Abstract
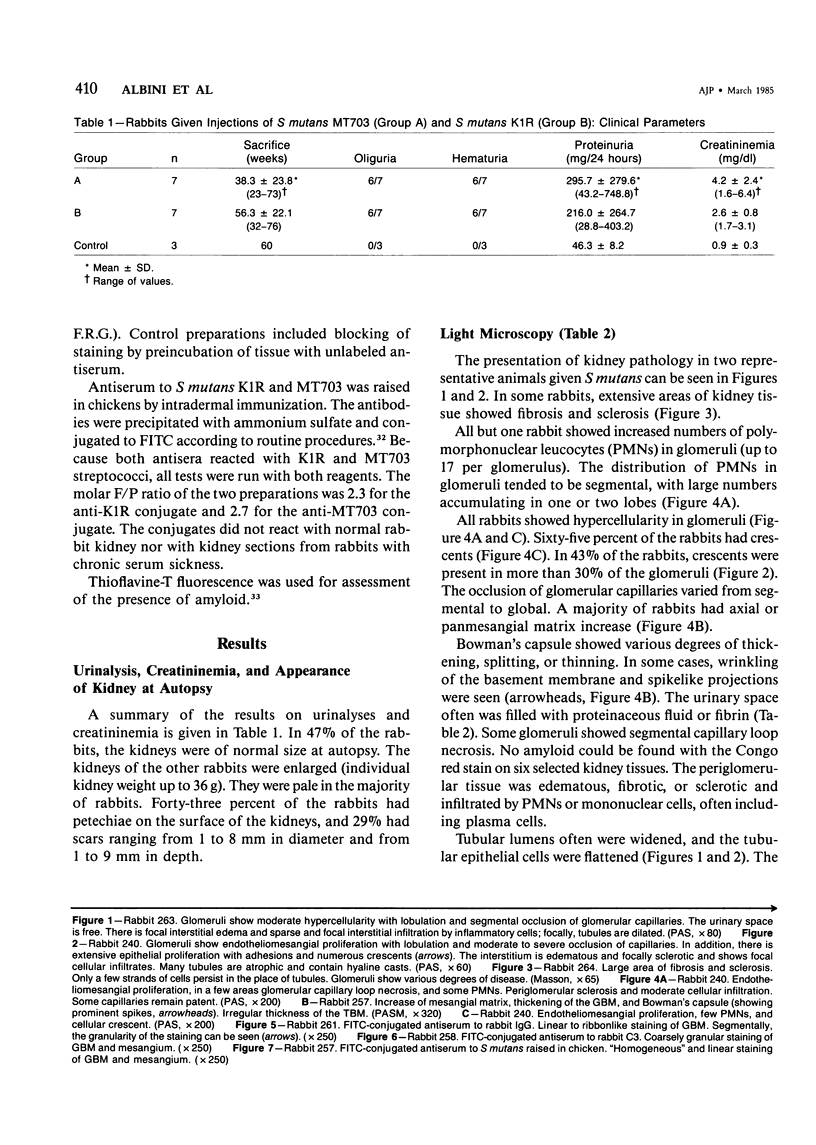
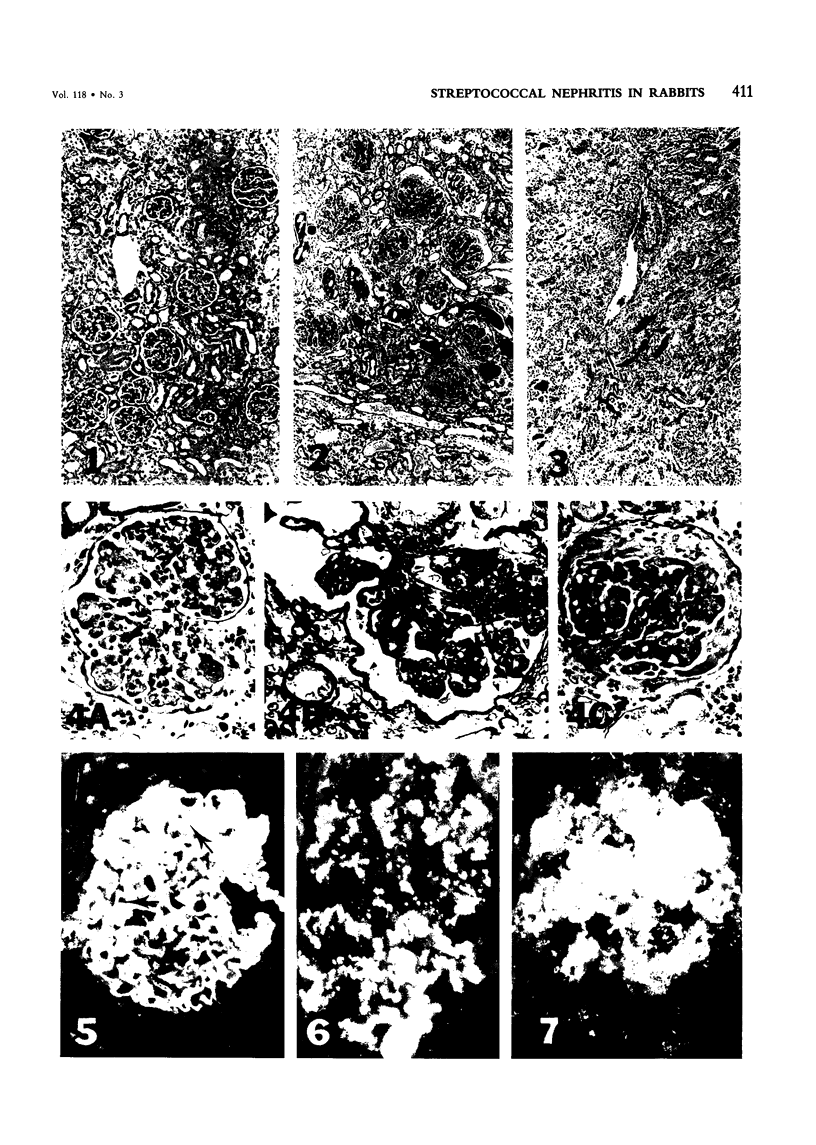
Intravenous administration of disrupted Streptococcus mutans into rabbits over 23-76 weeks led to severe nephritis involving glomeruli, tubules, and interstitium. Light-microscopic observation of glomeruli documented diffuse endocapillary proliferative glomerulonephritis accompanied often (65%) by epithelial crescents. Electron-microscopic observation revealed humps in glomeruli of 70% of kidney specimens. In the glomeruli of some rabbits, extensive fibrin deposits and sclerosis were evident. Immunofluorescence showed linear, granular, often ribbonlike or patchy immune deposits encompassing, in order of decreasing frequency, C3, IgG, streptococcal antigen, IgA, and IgM. The histopathologic and immunohistologic features of the nephritis seen in rabbits given S mutans thus shows many features of Streptococcus-associated nephritides in man, in particular, the diffuse glomerular nephritis encountered in subacute bacterial endocarditis. Further, analysis of nephritis induced by administration of S mutans may have implications for the evaluation and purification of dental caries vaccines.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa M., Abramowsky C., Powers K. G., Furrow R. Dirofilariasis. IV. Glomerulonephropathy induced by Dirofilaria immitis infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Jan;30(1):84–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres G. A., Accinni L., Hsu K. C., Zabriskie J. B., Seegal B. C. Electron microscopic studies of human glomerulonephritis with ferritin-conjugated antibody. Localization of antigen-antibody complexes in glomerular structures of patients with acute glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1966 Feb 1;123(2):399–412. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.2.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold S. B., Valone J. A., Askenase P. W., Kashgarian M., Freedman L. R. Diffuse glomerulonephritis in rabbits with Streptococcus viridans endocarditis. Lab Invest. 1975 Jun;32(6):681–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIN R. C., EDWARDS J. E., SCHEIFLEY C. H., GERACI J. E. Right-sided bacterial endocarditis and endarteritis; a clinical and pathologic study. Am J Med. 1958 Jan;24(1):98–110. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90365-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D. S., Gluck M. C., Schacht R. G., Gallo G. The long-term course of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Mar;80(3):342–358. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-3-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S., Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J., Guze L. B. Circulating immune complexes in experimental streptococcal endocarditis: a monitor of therapeutic efficacy. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutner E. H., Sepulveda M. R., Barnett E. V. Quantitative studies of immunofluorescent staining. Relationships of characteristics of unabsorbed antihuman IgG conjugates to their specific and non-specific staining properties in an indirect test for antinuclear factors. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(4):587–606. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield J. P., Farquhar M. G. Distribution of annionic sites in glomerular basement membranes: their possible role in filtration and attachment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1646–1650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge W. F., Spargo B. H., Travis L. B., Srivastava R. N., Carvajal H. F., DeBeukelaer M. M., Longley M. P., Menchaca J. A. Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. A prospective study in children. N Engl J Med. 1972 Feb 10;286(6):273–278. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197202102860601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison P. K., Freedman L. R. Experimental endocarditis I. Staphylococcal endocarditis in rabbits resulting from placement of a polyethylene catheter in the right side of the heart. Yale J Biol Med. 1970 Jun;42(6):394–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman R. A., Striker G. E., Gilliland B. C., Cutler R. E. The immune complex glomerulonephritis of bacterial endocarditis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1972 Jan;51(1):1–25. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197201000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder E. J., Wilkowske C. J., Washington J. A., 2nd, Geraci J. E. Streptococcus mutans endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Mar;80(3):364–368. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-3-364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm S. E. Precipitinogens in beta-hemolytic streptococci and some related human kidney antigens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;70(1):79–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb01272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holubar K., Stingl G., Albini B. Praxis und Methodologie der definierten Immunfluoreszenztechnik. Eine kurzgefasste Arbeitsamleitung für das klinische Laboratorium bzw. für die ärztliche Praxis. Hautarzt. 1976 Feb;27(2):78–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENNINGS R. B., EARLE D. P. Post-streptococcal glomerulo-nephritis: histopathologic and clinical studies of the acute, subsiding acute and early chronic latent phases. J Clin Invest. 1961 Aug;40:1525–1595. doi: 10.1172/JCI104382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshi G., Sridharan G., Thangavelu C. P., Shastry J. C. Streptococcal antibodies and complement components in tropical post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(2):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshi G., Webb J. K., Myers R. M. Association of preceding streptococcal skin infection and acute glomerulonephritis in children in South India. Indian J Med Res. 1968 Jul;56(7):951–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Challacombe S. J., Caldwell J. Immunologic basis for vaccination against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. J Dent Res. 1976 Apr;55(Spec No):C166–C180. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500311011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. L., Hong R. The immune nature of subacute bacterial endocarditis (SBE) nephritis. Am J Med. 1973 May;54(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood W. R., Lawson L. A., Smith D. L., McNeil K. M., Morrison F. S. Streptococcus mutans endocarditis. Report of a case. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Mar;80(3):369–370. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-3-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOWITZ A. S., LANGE C. F., Jr STREPTOCOCCAL RELATED GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. I. ISOLATION, IMMUNOCHEMISTRY AND COMPARATIVE CHEMISTRY OF SOLUBLE FRACTIONS FROM TYPE 12 NEPHRITOGENIC STREPTOCOCCI AND HUMAN GLOMERULI. J Immunol. 