Abstract
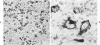
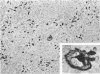
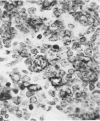
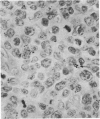
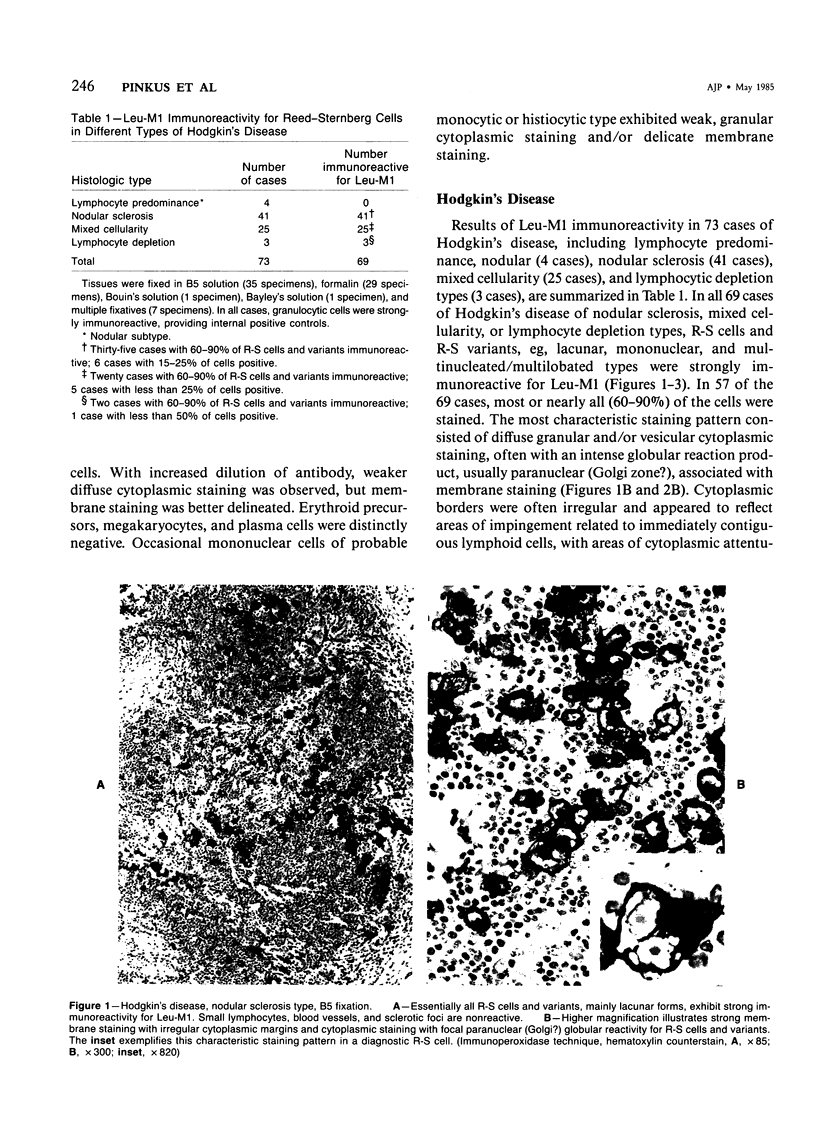
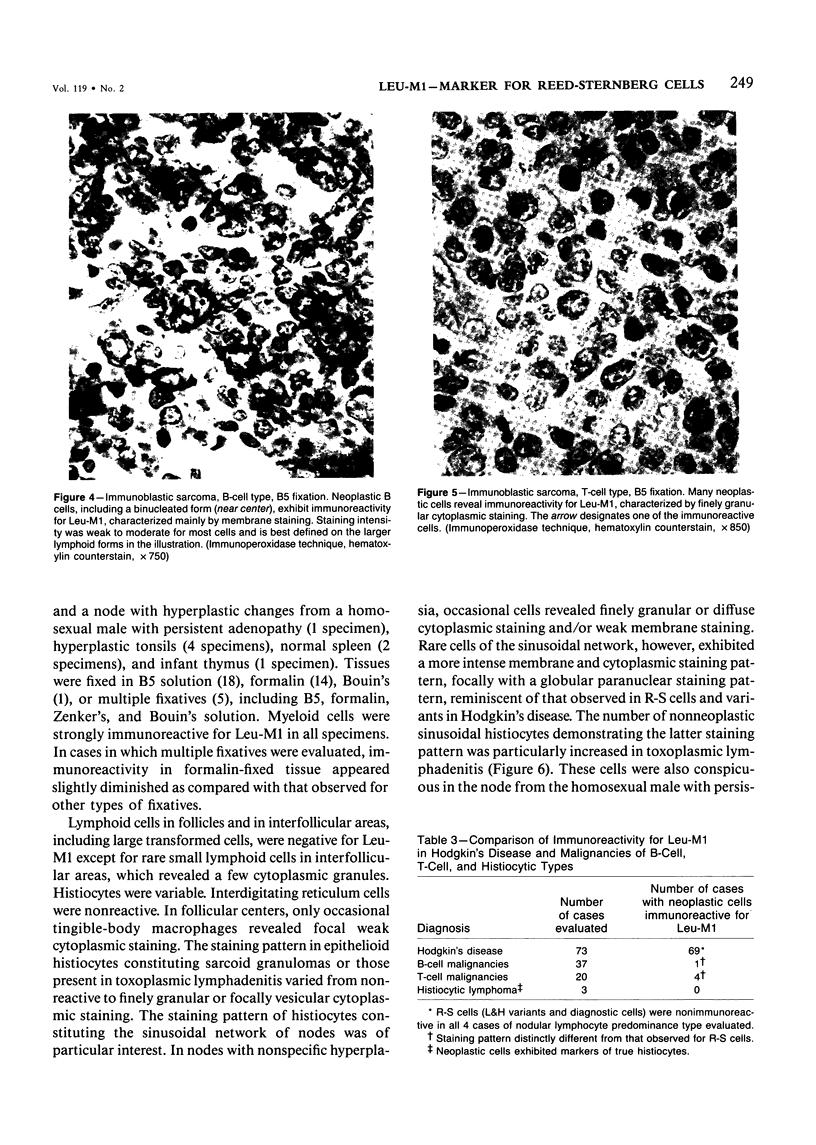
Monoclonal antibody to Leu-M1, a granulocyte-related differentiation antigen, represents a highly effective reagent for detection of diagnostic Reed-Sternberg (R-S) cells and variants in paraffin-embedded tissues of Hodgkin's disease. In 69 of 73 cases of Hodgkin's disease (41 nodular sclerosis, 25 mixed cellularity, 4 lymphocyte predominance, and 3 lymphocyte depletion types), R-S cells were strongly immunoreactive for Leu-M1. Four cases of lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin's disease (nodular) were uniformly nonreactive for Leu-M1. In most of the positive cases (57/69, 83%), the majority (60-90%) of R-S cells and variants exhibited immunoreactivity for Leu-M1. A characteristic staining pattern included granular and/or vesicular cytoplasmic immunoreactivity, often with a prominent globular paranuclear reaction product, and membrane staining with highly irregular cytoplasmic borders. Evaluation of B-cell (37 specimens), T-cell (20 specimens), and true histiocytic (3 specimens) neoplasms and a case of mastocytosis revealed immunoreactivity for Leu-M1 only in 1 B-cell and 4 T-cell malignancies. The staining patterns in these cases, however, clearly differed from that observed for R-S cells. Studies of nonneoplastic lymphoid tissues (38 total) demonstrated that lymphoid cells were typically nonreactive; histiocytes revealed variable reactivity for Leu-M1. Occasional histiocytes of the sinusoidal network of lymph nodes, particularly in toxoplasmic lymphadenitis, exhibited a staining pattern (membranous/cytoplasmic/paranuclear) similar to that observed for R-S cells. Leu-M1 represents a potentially helpful diagnostic discriminant in the assessment of Hodgkin's disease and its distinction from non-Hodgkin's lymphomas and other lymphoid proliferations.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdulaziz Z., Mason D. Y., Stein H., Gatter K. C., Nash J. R. An immunohistological study of the cellular constituents of Hodgkin's disease using a monoclonal antibody panel. Histopathology. 1984 Jan;8(1):1–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1984.tb02318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreesen R., Osterholz J., Löhr G. W., Bross K. J. A Hodgkin cell-specific antigen is expressed on a subset of auto- and alloactivated T (helper) lymphoblasts. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1299–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckstead J. H., Warnke R., Bainton D. F. Histochemistry of Hodgkin's disease. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):609–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran R. C., Jones E. L. Hodgkin's disease: an immunohistochemical and histological study. J Pathol. 1978 May;125(1):39–51. doi: 10.1002/path.1711250107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl V., Kirchner H. H., Burrichter H., Stein H., Fonatsch C., Gerdes J., Schaadt M., Heit W., Uchanska-Ziegler B., Ziegler A. Characteristics of Hodgkin's disease-derived cell lines. