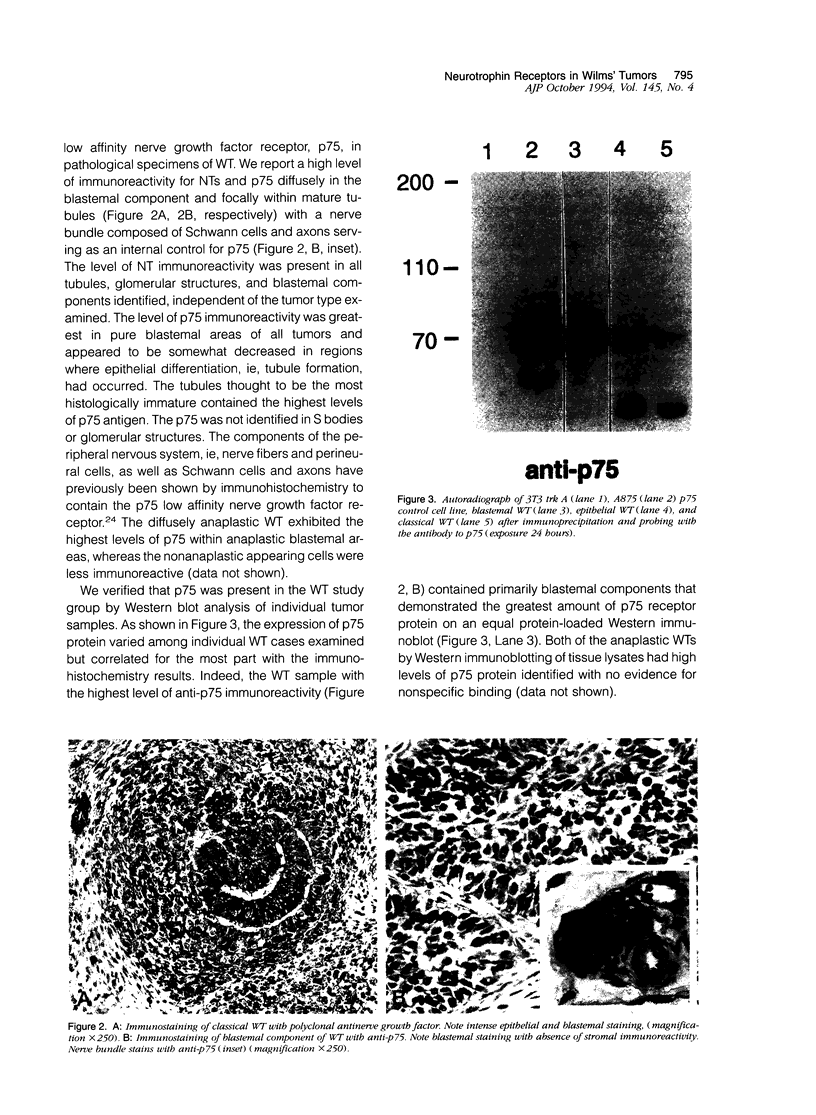
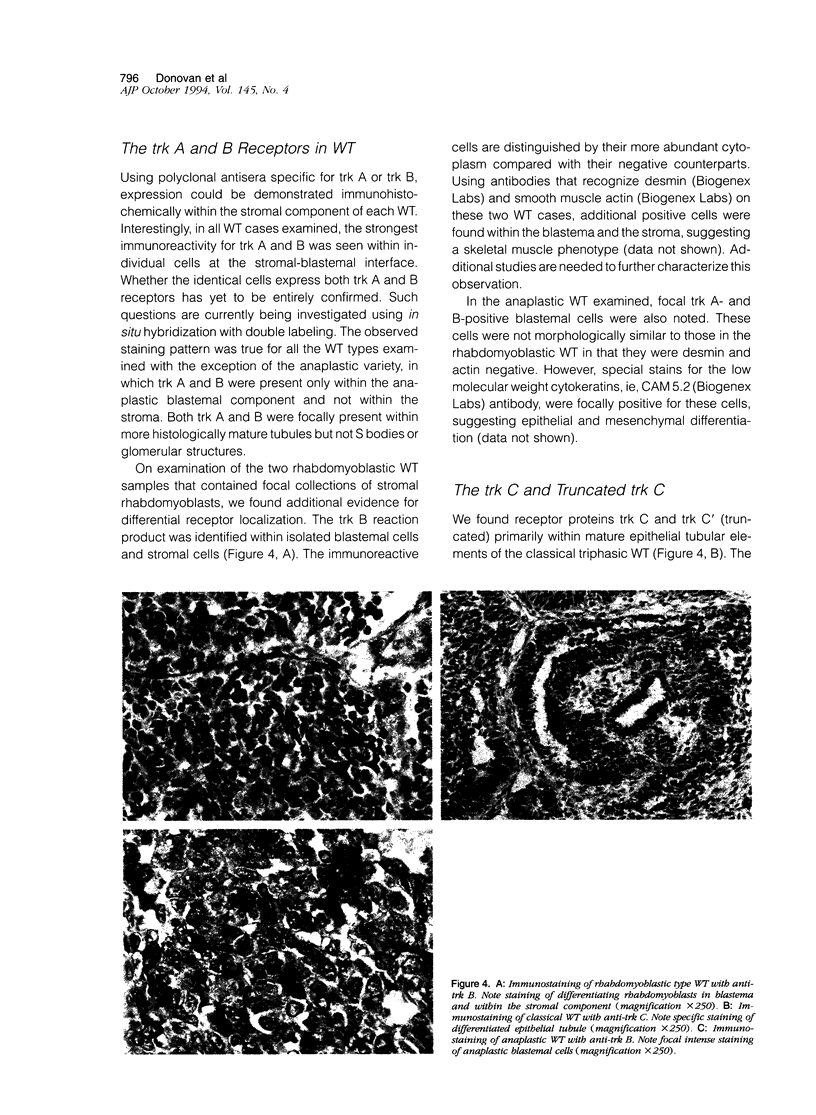
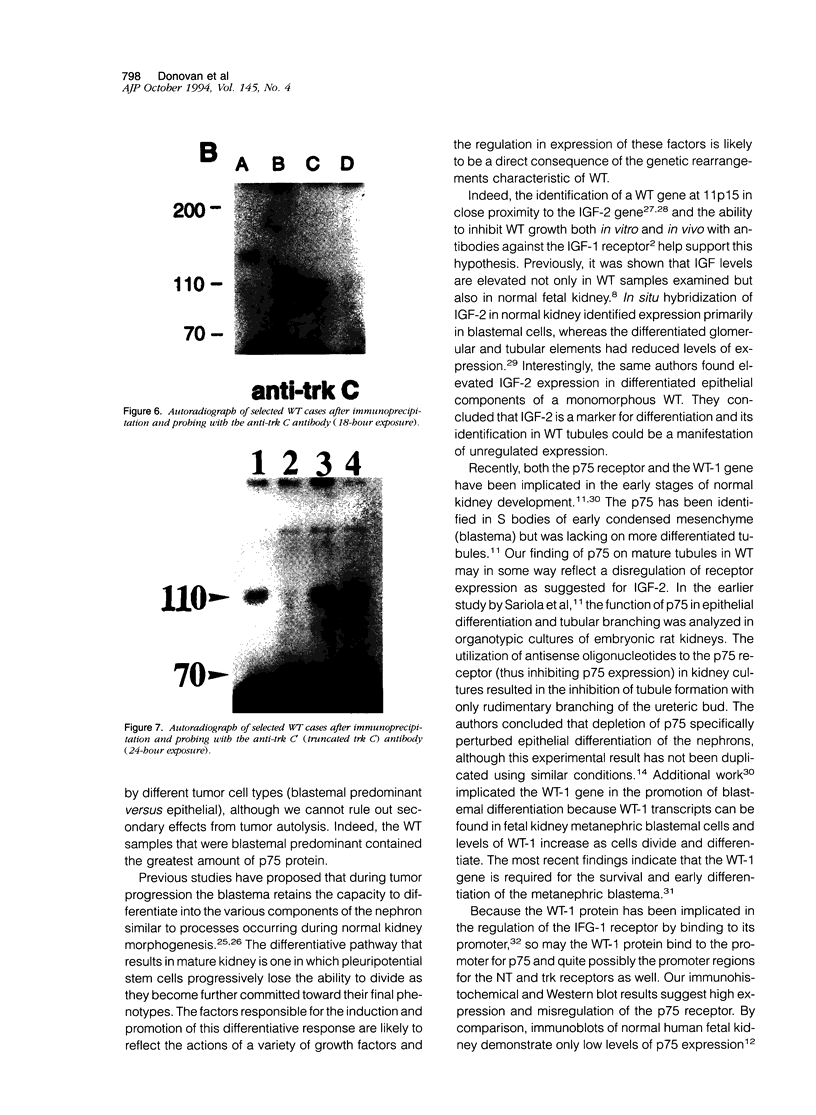
Abstract
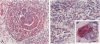
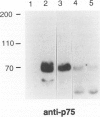
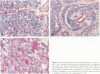
The molecular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of Wilms' tumor (WT) are poorly understood, although a variety of growth factors including platelet-derived growth factor and insulin-like growth factor are expressed and are thought to contribute to tumor development. In earlier studies, WT cells in culture were found to express the low affinity nerve growth factor receptor, p75. These WT cells were capable of responding to the neurotrophin (NT) NGF, suggesting that NT may be involved in WT pathogenesis. We have examined a group of WT immunohistochemically with antibodies recognizing known trk receptor proteins, the p75 receptor, and the NTs, NGF and NT-3. Confirmatory immunoprecipitation and Western blots were then performed on representative WT samples from the study group. The p75 receptor was found predominantly in the epithelial and blastemal components where high levels of NT were also identified. The trk A and B receptors were primarily within stromal components, whereas the trk C and C' receptors were present within epithelial structures. Western blot analyses confirmed the presence of the respective receptor proteins with variations correlating in some cases with histological type. The selective presence of NT receptors and growth factors in this series of WT implies autocrine/paracrine mechanisms for tumor development.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albeda F. W., Molenaar W. M., de Leij L., Thijs-Ipema A. H. Heterogeneity of Wilms' tumour blastema. An immunohistological study. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1989;414(3):263–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00822031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpers C. E., Hudkins K. L., Ferguson M., Johnson R. J., Schatteman G. C., Bothwell M. Nerve growth factor receptor expression in fetal, mature, and diseased human kidneys. Lab Invest. 1993 Dec;69(6):703–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith J. B., Palmer N. F. Histopathology and prognosis of Wilms tumors: results from the First National Wilms' Tumor Study. Cancer. 1978 May;41(5):1937–1948. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197805)41:5<1937::aid-cncr2820410538>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissenden J. E., Ullrich A., Francke U. Human chromosomal mapping of genes for insulin-like growth factors I and II and epidermal growth factor. