Abstract
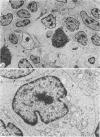
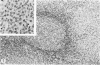
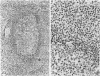
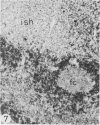
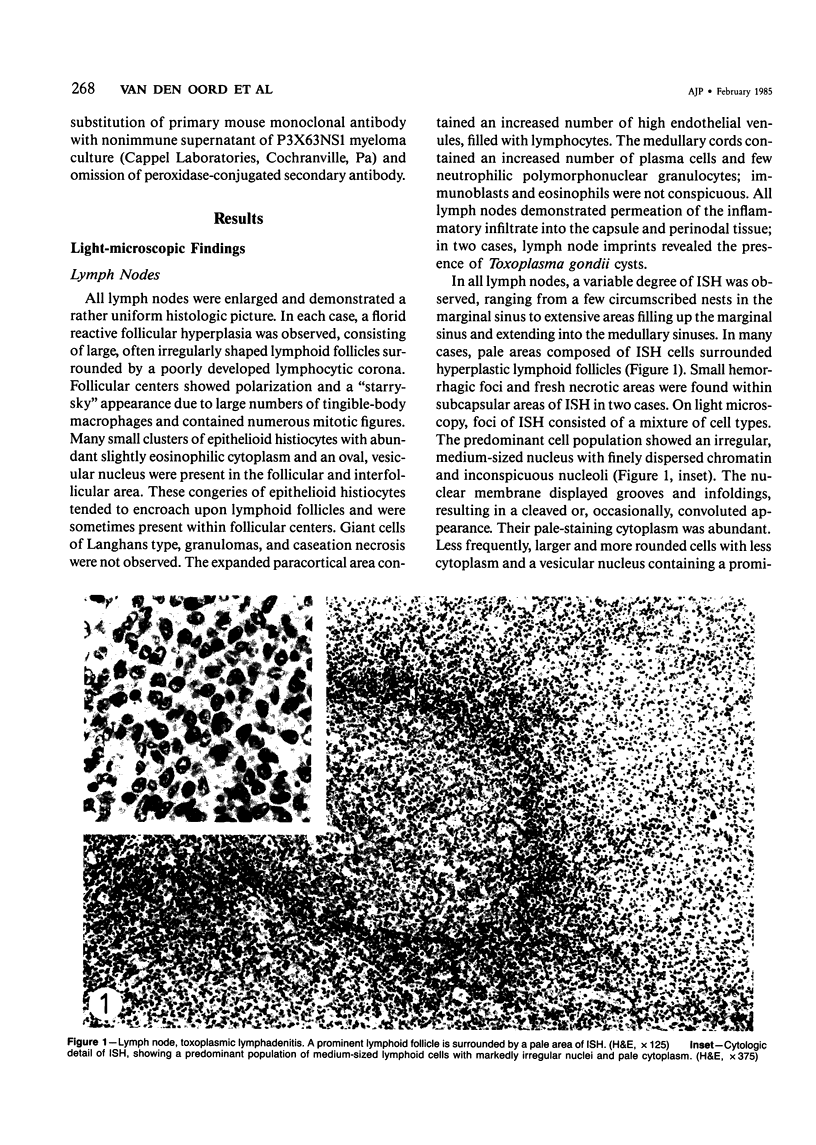
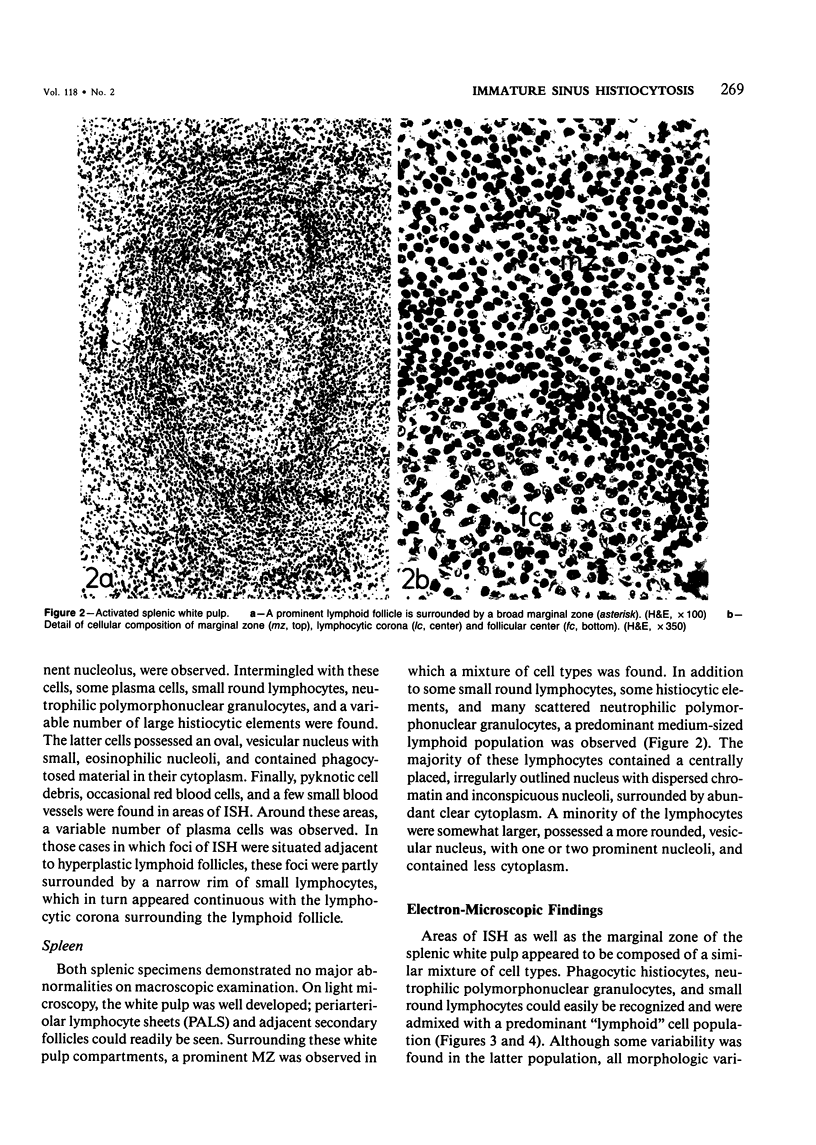
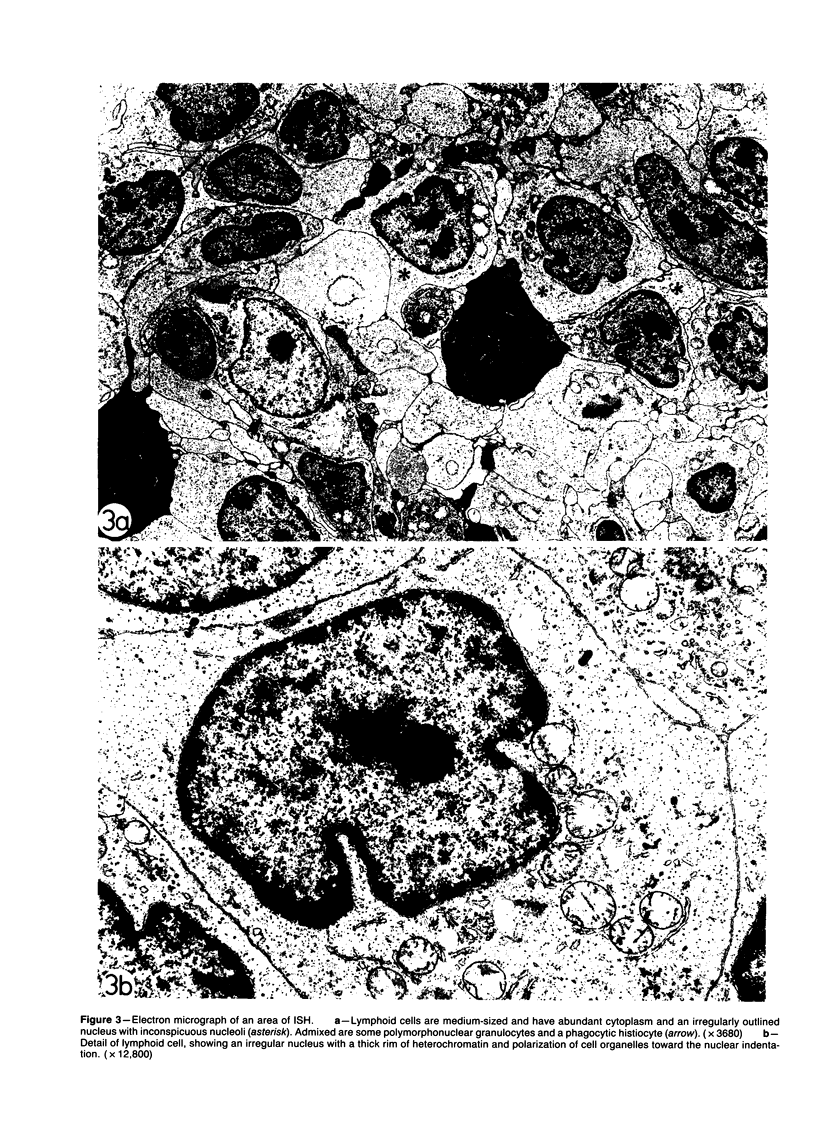
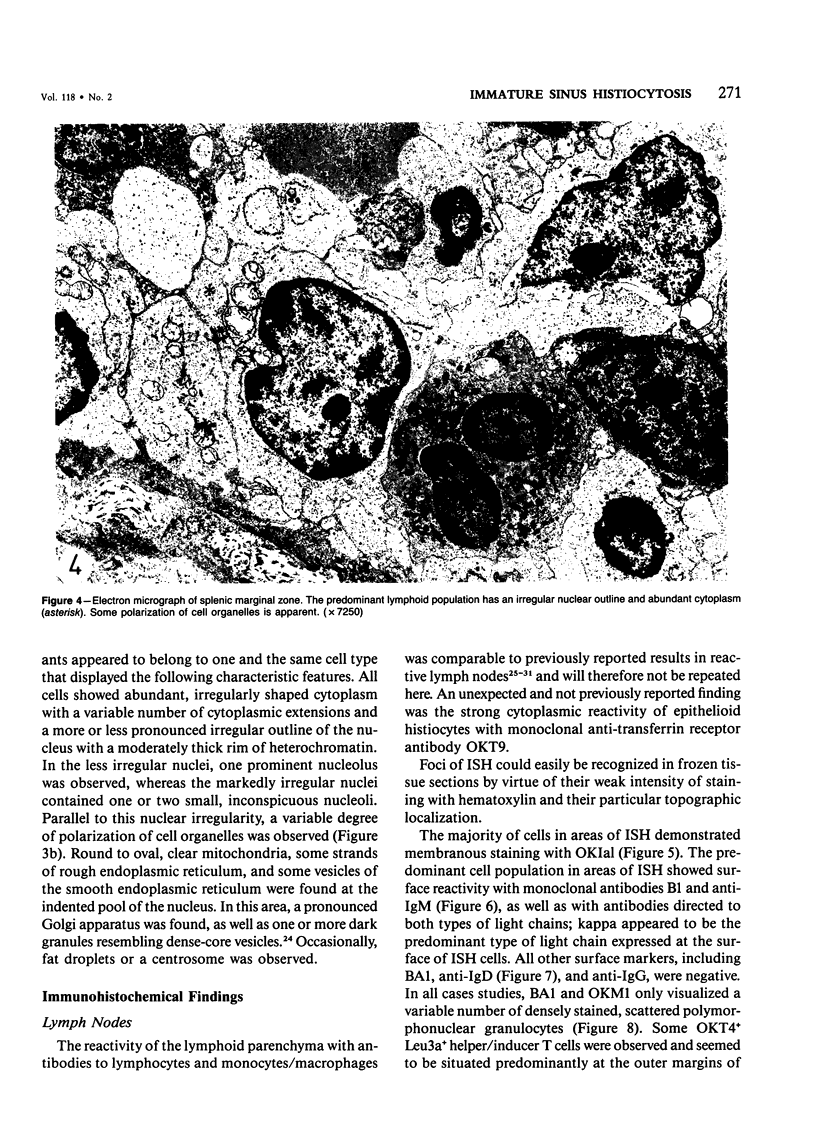
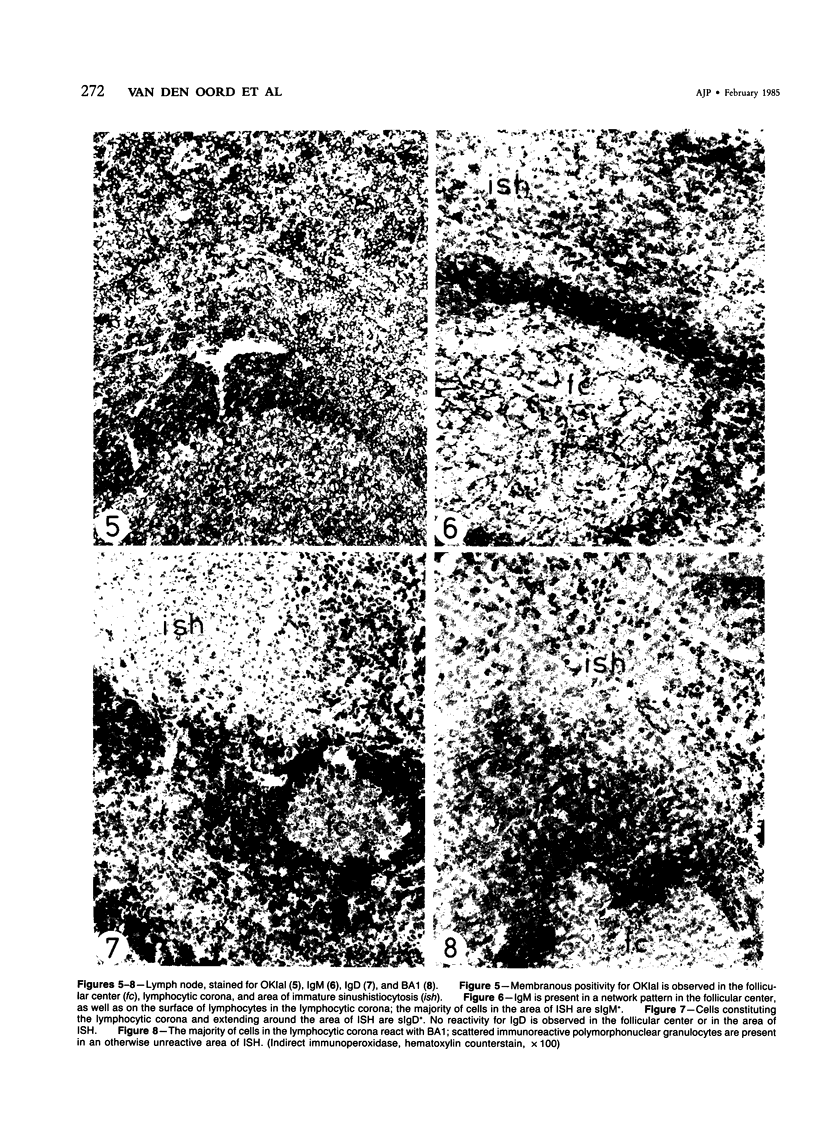
The light-microscopic, ultrastructural, and immunohistochemical features of immature sinus histiocytosis were studied in 10 lymph nodes with the histologic picture of toxoplasmic lymphadenitis and compared with the features of lymphoid cells present in the marginal zone of the splenic white pulp. Areas of immature sinus histiocytosis consisted largely of medium-sized lymphoid cells with markedly irregular nuclei and abundant pale cytoplasm. Using a panel of monoclonal antibodies, the predominating lymphoid cells were found to carry the B-cell phenotype B1+Ba1-sIgM+sIgD-OKIa1+. Admixed were variable numbers of larger, blastic lymphoid cells, small lymphocytes, histiocytic elements, and polymorphonuclear granulocytes. The marginal zone of the splenic white pulp was composed of a similar mixture of cells, and marginal-zone lymphocytes demonstrated an analogous immunohistochemical phenotype. Our results indicate that immature sinus histiocytes are B-lymphoid cells that are closely related to marginal zone lymphocytes. As such, immature sinus histiocytes may have a role similar to that of marginal-zone lymphocytes, which have been claimed to transport antigens or immune complexes toward the follicular center or to serve as precursors of plasma cells. We suggest that immature sinus histiocytosis represents an abnormal expansion of the marginal zone, normally present at the sinusoidal pole of lymphoid follicles. The reason for this marginal-zone hyperplasia, recognized as immature sinus histiocytosis in a variety of reactive lymph node conditions, may be a maturation arrest in the normal development of immature sinus histiocytes into small, sIgM+ sIgD+ lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson C. S., Kersey J. H., LeBien T. W. A monoclonal antibody (BA-1) reactive with cells of human B lymphocyte lineage. