Abstract
We investigated the mechanism of lethal injury following the disruption of microtubules in cultured hepatocytes treated with vinblastine (VBL) or colchicine (COL). These agents kill hepatocytes by a process readily distinguished from two well-known pathways that lead to a loss of viability, namely, oxidative stress and inhibition of mitochondrial electron transport. Cell killing with VBL and COL was accompanied by fragmentation of DNA. Both the loss of viability and the fragmentation of DNA were prevented by the inhibition of protein synthesis within 6 hours following exposure to VBL or COL. Cell death and the fragmentation of DNA were also prevented when Ca2+ was removed from the culture medium. By contrast, the inhibition of protein kinase C prevented cell killing by VBL or COL, but did not alter the extent of DNA fragmentation. The requirements here for protein synthesis, extracellular Ca2+, and protein kinase C activity define a model of apoptosis, or programmed cell death, that seems to involve mechanisms that can be dissociated from the fragmentation of DNA.
Full text
PDF

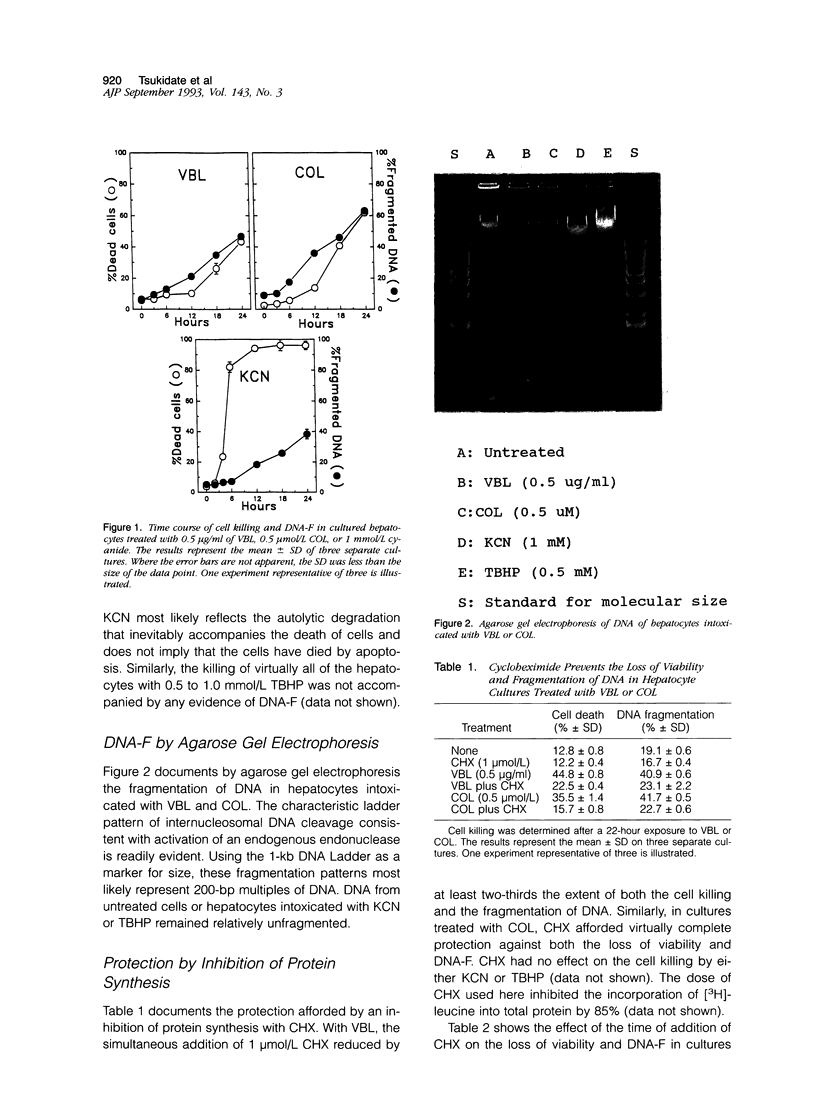


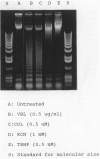
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry M. A., Behnke C. A., Eastman A. Activation of programmed cell death (apoptosis) by cisplatin, other anticancer drugs, toxins and hyperthermia. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 15;40(10):2353–2362. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90733-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursch W., Oberhammer F., Schulte-Hermann R. Cell death by apoptosis and its protective role against disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jun;13(6):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90077-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøe R., Gjertsen B. T., Vintermyr O. K., Houge G., Lanotte M., Døskeland S. O. The protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid induces morphological changes typical of apoptosis in mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Jul;195(1):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90523-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. M., Sun X. M., Snowden R. T., Dinsdale D., Skilleter D. N. Key morphological features of apoptosis may occur in the absence of internucleosomal DNA fragmentation. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 1;286(Pt 2):331–334. doi: 10.1042/bj2860331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C., Fadok V. A., Sellins K. S. Apoptosis and programmed cell death in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:267–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C. Glucocorticoid activation of a calcium-dependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins R. J., Harmon B. V., Gobé G. C., Kerr J. F. Internucleosomal DNA cleavage should not be the sole criterion for identifying apoptosis. Int J Radiat Biol. 1992 Apr;61(4):451–453. doi: 10.1080/09553009214551201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter T. G., Glynn J. M., Echeverri F., Green D. R. The induction of apoptosis by chemotherapeutic agents occurs in all phases of the cell cycle. Anticancer Res. 1992 May-Jun;12(3):773–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. L., Kyle M. E., Coleman J. B. Mechanisms of cell injury by activated oxygen species. Lab Invest. 1990 Jun;62(6):670–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. L., Young E. E. Accelerated phospholipid degradation in anoxic rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Oct 1;211(1):312–320. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90459-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iseki R., Mukai M., Iwata M. Regulation of T lymphocyte apoptosis. Signals for the antagonism between activation- and glucocorticoid-induced death. