Abstract
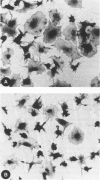
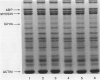
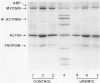
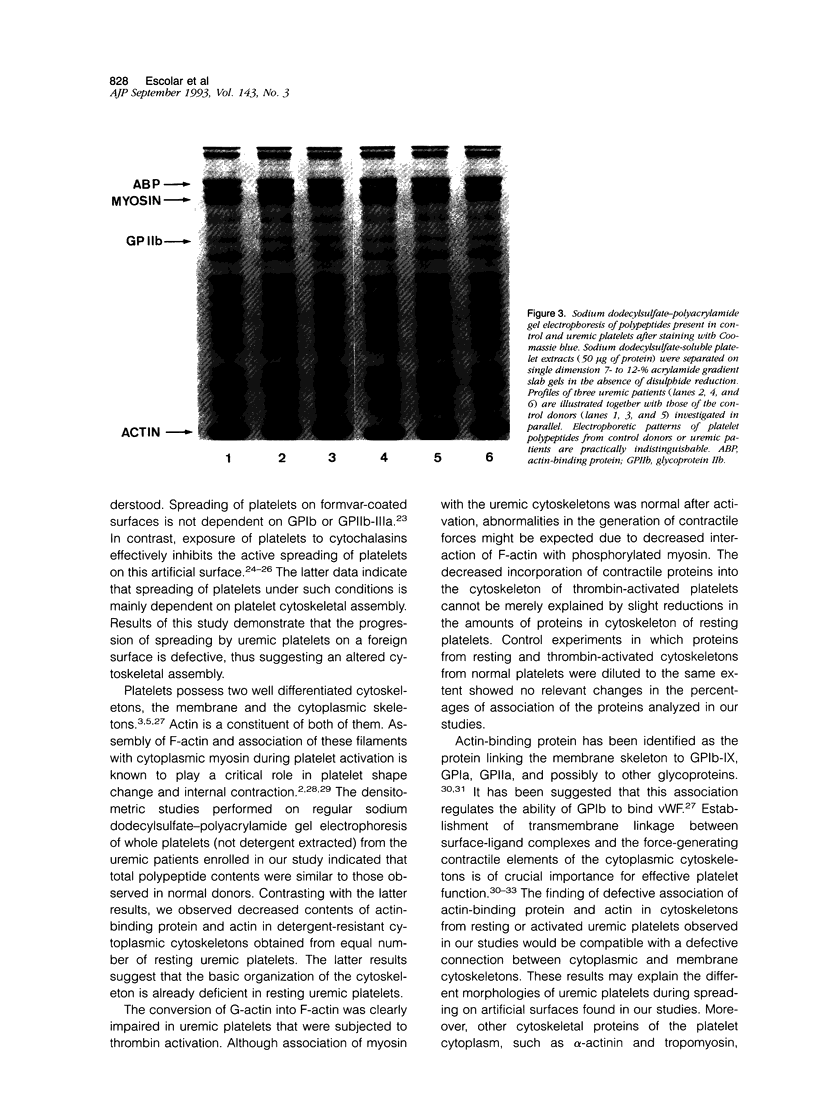
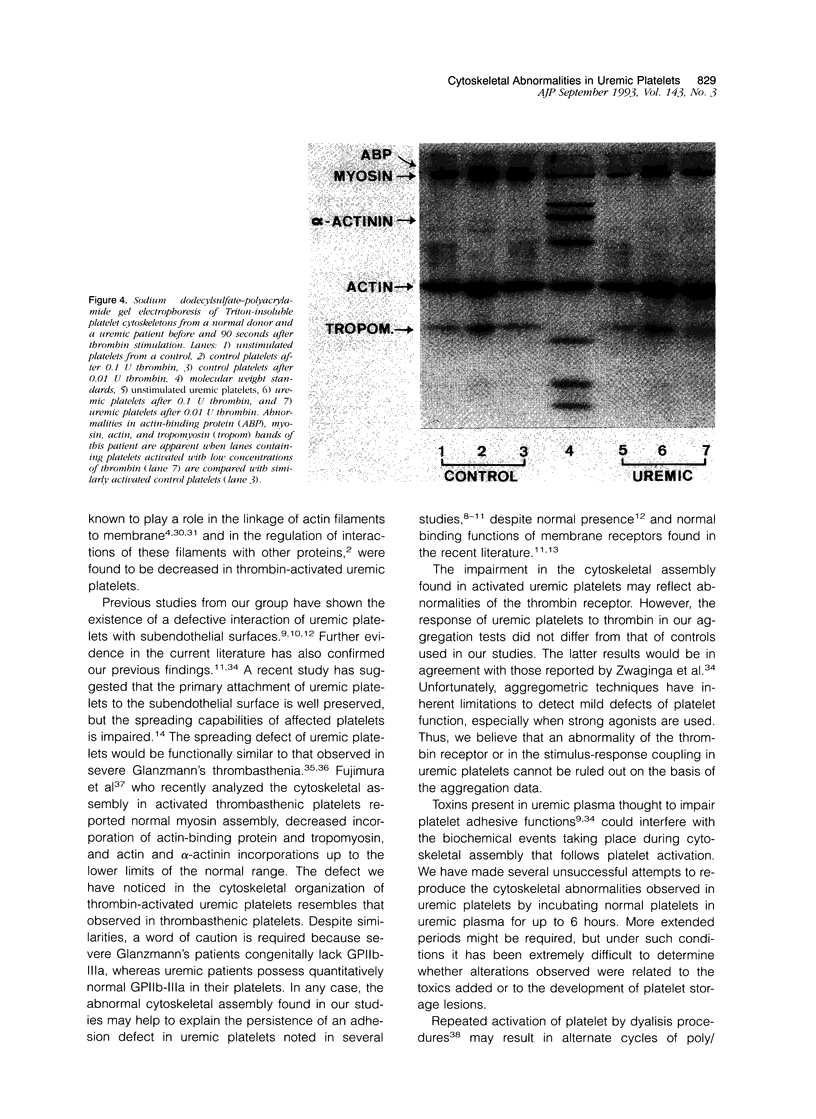
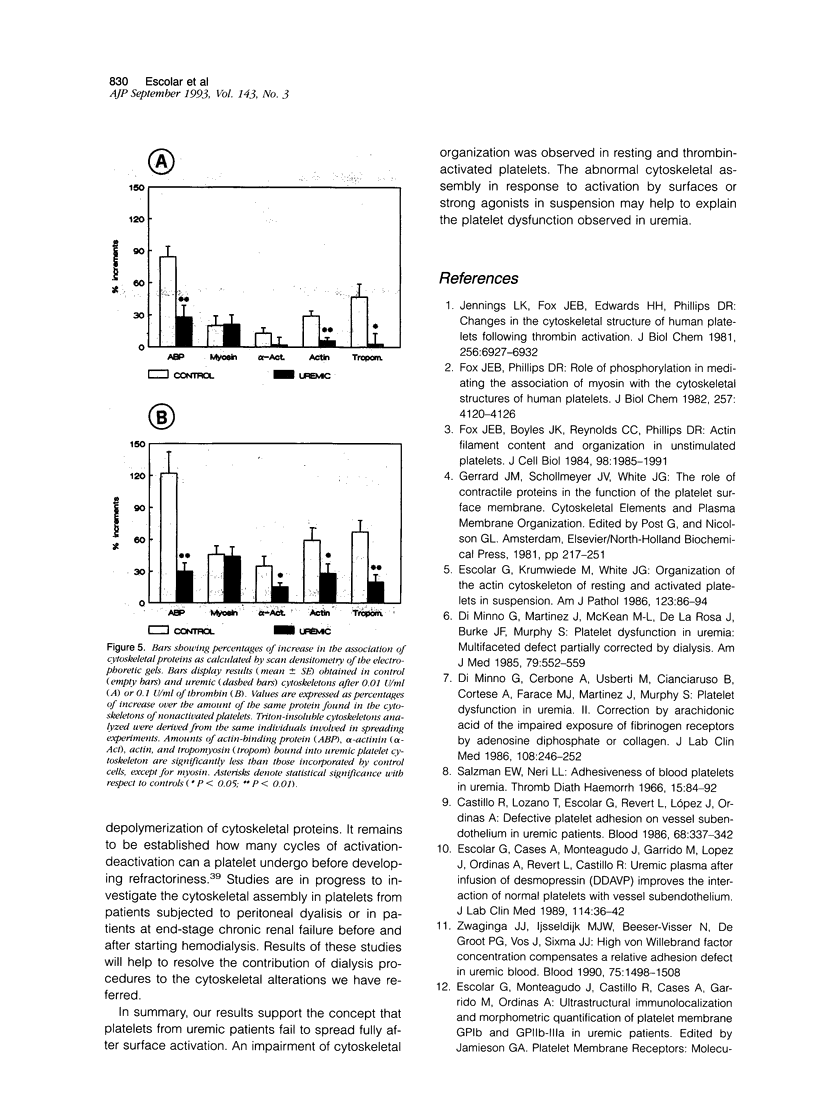
The mechanisms involved in the hemostatic abnormality of uremic patients remain obscure. We have explored the response of normal and uremic platelets to surface activation at the ultrastructural level and analyzed changes in the composition of proteins associated with normal and uremic platelet cytoskeletons after stimulation with thrombin (0.01 and 0.1 U/ml). Cytoskeletons were obtained by extraction with Triton X-100, processed by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and the presence of cytoskeletal proteins analyzed by densitometry. Under static conditions, uremic platelets spread with difficulty on formvar-coated grids. The percentage of platelets that spread fully on this polymer surface was statistically reduced compared with that of control platelets (11 +/- 1.4 vs. 21 +/- 1.6; P < 0.05). An impairment of cytoskeletal organization was observed in resting uremic platelets but abnormalities were more evident after thrombin activation. The incorporation of actin into the cytoskeletons of thrombin-stimulated uremic platelets was significantly reduced with respect to controls (6 +/- 3% vs. 29 +/- 5%; P < 0.01 after 0.01 U/ml and 28 +/- 9% vs. 59 +/- 10%; P < 0.05 after 0.1 U/ml). Decreased associations of actin-binding protein (P < 0.01), alpha-actinin (P < 0.05), and tropomyosin (P < 0.05) with the cytoskeletons of uremic platelets were also noted. No difference was observed for the incorporation of myosin into the cytoskeletons of activated uremic platelets. These results suggest functional and biochemical alterations of the platelet cytoskeleton in uremia, which may contribute to the impairment of platelet function observed in uremic patients.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckerle M. C., Miller D. E., Bertagnolli M. E., Locke S. J. Activation-dependent redistribution of the adhesion plaque protein, talin, in intact human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3333–3346. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. C., Gerrard J. M. Phosphorylation of platelet actin-binding protein during platelet activation. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):466–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo R., Lozano T., Escolar G., Revert L., López J., Ordinas A. Defective platelet adhesion on vessel subendothelium in uremic patients. Blood. 