1964 Apr;92:565–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOVAT H. Z., STEINER J. W., HUHN D. The fine structure of the glomerulus in acute glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1962 Feb;11:117–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Potter E. V. The presence of type 12 M-protein antigen in group G streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Oct;49(1):119–125. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh R. M. Cryoproteins in poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Nov;73(5):857–857. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-5-857_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow S. R. Poststreptococcal nephritis--a rare disease?. Arch Dis Child. 1975 May;50(5):379–382. doi: 10.1136/adc.50.5.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael A. F., Jr, Drummond K. N., Good R. A., Vernier R. L. Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis: immune deposit disease. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):237–248. doi: 10.1172/JCI105336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefe L. I., Chretien J. H., Delaha E. C., Garagusi V. F. Streptococcus mutans endocarditis. Confusion with enterococcal endocarditis by routine laboratory testing. JAMA. 1974 Dec 2;230(9):1298–1299. doi: 10.1001/jama.230.9.1298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindrey M., Barratt J., Hewitt J., Naish P. Infective endocarditis-associated glomerulonephritis in rabbits: evidence of a pathogenetic role for antiglobulins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Aug;45(2):253–260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Barua P. K., Bergey E. J., Nisengard R. J., Neiders M. E., Albini B. Binding of Streptococcus mutans antigens to heart and kidney basement membranes. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):145–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.145-151.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Bergey E. J. Isolation of heart- and kidney-binding protein from group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):335–342. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.335-342.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Nisengard R. J., Neiders M. E., Albini B. Serology and tissue lesions in rabbits immunized with Streptococcus mutans. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3021–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSAR P. S., CULLING C. F. Fluorescent stains, with special reference to amyloid and connective tissues. Arch Pathol. 1959 Nov;68:487–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Rijn I., Bleiweis A. S. Antigens of Streptococcus mutans. I. Characterization of a serotype-specific determinant from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.795-804.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt A., Schmidt H. U., Takamiya H., Batsford S. 'In situ' immune complex nephritis and basic proteins. Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc. 1980;17:613–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., Jr, KUNKEL H. G. Rheumatoid factor, complement, and conglutinin aberrations in patients with subacute bacterial endocarditis. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:666–675. doi: 10.1172/JCI104523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Calkins E., Humphrey R. L. Potassium permanganate reaction in amyloidosis. A histologic method to assist in differentiating forms of this disease. Lab Invest. 1977 Mar;36(3):274–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]