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):83–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. E., Bautista S., Remington J. S. Induction of resistance to Toxoplasma gondii in human macrophages by soluble lymphocyte products. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appel B. N., Mendelow H., Pasqual H. N. Acquired toxoplasma lymphadenitis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1979 Jun;47(6):529–532. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(79)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazin H., Gray D., Platteau B., MacLennan I. C. Distinct delta + and delta - B-lymphocyte lineages in the rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;399:157–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan A. K., Nadler L. M., Stashenko P., McCluskey R. T., Schlossman S. F. Stages of B cell differentiation in human lymphoid tissue. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):737–749. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue J., Weiss L. Species variation in the structure and function of the marginal zone--an electron microscope study of cat spleen. Am J Anat. 1981 Jun;161(2):169–187. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001610204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breard J., Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1943–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. C., Harris G., Papamichail M., Sljivić V. S., Holborow E. J. The localization of aggregated human -globulin in the spleens of normal mice. Immunology. 1973 Jun;24(6):955–968. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. S., Simon G. T. Electron microscopy of the spleen. I. Anatomy and microcirculation. Am J Pathol. 1970 Jan;58(1):127–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso De Almeida P., Harris N. L., Bhan A. K. Characterization of immature sinus histiocytes (monocytoid cells) in reactive lymph nodes by use of monoclonal antibodies. Hum Pathol. 1984 Apr;15(4):330–335. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra C. D., Döpp E. A. Ontogenetic development of T- and B-lymphocytes and non-lymphoid cells in the white pulp of the rat spleen. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;229(2):351–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00214978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman R. F., Remington J. S. Value of lymph-node biopsy in the diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Oct 25;289(17):878–881. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197310252891702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAM R. C., Jr, LUNDHOLM U., KARNOVSKY M. J. CYTOCHEMICAL DEMONSTRATION OF PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY WITH 3-AMINO-9-ETHYLCARBAZOLE. J Histochem Cytochem. 1965 Feb;13:150–152. doi: 10.1177/13.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garin Y., Audouin J., Diebold J. La lymphadénite toxoplasmique: aspects histopathologiques et étude en immunofluorescence. Arch Anat Cytol Pathol. 1977;25(4):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W., Burns G. F. Monoclonal antibody OKT-9 recognizes the receptor for transferrin on human acute lymphocytic leukemia cells. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1256–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. F., Jr, Kimball A. C., Kean B. H. The posterior cervical lymph node in toxoplasmosis. Am J Pathol. 1972 Nov;69(2):349–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Cossman J., Jaffe E. S. Lymphocyte subsets in normal human lymphoid tissues. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jul;80(1):21–30. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of B-lymphocytes. 1. Identification with monoclonal antibodies in normal lymphoid tissues. Am J Pathol. 1984 Mar;114(3):387–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. S., Shevach E. M., Sussman E. H., Frank M., Green I., Berard C. W. Membrane receptor sites for the identification of lymphoreticular cells in benign and malignant conditions. Br J Cancer Suppl. 1975 Mar;2:107–120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumararatne D. S., Bazin H., MacLennan I. C. Marginal zones: the major B cell compartment of rat spleens. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Nov;11(11):858–864. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumararatne D. S., MacLennan I. C. Cells of the marginal zone of the spleen are lymphocytes derived from recirculating precursors. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Nov;11(11):865–869. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung P., Goldstein G., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Monoclonal antibodies defining distinctive human T cell surface antigens. Science. 1979 Oct 19;206(4416):347–349. doi: 10.1126/science.314668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layton J. E., Baker J., Bartlett P. F., Shortman K. Antigen-initiated B lymphocyte differentiation. XVIII. Pre-progenitor B cells that give primary adoptive responses are s-IgM+IgD-Ia+. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1227–1233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Evans R. L., Lipinski M., Cunningham-Rundles C., Good R. A., Herzenberg L. A. Evolutionary conservation of surface molecules that distinguish T lymphocyte helper/inducer and cytotoxic/suppressor subpopulations in mouse and man. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):310–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masihi K. N., Werner H. Types of cells involved in antigen-stimulated and spontaneous rosette formation with Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2056–2059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod R., Remington J. S. Influence of infection with Toxoplasma on macrophage function, and role of macrophages in resistance to Toxoplasma. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 2):170–186. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M. Histological differential diagnosis between lymph node toxoplasmosis and other benign lymph node hyperplasias. Histopathology. 1981 Mar;5(2):205–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1981.tb01778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millikin P. D. The nodular white pulp of the human spleen. Arch Pathol. 1969 Mar;87(3):247–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J., Abbot A. Antigens in immunity. XVI. A light and electron microscope study of antigen localization in the rat spleen. Immunology. 1971 Aug;21(2):207–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Ritz J., Hardy R., Pesando J. M., Schlossman S. F., Stashenko P. A unique cell surface antigen identifying lymphoid malignancies of B cell origin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):134–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI110005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuis P., Keuning F. J. Germinal centres and the origin of the B-cell system. II. Germinal centres in the rabbit spleen and popliteal lymph nodes. Immunology. 