Abstract
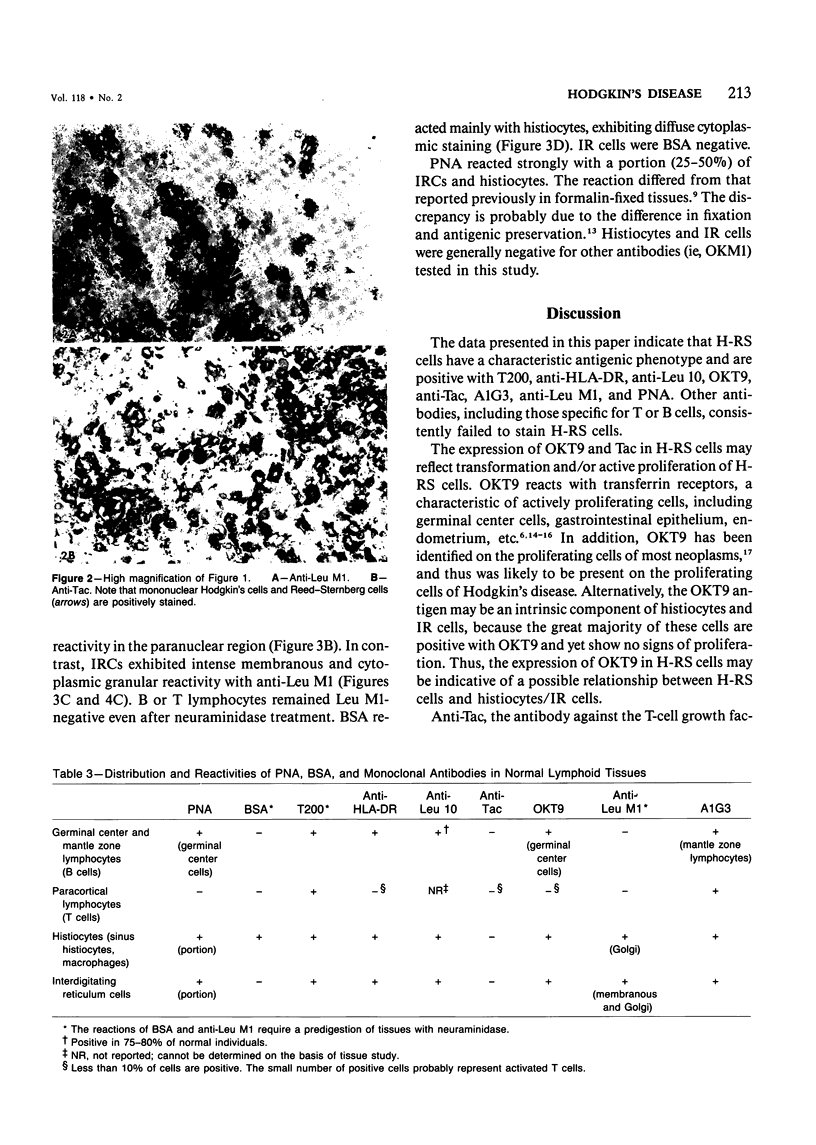
The phenotypic expression of Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg (H-RS) cells was determined by analysis with a panel of monoclonal antibodies and peanut agglutinin (PNA) by an immunohistochemical technique. Seven antibodies, including T200, anti-HLA-DR, anti-Leu 10, A1G3, anti-Tac, OKT9, and anti-Leu M1, were found to react with a great majority of H-RS cells. In some cases, H-RS cells also bound PNA. Other antibodies, including those highly specific for T cells (eg, Lyt 3) and B cells (eg, B1, anti-Leu 14) were consistently negative. The results argue against the derivation of H-RS cells from T or B lymphocytes. The H-RS cells were also negatively stained with antibodies which react with monocytes (OKM1, Mo-2, 63D-3), follicular dendritic cells (DRC-1), and natural killer/killer cells (Leu 7, Leu 11a, B73.1). The presence of Leu M1 and Tac in H-RS cells is of interest. Anti-Leu M1 positivity was seen in all 20 of Hodgkin's disease (HD) cases tested and should provide a very useful reagent for differential diagnosis of HD from other reactive and neoplastic conditions. Tac normally is present only on activated T cells. The presence of Tac in H-RS cells may reflect expression of T-cell growth factor receptor or a closely related protein during a stage of neoplastic transformation. Although the nature of the neoplastic cell of HD cannot be determined by these studies, they are consistent with an origin from interdigitating reticulum cells. Both H-RS cells and interdigitating reticulum cells have a similar antigenic phenotype (Leu M1+, T200+, HLA-DR+, Leu 10+, A1G3+, and OKT9+) and a similar pattern of lysosomal enzyme activity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisenberg A. C., Wilkes B. M. Lymph node T cells in Hodgkin's disease: analysis of suspensions with monoclonal antibody and rosetting techniques. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):522–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson L. C., Gahmberg C. G., Nilsson K., Wigzell H. Surface glycoprotein patterns of normal and malignant human lymphoid cells. I. T cells T blasts and leukemic T cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1977 Nov 15;20(5):702–707. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckstead J. H., Warnke R., Bainton D. F. Histochemistry of Hodgkin's disease. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):609–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossman J., Deegan M. J., Schnitzer B. Complement receptor B lymphocytes in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease. Cancer. 1977 May;39(5):2166–2173. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197705)39:5<2166::aid-cncr2820390533>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl V., Kirchner H. H., Burrichter H., Stein H., Fonatsch C., Gerdes J., Schaadt M., Heit W., Uchanska-Ziegler B., Ziegler A. Characteristics of Hodgkin's disease-derived cell lines. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):615–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W., Burns G. F. Monoclonal antibody OKT-9 recognizes the receptor for transferrin on human acute lymphocytic leukemia cells. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1256–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanjan S. N., Kearney J. F., Cooper M. D. A monoclonal antibody (MMA) that identifies a differentiation antigen on human myelomonocytic cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):172–188. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Harden E. A., Telen M. J., Hemler M. E., Strominger J. L., Palker T. J., Scearce R. M., Eisenbarth G. S. Differentiation of human T lymphocytes. I. Acquisition of a novel human cell surface protein (p80) during normal intrathymic T cell maturation. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1195–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F. Human T lymphocyte antigens as defined by monoclonal antibodies. Immunol Rev. 1981;57:127–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00445.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Cossman J., Jaffe E. S. Lymphocyte subsets in normal human lymphoid tissues. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jul;80(1):21–30. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of B-lymphocytes. 1. Identification with monoclonal antibodies in normal lymphoid tissues. Am J Pathol. 1984 Mar;114(3):387–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L. Versatility of biotin-labeled lectins and avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex for localization of carbohydrate in tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Feb;30(2):157–161. doi: 10.1177/30.2.7037937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Ree H. J. Histochemical studies on lectin binding in reactive lymphoid tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Apr;31(4):538–546. doi: 10.1177/31.4.6827084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Soban E. Color modification of diaminobenzidine (DAB) precipitation by metallic ions and its application for double immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Oct;30(10):1079–1082. doi: 10.1177/30.10.6182185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Yang K., Jaffe E. S. Hairy cell leukemia: a B cell neoplasm with a unique antigenic phenotype. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;80(4):421–428. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.4.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Zhang H. Z., Jaffe E. S. Monoclonal antibodies directed against human lymphoid, monocytic, and granulocytic cells: reactivities with other tissues. Hybridoma. 1983;2(4):403–412. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1983.2.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Glatstein E., Dorfman R. F. Clinicopathologic studies of 117 untreated patients subjected to laparotomy for the staging of Hodgkin's disease. Cancer. 1971 Jun;27(6):1277–1294. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197106)27:6<1277::aid-cncr2820270602>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E. Possible origin of the Reed-Sternberg cell from an interdigitating reticulum cell. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):601–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. S. On the biology and immunology of Hodgkin's disease. Haematol Blood Transfus. 1981;26:11–23. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67984-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Uchiyama T., Smith K. A., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. A monoclonal antibody that appears to recognize the receptor for human T-cell growth factor; partial characterization of the receptor. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):267–269. doi: 10.1038/300267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mir R., Kahn L. B. Immunohistochemistry of Hodgkin's disease. A study of 20 cases. Cancer. 1983 Dec 1;52(11):2064–2071. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19831201)52:11<2064::aid-cncr2820521116>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muresan V., Iwanij V., Smith Z. D., Jamieson J. D. Purification and use of limulin: a sialic acid-specific lectin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Sep;30(9):938–946. doi: 10.1177/30.9.6897073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., Barbuto D., Said J. W., Churchill W. H. Lymphocyte subpopulations of lymph nodes and spleens in Hodgkin's disease. Cancer. 1978 Sep;42(3):1270–1279. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197809)42:3<1270::aid-cncr2820420336>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppema S., Bhan A. K., Reinherz E. L., Posner M. R., Schlossman S. F. In situ immunologic characterization of cellular constituents in lymph nodes and spleens involved by Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1982 Feb;59(2):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausch E., Kaiserling E., Goos M. Langerhans cells and interdigitating reticulum cells in the thymus-dependent region in human dermatopathic lymphadenitis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1977 Nov 21;25(4):327–343. doi: 10.1007/BF02889443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ree H. J., Song J. Y., Leone L. A., Crowley J. P., Fanger H. Occurrence and patterns of muramidase containing cells in Hodgkin's disease, non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, and reactive hyperplasia. Hum Pathol. 1981 Jan;12(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro A., Cailou B., Belpomme D. T and B lymphocytes and monocytes in the spleen in Hodgkin's disease: the increase in T lymphocytes in involved spleens. Eur J Cancer. 1977 Apr-May;13(4-5):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(77)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Gerdes J., Kirchner H., Diehl V., Schaadt M., Bonk A., Steffen T. Immunohistological analysis of Hodgkin's and Sternberg-reed cells: detection of a new antigen and evidence for selective IgG uptake in the absence of B cell, T cell and histiocytic markers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1981;101(1):125–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00405073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Gerdes J., Mason D. Y. The normal and malignant germinal centre. Clin Haematol. 1982 Oct;11(3):531–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Gerdes J., Schwab U., Lemke H., Mason D. Y., Ziegler A., Schienle W., Diehl V. Identification of Hodgkin and Sternberg-reed cells as a unique cell type derived from a newly-detected small-cell population. Int J Cancer. 1982 Oct 15;30(4):445–459. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Uchánska-Ziegler B., Gerdes J., Ziegler A., Wernet P. Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells contain antigens specific to late cells of granulopoiesis. Int J Cancer. 1982 Mar 15;29(3):283–290. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R., Delia D., Schneider C., Newman R., Kemshead J., Greaves M. Ubiquitous cell-surface glycoprotein on tumor cells is proliferation-associated receptor for transferrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4515–4519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerman A. J. On the interdigitating cells in the thymus-dependent area of the rat spleen: a relation between the mononuclear phagocyte system and T-lymphocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 1974 Apr 11;148(2):247–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00224586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Al-Katib A., Lane C. L., Koziner B., Fu S. M. Induction of HLA-DC/DS (LEU 10) antigen expression by human precursor B cell lines. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1757–1762. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






