Abstract
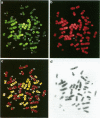
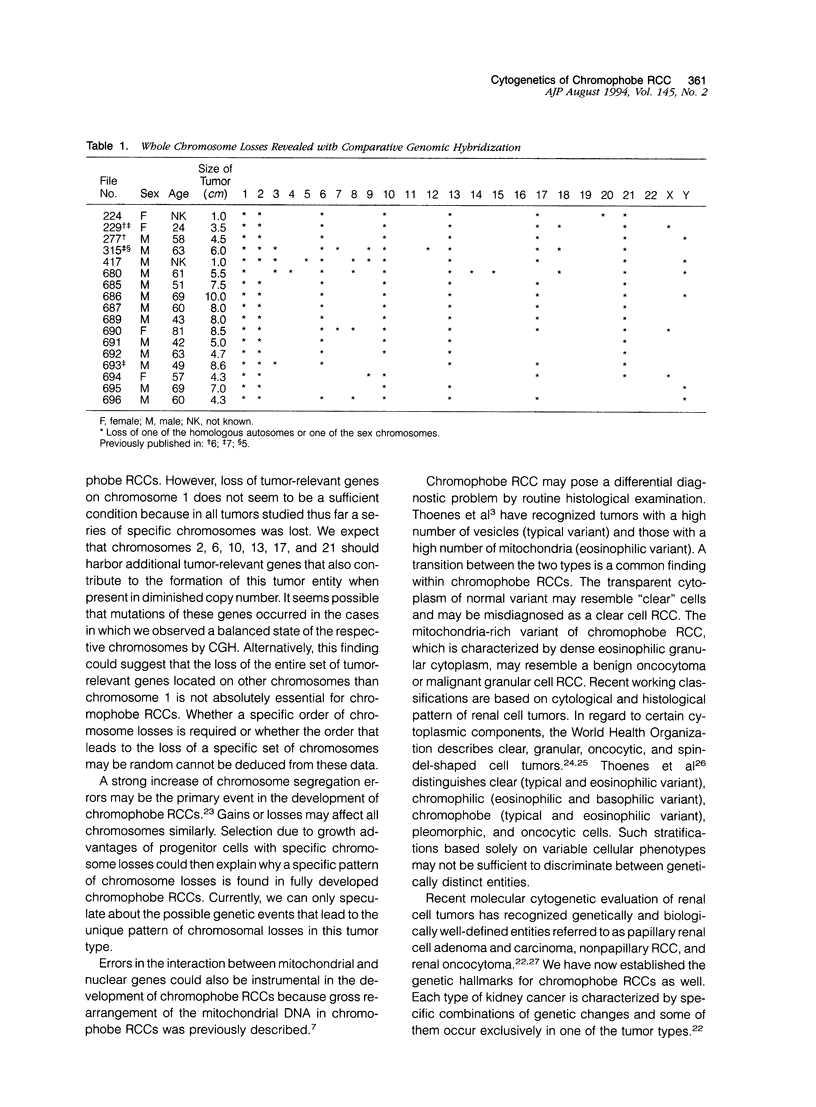
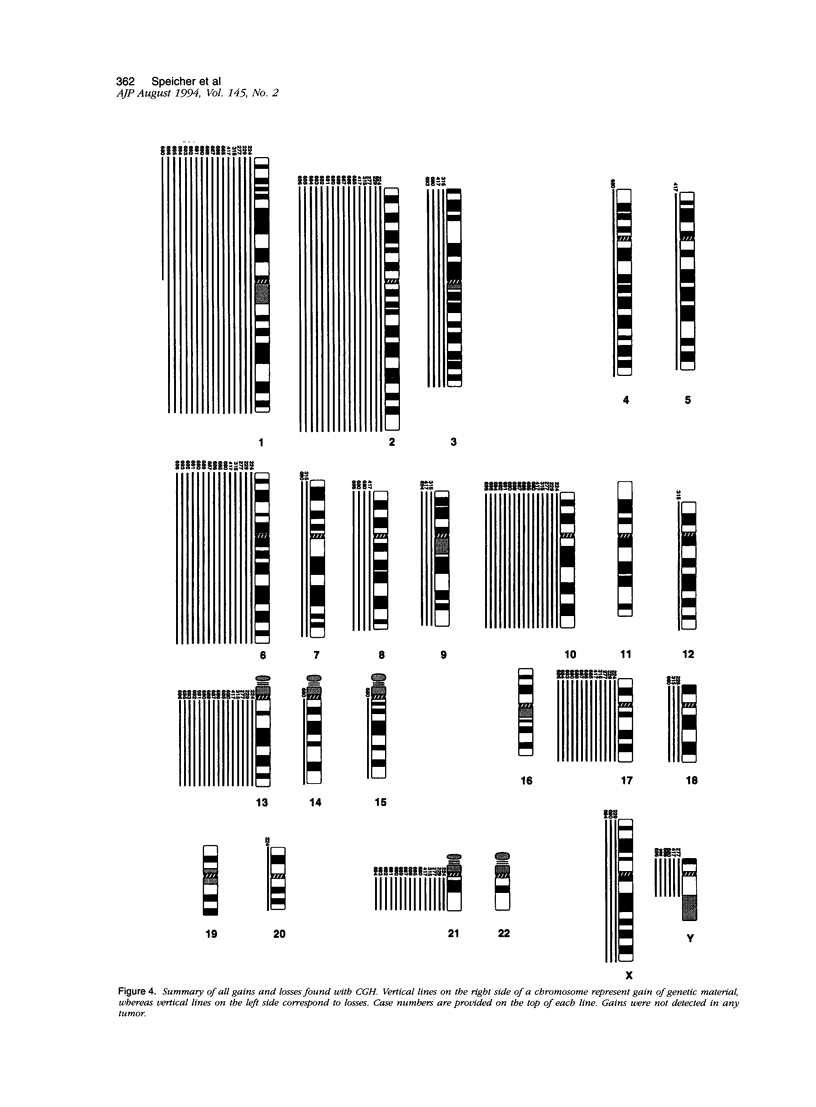
We analyzed 19 chromophobe renal cell carcinomas by means of comparative genomic hybridization. Two tumors revealed no numerical abnormalities. In the remaining 17 cases we found loss of entire chromosomes with underrepresentation of chromosome 1 occurring in all 17 cases; loss of chromosomes 2, 10, and 13 in 16 cases; loss of chromosomes 6 and 21 in 15 tumors; and loss of chromosome 17 in 13 cases. The loss of the Y chromosome was observed in 6 of 13 tumors from male patients, whereas 1 X chromosome was lost in 3 of 4 tumors obtained from females. Comparative genomic hybridization results were verified by interphase cytogenetics. We conclude that a specific combination of multiple chromosomal losses characterizes chromophobe renal cell carcinomas and may help to differentiate them unequivocally from other types of kidney cancer.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bannasch P., Schacht U., Storch E. Morphogenese und Mikromorphologie epithelialer Nierentumoren bei Nitrosomorpholin-vergifteten Ratten. I. Induktion und Histologie der Tumoren. Z Krebsforsch Klin Onkol Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1974;81(3-4):311–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00305032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonsib S. M., Lager D. J. Chromophobe cell carcinoma: analysis of five cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990 Mar;14(3):260–267. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199003000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Hindley J. Cloning of human satellite III DNA: different components are on different chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3177–3197. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crotty T. B., Lawrence K. M., Moertel C. A., Bartelt D. H., Jr, Batts K. P., Dewald G. W., Farrow G. M., Jenkins R. B. Cytogenetic analysis of six renal oncocytomas and a chromophobe cell renal carcinoma. Evidence that -Y, -1 may be a characteristic anomaly in renal oncocytomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1992 Jul 1;61(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(92)90372-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopman A. H., van Hooren E., van de Kaa C. A., Vooijs P. G., Ramaekers F. C. Detection of numerical chromosome aberrations using in situ hybridization in paraffin sections of routinely processed bladder cancers. Mod Pathol. 