1974 Mar;26(3):509–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuis P., van Nouhuijs C. E., Eggens J. H., Keuning F. J. Germinal centres and the origin of the B-cell system. I. Germinal centres in the rabbit appendix. Immunology. 1974 Mar;26(3):497–507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Austin C. M., Pye J., Mitchell J. Antigens in immunity. XII. Antigen trapping in the spleen. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(4):368–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Shortman K., Howard M., Pike B. L. Current problem areas in the study of B lymphocyte differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1977;37:187–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppema S., Bhan A. K., Reinherz E. L., McCluskey R. T., Schlossman S. F. Distribution of T cell subsets in human lymph nodes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):30–41. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Levey R. H., Schlossman S. F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Pesando J. M., Ritz J., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Ia determinants on human T-cell subsets defined by monoclonal antibody. Activation stimuli required for expression. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1472–1482. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rácz P., Tenner-Rácz K., Myrvik Q. N., Shannon B. T., Love S. H. Sinus reactions in the hilar lymph node complex of rabbits undergoing a pulmonary cell-mediated immune response: sinus macrophage clumping reaction, sinus lymphocytosis and immature sinus histiocytosis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Nov;24(5):499–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheibani K., Fritz R. M., Winberg C. D., Burke J. S., Rappaport H. "Monocytoid" cells in reactive follicular hyperplasia with and without multifocal histiocytic reactions: an immunohistochemical study of 21 cases including suspected cases of toxoplasmic lymphadenitis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Apr;81(4):453–458. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/81.4.