1986 Aug;68(2):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox A. C., Carroll R. C., White J. G., Rao G. H. Recycling of platelet phosphorylation and cytoskeletal assembly. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):8–15. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Weber K., Osborn M. The cytoskeleton of blood platelets viewed by immunofluorescence microscopy. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;24(1):45–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Minno G., Cerbone A., Usberti M., Cianciaruso B., Cortese A., Farace M. J., Martinez J., Murphy S. Platelet dysfunction in uremia. II. Correction by arachidonic acid of the impaired exposure of fibrinogen receptors by adenosine diphosphate or collagen. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Sep;108(3):246–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Minno G., Martinez J., McKean M. L., De La Rosa J., Burke J. F., Murphy S. Platelet dysfunction in uremia. Multifaceted defect partially corrected by dialysis. Am J Med. 1985 Nov;79(5):552–559. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escolar G., Cases A., Bastida E., Garrido M., López J., Revert L., Castillo R., Ordinas A. Uremic platelets have a functional defect affecting the interaction of von Willebrand factor with glycoprotein IIb-IIIa. Blood. 1990 Oct 1;76(7):1336–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escolar G., Cases A., Monteagudo J., Garrido M., Lopez J., Ordinas A., Revert L., Castillo R. Uremic plasma after infusion of desmopressin (DDAVP) improves the interaction of normal platelets with vessel subendothelium. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Jul;114(1):36–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escolar G., Diaz-Ricart M., Garrido M., Reverter J. C., Villamor N., Sanz C., Maragall S., Castillo R., Ordinas A., Nurden A. T. A variant of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia which fails to express a GPIIb-IIIa related epitope that is recognized by a specific monoclonal antibody (C17). Br J Haematol. 1992 Aug;81(4):545–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1992.tb02990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escolar G., Krumwiede M., White J. G. Organization of the actin cytoskeleton of resting and activated platelets in suspension. Am J Pathol. 1986 Apr;123(1):86–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escolar G., Leistikow E., White J. G. The fate of the open canalicular system in surface and suspension-activated platelets. Blood. 