1991 Jul;4(4):503–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi A., Kallioniemi O. P., Piper J., Tanner M., Stokke T., Chen L., Smith H. S., Pinkel D., Gray J. W., Waldman F. M. Detection and mapping of amplified DNA sequences in breast cancer by comparative genomic hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2156–2160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi A., Kallioniemi O. P., Sudar D., Rutovitz D., Gray J. W., Waldman F., Pinkel D. Comparative genomic hybridization for molecular cytogenetic analysis of solid tumors. Science. 1992 Oct 30;258(5083):818–821. doi: 10.1126/science.1359641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P., Kallioniemi A., Sudar D., Rutovitz D., Gray J. W., Waldman F., Pinkel D. Comparative genomic hybridization: a rapid new method for detecting and mapping DNA amplification in tumors. Semin Cancer Biol. 1993 Feb;4(1):41–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs A., Kovacs G. Low chromosome number in chromophobe renal cell carcinomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Apr;4(3):267–268. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870040313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs A., Storkel S., Thoenes W., Kovacs G. Mitochondrial and chromosomal DNA alterations in human chromophobe renal cell carcinomas. J Pathol. 1992 Jul;167(3):273–277. doi: 10.1002/path.1711670303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs G. Molecular cytogenetics of renal cell tumors. Adv Cancer Res. 1993;62:89–124. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs G. Molecular differential pathology of renal cell tumours. Histopathology. 1993 Jan;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs G., Soudah B., Hoene E. Binucleated cells in a human renal cell carcinoma with 34 chromosomes. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Apr;31(2):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed A. N., Macoska J. A., Kallioniemi A., Kallioniemi O. P., Waldman F., Ratanatharathorn V., Wolman S. R. Extrachromosomal gene amplification in acute myeloid leukemia; characterization by metaphase analysis, comparative genomic hybridization, and semi-quantitative PCR. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1993 Nov;8(3):185–189. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870080308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ried T., Petersen I., Holtgreve-Grez H., Speicher M. R., Schröck E., du Manoir S., Cremer T. Mapping of multiple DNA gains and losses in primary small cell lung carcinomas by comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 1;54(7):1801–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröck E., Thiel G., Lozanova T., du Manoir S., Meffert M. C., Jauch A., Speicher M. R., Nürnberg P., Vogel S., Jänisch W. Comparative genomic hybridization of human malignant gliomas reveals multiple amplification sites and nonrandom chromosomal gains and losses. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jun;144(6):1203–1218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher M. R., du Manoir S., Schröck E., Holtgreve-Grez H., Schoell B., Lengauer C., Cremer T., Ried T. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded solid tumors by comparative genomic hybridization after universal DNA-amplification. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Nov;2(11):1907–1914. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.11.1907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenes W., Störkel S., Rumpelt H. J. Histopathology and classification of renal cell tumors (adenomas, oncocytomas and carcinomas). The basic cytological and histopathological elements and their use for diagnostics. Pathol Res Pract. 1986 May;181(2):125–143. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(86)80001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenes W., Störkel S., Rumpelt H. J. Human chromophobe cell renal carcinoma. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1985;48(3):207–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02890129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenes W., Störkel S., Rumpelt H. J., Moll R., Baum H. P., Werner S. Chromophobe cell renal carcinoma and its variants--a report on 32 cases. J Pathol. 1988 Aug;155(4):277–287. doi: 10.1002/path.1711550402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Waye J. S. Chromosome-specific subsets of human alpha satellite DNA: analysis of sequence divergence within and between chromosomal subsets and evidence for an ancestral pentameric repeat. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(3):207–214. doi: 10.1007/BF02100014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- du Manoir S., Speicher M. R., Joos S., Schröck E., Popp S., Döhner H., Kovacs G., Robert-Nicoud M., Lichter P., Cremer T. Detection of complete and partial chromosome gains and losses by comparative genomic in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1993 Feb;90(6):590–610. doi: 10.1007/BF00202476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg E., van der Hout A. H., Oosterhuis J. W., Störkel S., Dijkhuizen T., Dam A., Zweers H. M., Mensink H. J., Buys C. H., de Jong B. Cytogenetic analysis of epithelial renal-cell tumors: relationship with a new histopathological classification. Int J Cancer. 1993 Sep 9;55(2):223–227. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910550210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]