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):781–784. doi: 10.1038/310781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesa P. G., Rettig W. J., Thomson T. M., Old L. J., Melamed M. R. Immunohistochemical analysis of nerve growth factor receptor expression in normal and malignant human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Apr;36(4):383–389. doi: 10.1177/36.4.2831267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F. Polypeptide growth factors: roles in normal and abnormal cell growth. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:443–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan M. J., Hempstead B. L., Horvath C., Chao M. V., Schofield D. Immunohistochemical localization of Trk receptor protein in pediatric small round blue cell tumors. Am J Pathol. 1993 Dec;143(6):1560–1567. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durbeej M., Söderström S., Ebendal T., Birchmeier C., Ekblom P. Differential expression of neurotrophin receptors during renal development. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):977–989. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernfors P., Wetmore C., Eriksdotter-Nilsson M., Bygdeman M., Strömberg I., Olson L., Persson H. The nerve growth factor receptor gene is expressed in both neuronal and non-neuronal tissues in the human fetus. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1991;9(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(91)90073-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraizer G. E., Bowen-Pope D. F., Vogel A. M. Production of platelet-derived growth factor by cultured Wilms' tumor cells and fetal kidney cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Oct;133(1):169–174. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gansler T., Furlanetto R., Gramling T. S., Robinson K. A., Blocker N., Buse M. G., Sens D. A., Garvin A. J. Antibody to type I insulinlike growth factor receptor inhibits growth of Wilms' tumor in culture and in athymic mice. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):961–966. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin A. J., Surrette F., Hintz D. S., Rudisill M. T., Sens M. A., Sens D. A. The in vitro growth and characterization of the skeletal muscle component of Wilms' tumor. Am J Pathol. 1985 Nov;121(2):298–310. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goustin A. S., Leof E. B., Shipley G. D., Moses H. L. Growth factors and cancer. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1015–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G. K., Irminger J. C., Zapf J., Ziegler W. H., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factor II in human adrenal pheochromocytomas and Wilms tumors: expression at the mRNA and protein level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1104–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen-Martin D. J., Garvin A. J., Gansler T., Tarnowski B. I., Sens D. A. Morphology and growth characteristics of epithelial cells from classic Wilms' tumors. Am J Pathol. 1993 Mar;142(3):893–905. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):678–683. doi: 10.1038/350678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
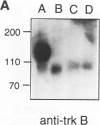
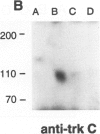
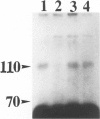
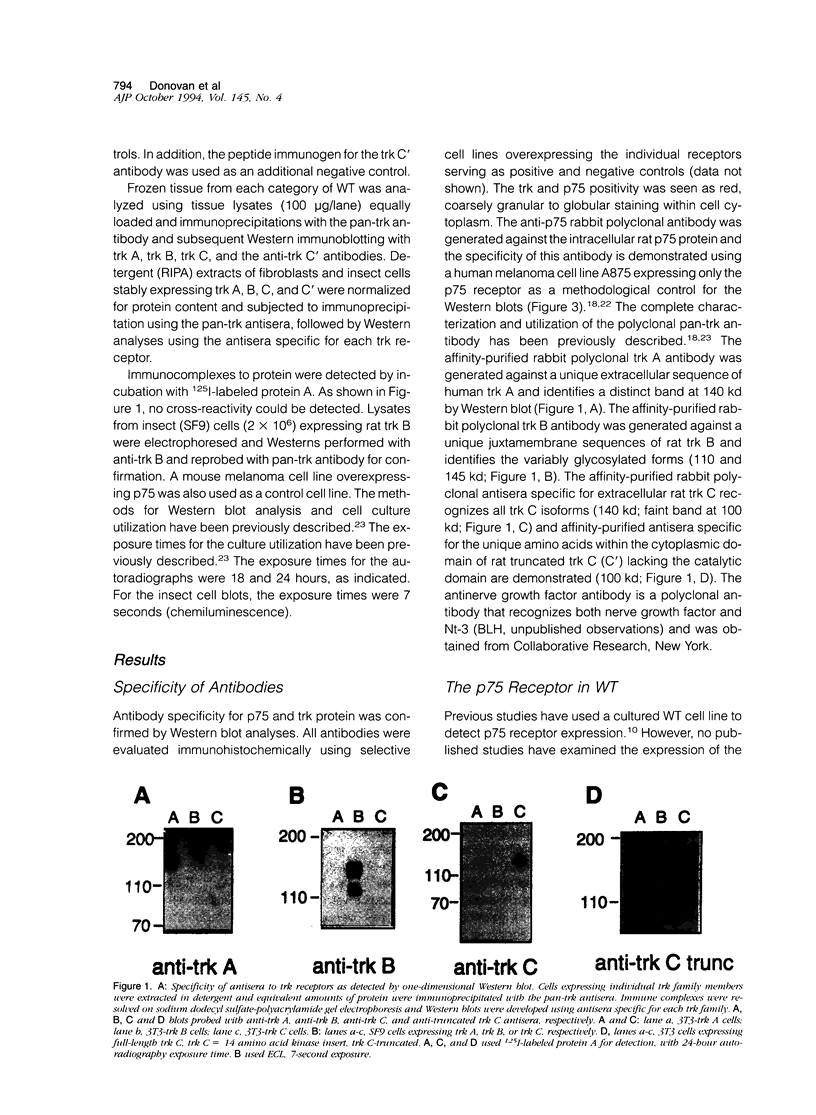
- Horvath C. M., Wolven A., Machadeo D., Huber J., Boter L., Benedetti M., Hempstead B., Chao M. V. Analysis of the trk NGF receptor tyrosine kinase using recombinant fusion proteins. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:223–228. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibáez C. F., Ebendal T., Barbany G., Murray-Rust J., Blundell T. L., Persson H. Disruption of the low affinity receptor-binding site in NGF allows neuronal survival and differentiation by binding to the trk gene product. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90413-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Stitt T. N., Tapley P., Klein R., Glass D. J., Fandl J., Greene L. A., Barbacid M., Yancopoulos G. D. Similarities and differences in the way neurotrophins interact with the Trk receptors in neuronal and nonneuronal cells. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):137–149. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90306-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Conway D., Parada L. F., Barbacid M. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase gene codes for a second neurogenic receptor that lacks the catalytic kinase domain. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):647–656. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90476-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreidberg J. A., Sariola H., Loring J. M., Maeda M., Pelletier J., Housman D., Jaenisch R. WT-1 is required for early kidney development. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):679–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90515-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawara A., Arima-Nakagawara M., Scavarda N. J., Azar C. G., Cantor A. B., Brodeur G. M. Association between high levels of expression of the TRK gene and favorable outcome in human neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 1993 Mar 25;328(12):847–854. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199303253281205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawara A., Arima M., Azar C. G., Scavarda N. J., Brodeur G. M. Inverse relationship between trk expression and N-myc amplification in human neuroblastomas. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 1;52(5):1364–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik S., Rosen N., Jung W., You J. M., Lippman M. E., Perdue J. F., Yee D. Expression of insulin-like growth factor-II mRNA in fetal kidney and Wilms' tumor. An in situ hybridization study. Lab Invest. 1989 Nov;61(5):522–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard-Jones K., Fleming S., Davidson D., Bickmore W., Porteous D., Gosden C., Bard J., Buckler A., Pelletier J., Housman D. The candidate Wilms' tumour gene is involved in genitourinary development. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):194–197. doi: 10.1038/346194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabizadeh S., Oh J., Zhong L. T., Yang J., Bitler C. M., Butcher L. L., Bredesen D. E. Induction of apoptosis by the low-affinity NGF receptor. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):345–348. doi: 10.1126/science.8332899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve A. E., Eccles M. R., Wilkins R. J., Bell G. I., Millow L. J. Expression of insulin-like growth factor-II transcripts in Wilms' tumour. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):258–260. doi: 10.1038/317258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariola H., Saarma M., Sainio K., Arumäe U., Palgi J., Vaahtokari A., Thesleff I., Karavanov A. Dependence of kidney morphogenesis on the expression of nerve growth factor receptor. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):571–573. doi: 10.1126/science.1658930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarisbrick I. A., Jones E. G., Isackson P. J. Coexpression of mRNAs for NGF, BDNF, and NT-3 in the cardiovascular system of the pre- and postnatal rat. J Neurosci. 1993 Mar;13(3):875–893. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-00875.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessarollo L., Tsoulfas P., Martin-Zanca D., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Parada L. F. trkC, a receptor for neurotrophin-3, is widely expressed in the developing nervous system and in non-neuronal tissues. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):463–475. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson T. M., Pellicer A., Greene L. A. Functional receptors for nerve growth factor on Ewing's sarcoma and Wilm's tumor cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Oct;141(1):60–64. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricoli J. V., Rall L. B., Scott J., Bell G. I., Shows T. B. Localization of insulin-like growth factor genes to human chromosomes 11 and 12. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):784–786. doi: 10.1038/310784a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoulfas P., Soppet D., Escandon E., Tessarollo L., Mendoza-Ramirez J. L., Rosenthal A., Nikolics K., Parada L. F. The rat trkC locus encodes multiple neurogenic receptors that exhibit differential response to neurotrophin-3 in PC12 cells. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):975–990. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90212-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno H., Colbert H., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Inhibition of PDGF beta receptor signal transduction by coexpression of a truncated receptor. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):844–848. doi: 10.1126/science.1851331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heyningen V., Hastie N. D. Wilms' tumour: reconciling genetics and biology. Trends Genet. 1992 Jan;8(1):16–21. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90019-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Y., Madden S. L., Deuel T. F., Rauscher F. J., 3rd The Wilms' tumor gene product, WT1, represses transcription of the platelet-derived growth factor A-chain gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):21999–22002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H., Re G. G., Drummond I. A., Sukhatme V. P., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sens D. A., Garvin A. J., LeRoith D., Roberts C. T., Jr Increased expression of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene, IGF1R, in Wilms tumor is correlated with modulation of IGF1R promoter activity by the WT1 Wilms tumor gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5828–5832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H., Re G. G., Drummond I. A., Sukhatme V. P., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sens D. A., Garvin A. J., LeRoith D., Roberts C. T., Jr Increased expression of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene, IGF1R, in Wilms tumor is correlated with modulation of IGF1R promoter activity by the WT1 Wilms tumor gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5828–5832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]