Abstract
Schistosomiasis mansoni is characterized by granulomatous inflammations, deposition of collagen, and irreversible liver fibrosis. In chronic infections fibrosis is cumulative, while collagen synthesis and degradation are diminished. In the present study, we compared collagenase, elastase, and nonspecific neutral protease (NP) activities in isolated vigorous (8-week infection) and immunomodulated (18-20-week infection) liver granulomas. Enzyme activity was localized in the adherent macrophage (greater than 90% purity) and nonadherent eosinophil-rich (greater than 70% purity) cell fractions of the disaggregated granulomas. Collagenase levels were approximately two times higher in granuloma extracts and explant culture supernates of the vigorous as compared with the immunoregulated lesions. However, macrophages and eosinophil-rich cells derived from either type of granuloma secreted similar enzyme levels. Elastase and NP levels in granuloma extracts and secretions of adherent macrophage and eosinophil-rich cell populations were the same in vigorous or immunomodulated lesions but were significantly greater in vigorous granuloma culture supernates. In addition to active collagenase, trypsin activatable latent collagenase was also present in both types of granuloma extracts, explants and eosinophil-rich cell culture supernates. Latent elastase was also detected in granuloma extracts or explant supernates but was absent from secretions of granuloma cells. These results suggest that the presence of active neutral proteases within granulomas may play an important role in the regulation of tissue repair and remodeling during the fibrotic process.
Full text
PDF


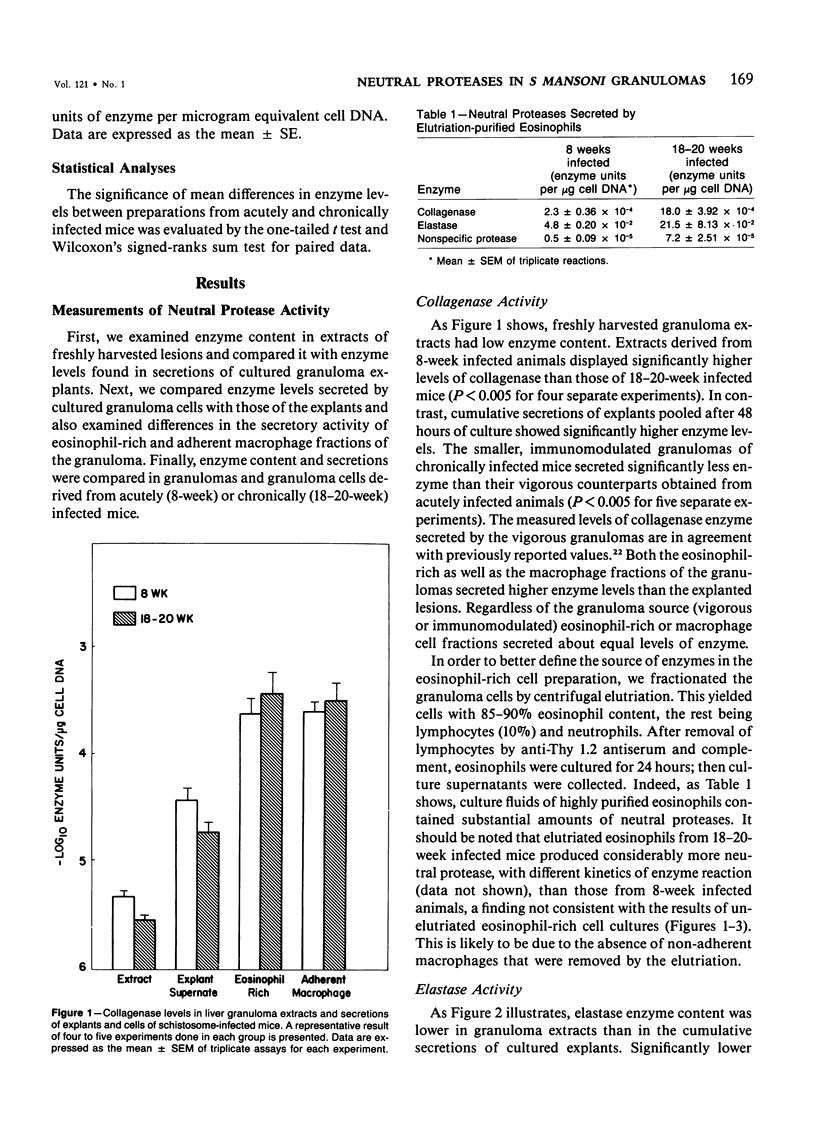
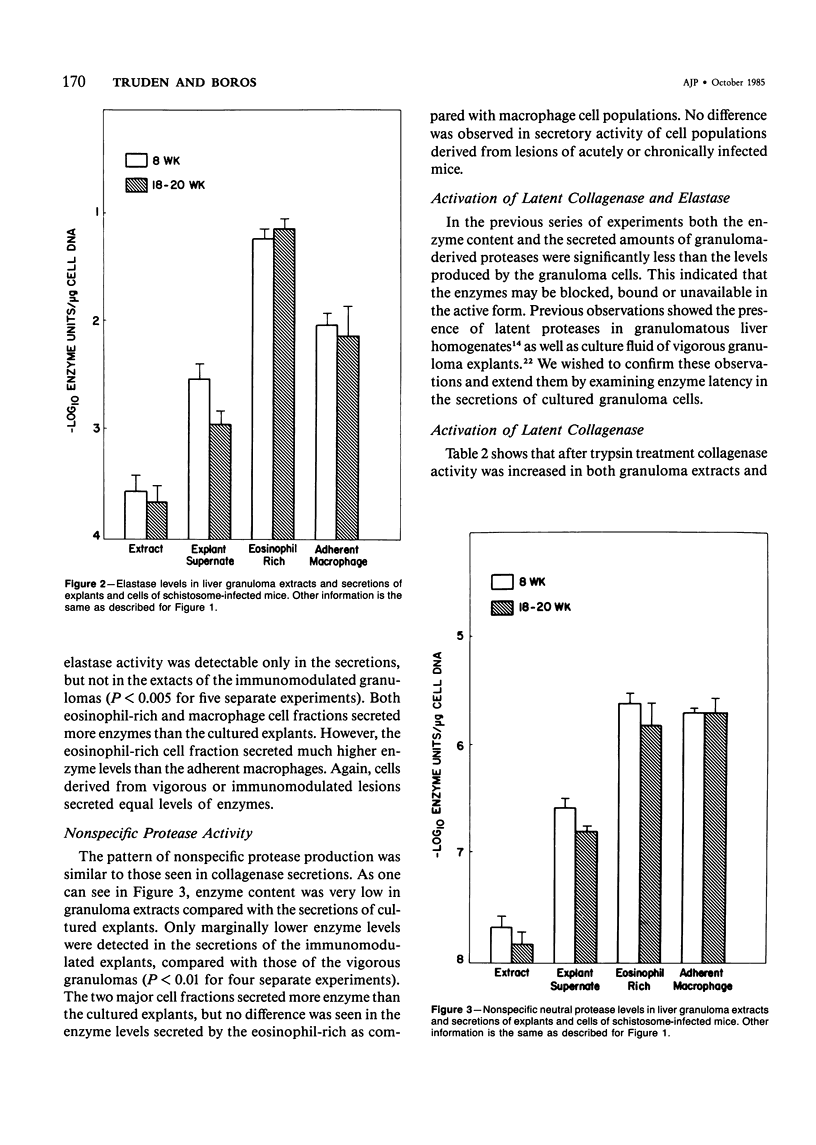
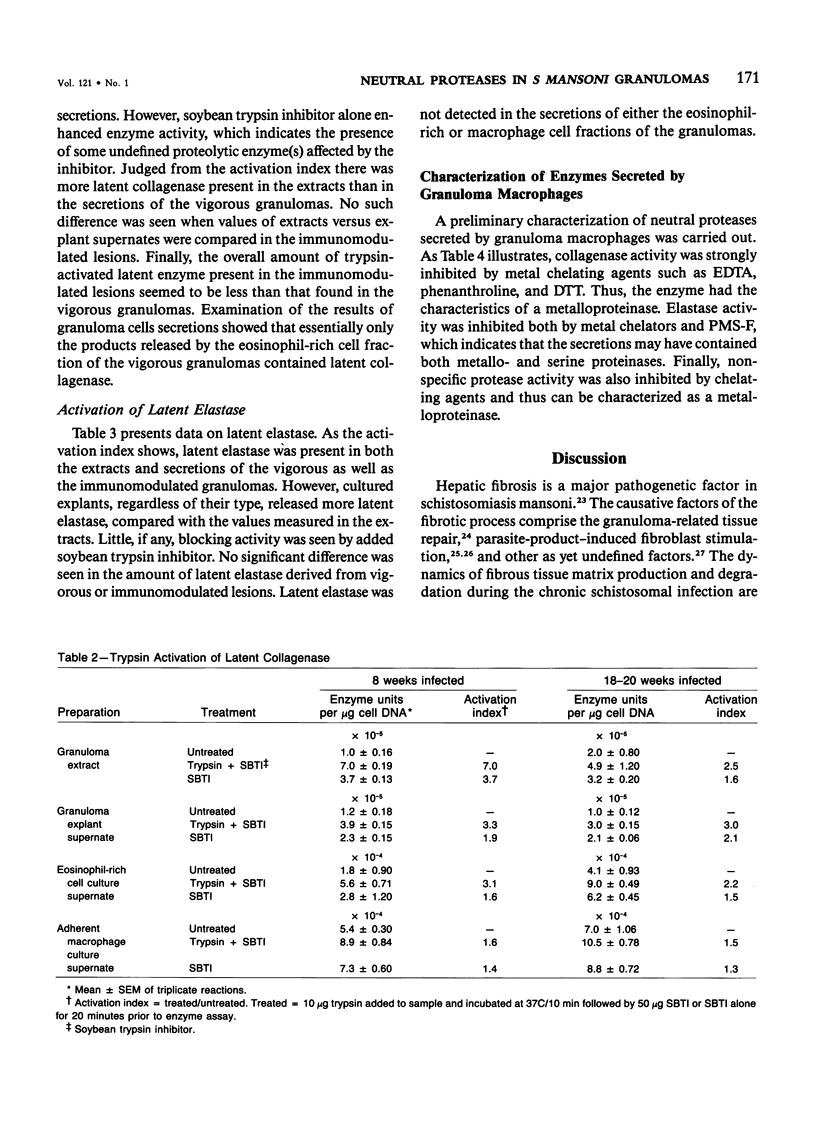



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRADE Z. A. WARREN KS: MILD PROLONGED SCHISTOSOMIASIS IN MICE: ALTERATIONS IN HOST RESPONSE WITH TIME AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF PORTAL FIBROSIS. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1964 Jan;58:53–57. