Abstract
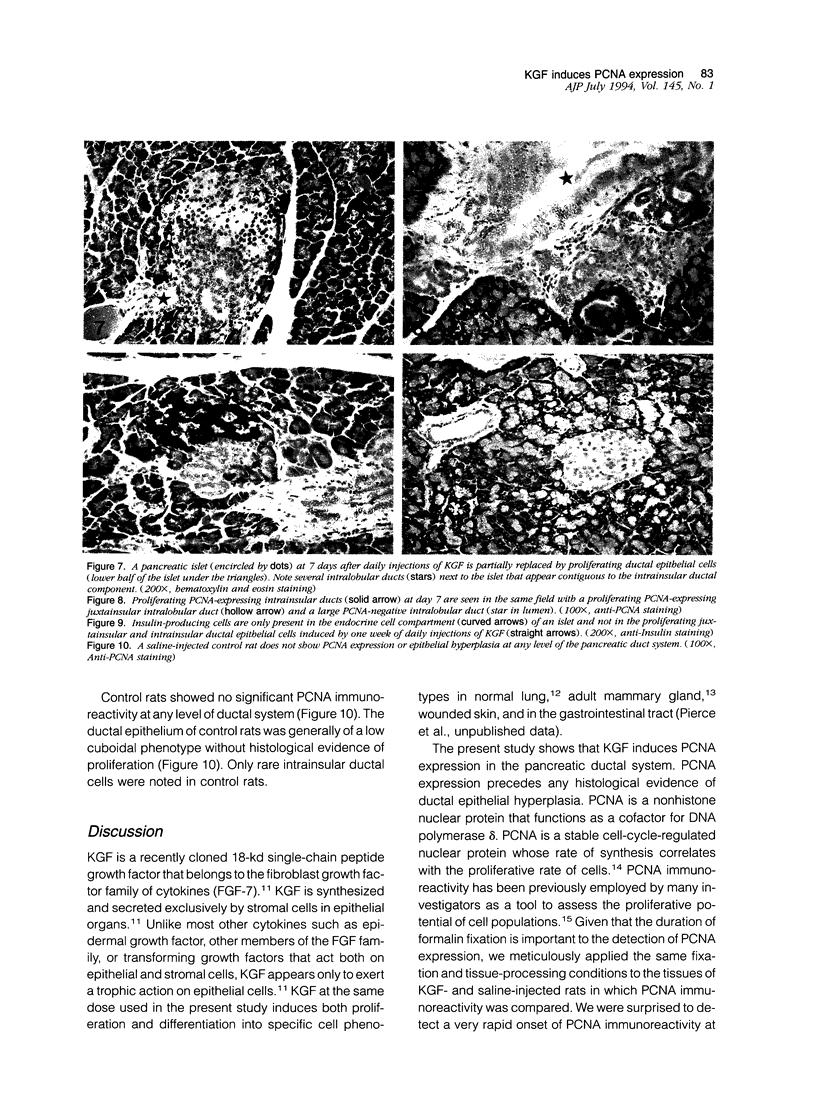
Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) causes a proliferation of pancreatic ductal epithelial cells in adult rats after daily systemic administration for 1 to 2 weeks. Even before the proliferation of intralobular ducts is histologically evident, KGF also induces proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression within the ductal epithelium of intercalated, intralobular, and interlobular ducts. KGF also causes incorporation of 5-bromodeoxyuridine in ductal epithelial cells. Epithelial cell proliferation is histologically most prominent at the level of the intralobular ducts adjacent to and within the islets of Langerhans. Pancreatic ductal proliferation is not histologically apparent in rats sacrificed 7 to 10 days after the cessation of KGF administration. The pancreatic hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide are normally distributed within islets that demonstrate intrainsular ductal proliferation. The proliferating ductal epithelium does not show endocrine differentiation as evidenced by the lack of immunoreactivity for pancreatic hormones. KGF is a potent in vivo mitogen for pancreatic ductal epithelial cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bockman D. E., Merlino G. Cytological changes in the pancreas of transgenic mice overexpressing transforming growth factor alpha. Gastroenterology. 1992 Dec;103(6):1883–1892. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91448-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton W. E., Mikulka W. R., Healy C. G., Schmittling R. J., Kenyon N. S. Expression of proliferation associated antigens in the cell cycle of synchronized mammalian cells. Cytometry. 1992;13(2):117–126. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990130203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockenbrough J. S., Weir G. C., Bonner-Weir S. Discordance of exocrine and endocrine growth after 90% pancreatectomy in rats. Diabetes. 1988 Feb;37(2):232–236. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Tsuchiya K., Batchelor R. H., Rabinovitch P. S., Kulander B. G., Haggitt R. C., Burmer G. C. Deletion mapping of chromosome 8p in colorectal carcinoma and dysplasia arising in ulcerative colitis, prostatic carcinoma, and malignant fibrous histiocytomas. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jan;144(1):1–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. W., Rubin J. S., Miki T., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Human KGF is FGF-related with properties of a paracrine effector of epithelial cell growth. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):752–755. doi: 10.1126/science.2475908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., Levison D. A., Woods A. L., Yu C. C., Kellock D. B., Watkins J. A., Barnes D. M., Gillett C. E., Camplejohn R., Dover R. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunolocalization in paraffin sections: an index of cell proliferation with evidence of deregulated expression in some neoplasms. J Pathol. 1990 Dec;162(4):285–294. doi: 10.1002/path.1711620403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. The use of antiavidin antibody and avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex in immunoperoxidase technics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jun;75(6):816–821. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.6.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafaeloff R., Rosenberg L., Vinik A. I. Expression of growth factors in a pancreatic islet regeneration model. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;321:133–141. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3448-8_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. S., Dwivedi R. S., Yeldandi A. V., Subbarao V., Tan X. D., Usman M. I., Thangada S., Nemali M. R., Kumar S., Scarpelli D. G. Role of periductal and ductular epithelial cells of the adult rat pancreas in pancreatic hepatocyte lineage. A change in the differentiation commitment. Am J Pathol. 1989 May;134(5):1069–1086. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J. K., Rao M. S., Yeldandi A. V., Tan X. D., Dwivedi R. S. Pancreatic hepatocytes. An in vivo model for cell lineage in pancreas of adult rat. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Apr;36(4):502–509. doi: 10.1007/BF01298883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Vinik A. I. Induction of endocrine cell differentiation: a new approach to management of diabetes. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Jul;114(1):75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. E., Rosen K. M., Villa-Komaroff L., Weir G. C., Bonner-Weir S. Enhanced insulin-like growth factor I gene expression in regenerating rat pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6152–6156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]