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K., Howard M., Teale J., Baker J. Antigen-initiated B lymphocyte differentiation. XVI. Primary and secondary adoptive responses involve two sequential stages, antigen nonspecific then antigen specific, in the generation of specific AFC. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2465–2472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Si L., Whiteside T. L. Tissue distribution of human NK cells studied with anti-Leu-7 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2149–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfeld A. G. The histological diagnosis of toxoplasmic lymphadenitis. J Clin Pathol. 1961 Nov;14(6):565–573. doi: 10.1136/jcp.14.6.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Bonk A., Tolksdorf G., Lennert K., Rodt H., Gerdes J. Immunohistologic analysis of the organization of normal lymphoid tissue and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Aug;28(8):746–760. doi: 10.1177/28.8.7003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerman A. J., van Ewijk W. White pulp compartments in the spleen of rats and mice. A light and electron microscopic study of lymphoid and non-lymphoid celltypes in T- and B-areas. Cell Tissue Res. 1975;156(4):417–441. doi: 10.1007/BF00225103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerman A. J., van Rooijen N. Lymphocyte capping and lymphocyte migration as associated events in the in vivo antigen trapping process. An electron-microscopic autoradiographic study in the spleen of mice. Cell Tissue Res. 1975 Aug 18;161(2):211–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00220369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rooijen N. Mechanism of follicular antigen trapping. Migration of antigen-antibody complexes from marginal zone towards follicle centres. Immunology. 1973 Nov;25(5):847–852. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Valk P., van der Loo E. M., Jansen J., Daha M. R., Meijer C. J. Analysis of lymphoid and dendritic cells in human lymph node, tonsil and spleen. A study using monoclonal and heterologous antibodies. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1984;45(2):169–185. doi: 10.1007/BF02889863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]