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(64)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade Z. A. Hepatic Schistosomiasis. Morphological aspects. Prog Liver Dis. 1965;2:228–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banda M. J., Werb Z. Mouse macrophage elastase. Purification and characterization as a metalloproteinase. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):589–605. doi: 10.1042/bj1930589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett E. G., Baker J. R., BAKER P. A., MYERS D. B. Comparison of collagenase activity in eosinophil and neutrophil fractions from rat peritoneal exudates. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1976 Oct;54(5):459–465. doi: 10.1038/icb.1976.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biempica L., Dunn M. A., Kamel I. A., Kamel R., Hait P. K., Fleischner C., Biempica S. L., Wu C. H., Rojkind M. Liver collagen-type characterization in human schistosomiasis. A histological, ultrastructural, and immunocytochemical correlation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Mar;32(2):316–325. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biempica L., Takahashi S., Biempica S., Kobayashi M. Immunohistochemical localization of collagenase in hepatic murine schistosomiasis. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Apr;31(4):488–494. doi: 10.1177/31.4.6298308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H., Cobb C. M., Taylor R. E., Fullmer H. M. Synthesis and release of procollagenase by cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3162–3168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonney R. J., Gery I., Lin T. Y., Meyenhofer M. F., Acevedo W., Davies P. Mononuclear phagocytes from carrageenan-induce granulomas. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):261–275. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Lande M. A. Induction of collagen synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts by live Schistosoma mansoni eggs and soluble egg antigens (SEA). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jan;32(1):78–82. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Pelley R. P., Warren K. S. Spontaneous modulation of granulomatous hypersensitivity in schistosomiasis mansoni. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1437–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S. Delayed hypersensitivity-type granuloma formation and dermal reaction induced and elicited by a soluble factor isolated from Schistosoma mansoni eggs. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):488–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Kunkel S. L., Higashi G. I., Ward P. A., Boros D. L. Production of superoxide anion, prostaglandins, and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids by macrophages from hypersensitivity-type (Schistosoma mansoni egg) and foreign body-type granulomas. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1116–1125. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1116-1125.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G. Immune responses to a soluble schistosomal egg antigen preparation during chronic primary infection with Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlgren M. E., Davies P., Bonney R. J. Phorbol myristate acetate induces the secretion of an elastase by populations of resident and elicited mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 3;630(3):338–351. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90282-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessau W., Adelmann B. C., Timpl R. Identification of the sites in collagen alpha-chains that bind serum anti-gelatin factor (cold-insoluble globulin). Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):55–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1690055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. A., Kamel R. Hepatic schistosomiasis. Hepatology. 1981 Nov-Dec;1(6):653–661. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. A., Kamel R., Kamel I. A., Biempica L., Kholy A. E., Hait P. K., Rojkind M., Warren K. S., Mahmoud A. A. Liver collagen synthesis in schistosomiasis mansoni. Gastroenterology. 