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):615–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick A. D., Leech J. H., Flexner J. M., Collins R. D. Ultrastructural study of Reed-Sternberg cells. Comparison with transformed lymphocytes and histiocytes. Am J Pathol. 1976 Oct;85(1):195–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanjan S. N., Kearney J. F., Cooper M. D. A monoclonal antibody (MMA) that identifies a differentiation antigen on human myelomonocytic cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):172–188. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansmann M. L., Kaiserling E. Electron-microscopic aspects of Hodgkin's disease. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1981;101(1):135–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00405074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Leu M1 and peanut agglutinin stain the neoplastic cells of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jul;82(1):29–32. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Zhang H. Z., Jaffe E. S. Utility of monoclonal antibodies directed against B and T lymphocytes and monocytes in paraffin-embedded sections. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;80(4):415–420. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E. Possible origin of the Reed-Sternberg cell from an interdigitating reticulum cell. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):601–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Stites D. P., Levy R., Warnke R. Exogenous immunoglobulin and the macrophage origin of Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 30;299(22):1208–1214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811302992203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin K. J., Ranchod M., Dorfman R. F. Lymphomas of the gastrointestinal tract: a study of 117 cases presenting with gastrointestinal disease. Cancer. 1978 Aug;42(2):693–707. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197808)42:2<693::aid-cncr2820420241>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukes R. J., Butler J. J. The pathology and nomenclature of Hodgkin's disease. Cancer Res. 1966 Jun;26(6):1063–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukes R. J. Criteria for involvement of lymph node, bone marrow, spleen, and liver in Hodgkin's disease. Cancer Res. 1971 Nov;31(11):1755–1767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Franssila K. O., Saxén E. Hodgkin's disease, lymphocytic predominance nodular. Increased risk for subsequent non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Cancer. 1983 Jun 15;51(12):2293–2300. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830615)51:12<2293::aid-cncr2820511221>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. P., Byrne G. E., Jones S. E. Mistaken clinical and pathologic diagnoses of Hodgkin's disease: a Southwest oncology group study. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mir R., Kahn L. B. Immunohistochemistry of Hodgkin's disease. A study of 20 cases. Cancer. 