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4286–4292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. P., McConkey D. J., Nicotera P., Orrenius S. Calcium-activated DNA fragmentation in rat liver nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6398–6403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Induction of endonucleolytic DNA cleavage in human acute myelogenous leukemia cells by etoposide, camptothecin, and other cytotoxic anticancer drugs: a cautionary note. Cancer Res. 1989 Nov 1;49(21):5870–5878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Searle J. A suggested explanation for the paradoxically slow growth rate of basal-cell carcinomas that contain numerous mitotic figures. J Pathol. 1972 May;107(1):41–44. doi: 10.1002/path.1711070107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Searle J. Deletion of cells by apoptosis during castration-induced involution of the rat prostate. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1973 Jun 25;13(2):87–102. doi: 10.1007/BF02889300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kizaki H., Tadakuma T., Odaka C., Muramatsu J., Ishimura Y. Activation of a suicide process of thymocytes through DNA fragmentation by calcium ionophores and phorbol esters. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1790–1794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Duddy S. K., Håkansson H., Orrenius S. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin kills immature thymocytes by Ca2+-mediated endonuclease activation. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):256–259. doi: 10.1126/science.3262923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Nicotera P., Orrenius S. Calcium-activated DNA fragmentation kills immature thymocytes. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1843–1849. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2497041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell M. K., Haughn L. J., Maroun C. R., Julius M. H. Death of mature T cells by separate ligation of CD4 and the T-cell receptor for antigen. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):286–289. doi: 10.1038/347286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Masliah E., Jin L. W., Cole G. M., Wieloch T., Shapiro I. P. Protein kinases and phosphorylation in neurologic disorders and cell death. Lab Invest. 1991 May;64(5):596–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow B. A., West N. B., Norman R. L., Brenner R. M. Hormonal control of apoptosis in hamster uterine luminal epithelium. Am J Anat. 1979 Sep;156(1):15–35. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001560103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle J., Kerr J. F., Bishop C. J. Necrosis and apoptosis: distinct modes of cell death with fundamentally different significance. Pathol Annu. 1982;17(Pt 2):229–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:29–83. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellins K. S., Cohen J. J. Gene induction by gamma-irradiation leads to DNA fragmentation in lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3199–3206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen S., D'Incalci M. Apoptosis. Biochemical events and relevance to cancer chemotherapy. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 27;307(1):122–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80914-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. The biology of cell death in tumours. Anticancer Res. 1985 Jan-Feb;5(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Ohyama H. Radiation-induced interphase death of rat thymocytes is internally programmed (apoptosis). Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1988 Jan;53(1):65–75. doi: 10.1080/09553008814550431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng L. M., Zychlinsky A., Liu C. C., Ojcius D. M., Young J. D. Extracellular ATP as a trigger for apoptosis or programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(2):279–288. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]