1989 Nov 1;74(6):1983–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Boyles J. K., Berndt M. C., Steffen P. K., Anderson L. K. Identification of a membrane skeleton in platelets. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1525–1538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Boyles J. K., Reynolds C. C., Phillips D. R. Actin filament content and organization in unstimulated platelets. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1985–1991. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E. Identification of actin-binding protein as the protein linking the membrane skeleton to glycoproteins on platelet plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11970–11977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E. Linkage of a membrane skeleton to integral membrane glycoproteins in human platelets. Identification of one of the glycoproteins as glycoprotein Ib. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1673–1683. doi: 10.1172/JCI112153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Phillips D. R. Role of phosphorylation in mediating the association of myosin with the cytoskeletal structures of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4120–4126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura K., Fujimoto T., Takemoto M., Oda K., Shimomura T., Maehama S., Kuramoto A. Analysis of platelet cytoskeleton assembly during platelet activation in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome and thrombasthenia. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Feb 19;63(1):103–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., McKeown L. P., Williams S. B., Shafer B. C., Pierce L. Plasma and platelet von Willebrand factor defects in uremia. Am J Med. 1988 Dec;85(6):806–810. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(88)80025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H. Mechanisms of actin rearrangements mediating platelet activation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1421–1442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings L. K., Fox J. E., Edwards H. H., Phillips D. R. Changes in the cytoskeletal structure of human platelets following thrombin activation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kometani M., Sato T., Fujii T. Platelet cytoskeletal components involved in shape change and secretion. Thromb Res. 1986 Mar 15;41(6):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus J. C., Albrecht R. M. Redistribution of the fibrinogen receptor of human platelets after surface activation. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):822–829. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Dupuis D., Kunicki T. J., Caen J. P. Analysis of the glycoprotein and protein composition of Bernard-Soulier platelets by single and two-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1431–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI110172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jennings L. K., Edwards H. H. Identification of membrane proteins mediating the interaction of human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):77–86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao G. H., Escolar G., White J. G. Epinephrine reverses the inhibitory influence of aspirin on platelet-vessel wall interactions. Thromb Res. 1986 Oct 1;44(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman E. W., Neri L. L. Adhesiveness of blood platelets in uremia. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Jan 31;15(1):84–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Turitto V. T., Baumgartner H. R. Further evidence that glycoprotein IIb-IIIa mediates platelet spreading on subendothelium. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Feb 12;65(2):202–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Turitto V. T., Baumgartner H. R. Platelet adhesion and thrombus formation on subendothelium in platelets deficient in glycoproteins IIb-IIIa, Ib, and storage granules. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):322–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Escolar G. Mobility of GPIIb-IIIa receptors within membranes of surface- and suspension-activated platelets does not depend on assembly and contraction of cytoplasmic actin. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;52(2):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Leistikow E. L., Escolar G. Platelet membrane responses to surface and suspension activation. Blood Cells. 1990;16(1):43–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaginga J. J., IJsseldijk M. J., de Groot P. G., Vos J., de Bos Kuil R. L., Sixma J. J. Defects in platelet adhesion and aggregate formation in uremic bleeding disorder can be attributed to factors in plasma. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 May-Jun;11(3):733–744. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.3.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaginga J. J., Ijsseldijk M. J., Beeser-Visser N., de Groot P. G., Vos J., Sixma J. J. High von Willebrand factor concentration compensates a relative adhesion defect in uremic blood. Blood. 1990 Apr 1;75(7):1498–1508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]