1983 Dec 1;52(11):2064–2071. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19831201)52:11<2064::aid-cncr2820521116>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., Said J. W. Characterization of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas using multiple cell markers. Immunologic, morphologic, and cytochemical studies of 72 cases. Am J Pathol. 1979 Feb;94(2):349–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppema S., Bhan A. K., Reinherz E. L., Posner M. R., Schlossman S. F. In situ immunologic characterization of cellular constituents in lymph nodes and spleens involved by Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1982 Feb;59(2):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppema S., Kaiserling E., Lennert K. Hodgkin's disease with lymphocytic predominance, nodular type (nodular paragranuloma) and progressively transformed germinal centres--a cytohistological study. Histopathology. 1979 Jul;3(4):295–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1979.tb03011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppema S. The diversity of the immunohistological staining pattern of Sternberg-Reed cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Aug;28(8):788–791. doi: 10.1177/28.8.6777426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said J. W., Shintaku I. P., Chien K., Sassoon A. F. Peripheral T cell lymphoma (immunoblastic sarcoma of T cell type): an immuno-ultrastructural study. Hum Pathol. 1984 Apr;15(4):324–329. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schienle H. W., Stein N., Müller-Ruchholtz W. Neutrophil granulocytic cell antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody--its distribution within normal haemic and non-haemic tissue. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):959–966. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.9.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab U., Stein H., Gerdes J., Lemke H., Kirchner H., Schaadt M., Diehl V. Production of a monoclonal antibody specific for Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells of Hodgkin's disease and a subset of normal lymphoid cells. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):65–67. doi: 10.1038/299065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Gerdes J., Schwab U., Lemke H., Diehl V., Mason D. Y., Bartels H., Ziegler A. Evidence for the detection of the normal counterpart of Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells. Hematol Oncol. 1983 Jan-Mar;1(1):21–29. doi: 10.1002/hon.2900010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Gerdes J., Schwab U., Lemke H., Mason D. Y., Ziegler A., Schienle W., Diehl V. Identification of Hodgkin and Sternberg-reed cells as a unique cell type derived from a newly-detected small-cell population. Int J Cancer. 1982 Oct 15;30(4):445–459. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Uchánska-Ziegler B., Gerdes J., Ziegler A., Wernet P. Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells contain antigens specific to late cells of granulopoiesis. Int J Cancer. 1982 Mar 15;29(3):283–290. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]