may be mutually exclusive. We have studied the p53 gene in 35 primary cervical carcinomas. DNA sequence and single strand conformational polymorphism analyses were used to evaluate p53 in 27 squamous carcinomas (25 HPV-positive) and eight adenocarcinomas (four HPV-positive). A missense mutation of p53 was observed in one HPV 16-positive squamous carcinoma, demonstrating that p53 mutations can occur in combination with HPV infection. The HPV-negative tumors all lacked p53 gene mutations. The absence of p53 mutations in HPV-negative cases prompted an assessment of tumors for MDM2 gene amplification. The MDM2 gene encodes a p53 binding protein and has been found to be amplified in some human tumors lacking p53 mutations. MDM2 amplification was not identified in any of the tumors we examined, including four HPV-negative cases. Our findings show that HPV infection and p53 gene mutation are not mutually exclusive and suggest that many HPV-negative carcinomas may arise via a pathway independent of p53 inactivation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Phelps W. C., Lindgren V., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Howley P. M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.962-971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F. X., Muñoz N., de Sanjosé S., Izarzugaza I., Gili M., Viladiu P., Tormo M. J., Moreo P., Ascunce N., Gonzalez L. C. Risk factors for cervical cancer in Colombia and Spain. Int J Cancer. 1992 Nov 11;52(5):750–758. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone D., Chiba I., Mitsudomi T. Polymorphism at codon 213 within the p53 gene. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1691–1692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J. L., Pannetier C., Jaulin C., Kourilsky P. Optimal conditions for directly sequencing double-stranded PCR products with sequenase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4028–4028. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Tidy J. A., Vousden K. H. Degradation of p53 can be targeted by HPV E6 sequences distinct from those required for p53 binding and trans-activation. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90529-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Wrede D., Tidy J. A., Mason W. P., Evans D. J., Vousden K. H. Clonal p53 mutation in primary cervical cancer: association with human-papillomavirus-negative tumours. Lancet. 1992 May 2;339(8801):1070–1073. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90662-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Wrede D., Vousden K. H. p53 point mutation in HPV negative human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Oncogene. 1991 May;6(5):873–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B. Clonal analysis of human colorectal tumors. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):193–197. doi: 10.1126/science.2889267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita M., Inoue M., Tanizawa O., Iwamoto S., Enomoto T. Alterations of the p53 gene in human primary cervical carcinoma with and without human papillomavirus infection. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5323–5328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Vousden K. H., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. HPV16 E6 and E7 proteins cooperate to immortalize human foreskin keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3905–3910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelbling M., Burk R. D., Atkin N. B., Johnson A. B., Klinger H. P. Loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 17p and mutant p53 in HPV-negative cervical carcinomas. Lancet. 1992 Jul 18;340(8812):140–142. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessis T. D., Slebos R. J., Nelson W. G., Kastan M. B., Plunkett B. S., Han S. M., Lorincz A. T., Hedrick L., Cho K. R. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 expression disrupts the p53-mediated cellular response to DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3988–3992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoleon S., Vissing H., Luo X. Y., Magenis R. E., Kellogg J., Litt M. A hypervariable RFLP on chromosome 17p13 is defined by an arbitrary single copy probe p144-D6 [HGM9 No. D17S34]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10605–10605. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuerbitz S. J., Plunkett B. S., Walsh W. V., Kastan M. B. Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladanyi M., Cha C., Lewis R., Jhanwar S. C., Huvos A. G., Healey J. H. MDM2 gene amplification in metastatic osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1993 Jan 1;53(1):16–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz N., Bosch F. X., de Sanjosé S., Tafur L., Izarzugaza I., Gili M., Viladiu P., Navarro C., Martos C., Ascunce N. The causal link between human papillomavirus and invasive cervical cancer: a population-based case-control study in Colombia and Spain. Int J Cancer. 1992 Nov 11;52(5):743–749. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Phelps W. C., Bubb V., Howley P. M., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of the human papillomavirus type 16 together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4417–4421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4417-4421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Ballard L., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence (pYNZ22) on chromosome 17p [D17S30]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5707–5707. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Bragg T., Ballard L., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence pYNH37.3 on chromosome 17p [D17S28]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):782–782. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou G., Favre M., Jeannel D., Bourhis J., Le Doussal V., Orth G. Association between poor prognosis in early-stage invasive cervical carcinomas and non-detection of HPV DNA. Lancet. 1990 May 19;335(8699):1171–1174. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92693-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Münger K., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. The state of the p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5523–5527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Freese U. K., Gissmann L., Mayer W., Roggenbuck B., Stremlau A., zur Hausen H. Structure and transcription of human papillomavirus sequences in cervical carcinoma cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):111–114. doi: 10.1038/314111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D. K., Arnheim N., Martin W. J. Detection of human papilloma virus in paraffin-embedded tissue using the polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):225–230. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werness B. A., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2157286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]