Abstract
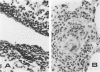
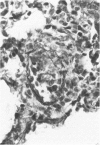
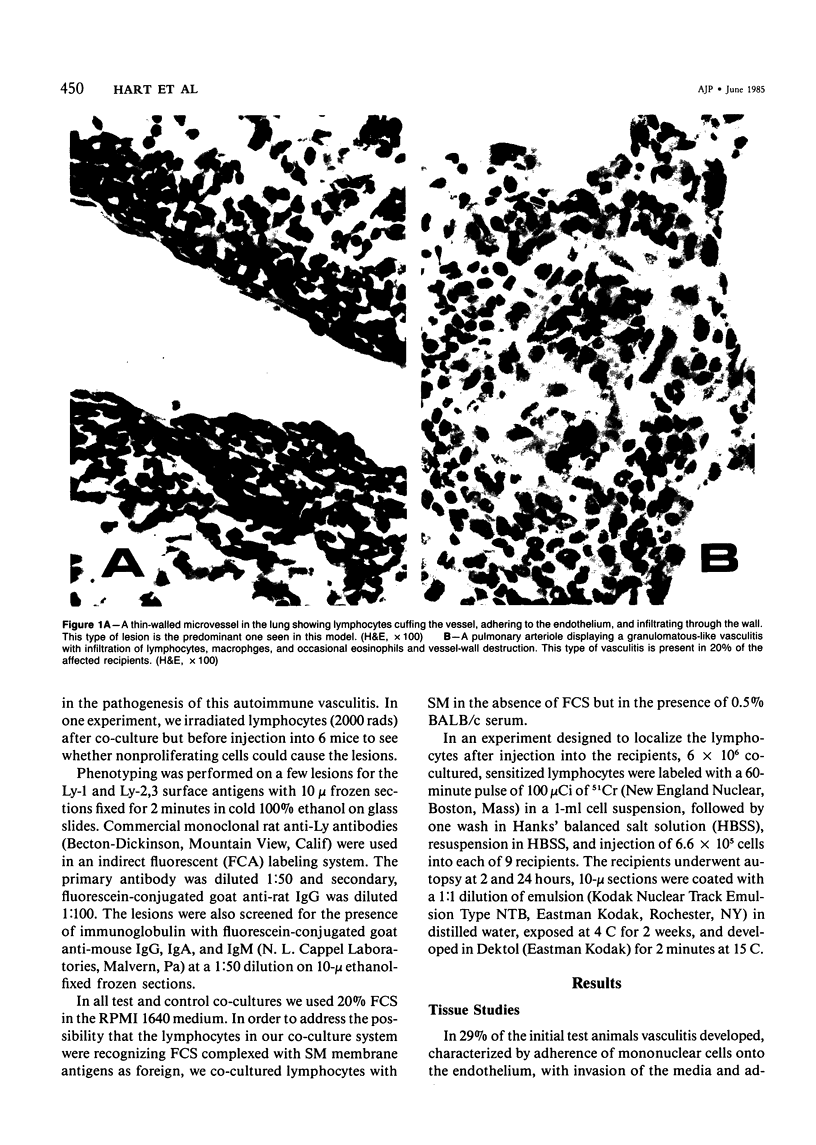
Lymphocytes sensitized in vitro to syngenic microvascular smooth muscle and transferred to syngeneic recipients produced in vivo microvessel vasculitis characterized by mononuclear cells which adhered to endothelium, infiltrated the vessel wall, and formed a perivascular cuff. A granulomatous type of vascular inflammation was seen in 20% of the affected recipients in which the vessel smooth muscle appeared to be preferentially attacked. These lesions bear a striking resemblance to certain human vasculitides, and the model provides an important means of studying vasculitis as well as general cellular autoimmune disease mechanisms.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askenase P. W., Hayden B. J., Gershon R. K. Augmentation of delayed-type hypersensitivity by doses of cyclophosphamide which do not affect antibody responses. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):697–702. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charreire J., Michel-Bechet M. Syngeneic sensitization of mouse lymphocytes on monolayers of thyroid epithelial cells. III. Induction of thyroiditis by thyroid-sensitized T lymphoblasts. Eur J Immunol. 1982 May;12(5):421–425. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Wekerle H. Autosensitization of lymphocytes against thymus reticulum cells. Science. 1972 Jun 23;176(4041):1324–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4041.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui Y. C., Tai P. C., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y., Spry C. J. A vascular endothelial cell antigen with restricted distribution in human foetal, adult and malignant tissues. Immunology. 1983 May;49(1):183–189. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnule A. T., Stotzky G., Darnule T. V., Turino G. M., Mandl I. Identification of surface antigens of endothelial cells. Immunol Commun. 1983;12(4):351–362. doi: 10.3109/08820138309050756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFreitas E. C., Chesnut R. W., Grey H. M., Chiller J. M. Macrophage-dependent activation of antigen-specific T cells requires antigen and a soluble monokine. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):23–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach M. Defective T cell response to presented antigen in autoimmune mice. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2365–2368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimcher L. H., Longo D. L., Green I., Schwartz R. H. Murine syngeneic mixed lymphocyte response. I. Target antigens are self Ia molecules. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1652–1670. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Hiai H., Elder J. H., Schwartz R. S., Khiroya R. H., Thomas C. Y., Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. Expression of leukemogenic recombinant viruses associated with a recessive gene in HRS/J mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):249–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. N., Sadewasser K. L., Cancilla P. A., DeBault L. E. Experimental autoimmune type of vasculitis resulting from activation of mouse lymphocytes to cultured endothelium. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):419–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman P. B., Stites D. P., Stobo J. D. Antigen-reactive T cells can be activated buy autologous macrophages in the absence of added antigen. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):476–481. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinglais N., Kazatchkine M. D., Charron D. J., Appay M. D., Mandet C., Paing M., Bariety J. Immunohistochemical study of Ia antigen in the normal and diseased human kidney. Kidney Int. 1984 Mar;25(3):544–550. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg H., Braathen L. R., Thorsby E. Antigen presentation by vascular endothelial cells and epidermal Langerhans cells: the role of HLA-DR. Immunol Rev. 1982;66:57–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Glovsky M., Schrier D. Pulmonary granulomatous vasculitis. Pulmonary granulomatous vasculitis induced in rats by treatment with glucan. Am J Pathol. 1984 Mar;114(3):515–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röllinghoff M., Starzinski-Powitz A., Pfizenmaier K., Wagner H. Cyclophosphamide-sensitive T lymphocytes suppress the in vivo generation of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):455–459. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriram S., Steinman L. Anti I-A antibody suppresses active encephalomyelitis: treatment model for diseases linked to IR genes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1362–1367. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Autoimmune diseases: immunopathology and etiopathogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1982 Sep;108(3):319–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H. Smooth muscle autoantibodies and autoantigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Dec;38(3):621–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]