1979 May;76(5 Pt 1):978–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. A., Rojkind M., Warren K. S., Hait P. K., Rifas L., Seifter S. Liver collagen synthesis in murine schistosomiasis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;59(4):666–674. doi: 10.1172/JCI108685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott D. E., Boros D. L. Schistosome egg antigen(s) presentation and regulatory activity by macrophages isolated from vigorous or immunomodulated liver granulomas of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1506–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. L., Fukuyama K., Danno K., Kwan-Wong E. Granulomatous inflammation in normal and athymic mice infected with schistosoma mansoni: an ultrastructural study. J Pathol. 1979 Apr;127(4):207–215. doi: 10.1002/path.1711270408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. S., Mainardi C. L., Kang A. H. Type-specific collagen degradation by eosinophils. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):621–624. doi: 10.1042/bj2070621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Garrett K. C., Richerson H. B., Fantone J. C., Ward P. A., Rennard S. I., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Pathogenesis of the granulomatous lung diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Sep;130(3):476–496. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.3.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaki S., Goldstein S. M., Fukuyama K., Epstein W. L. Fibrin deposition and clearance in chronic granulomatous inflammation: correlation with T-cell function and proteinase inhibitor activity in tissue. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Dec;73(6):561–565. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12541600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveless S. E., Wellhausen S. R., Boros D. L., Heppner G. H. Tumoricidal macrophages isolated from liver granulomas of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):284–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren D. J., Boros D. L. Schistosoma mansoni: schistosomulicidal activity of macrophages isolated from liver granulomas of infected mice. Exp Parasitol. 1983 Dec;56(3):346–357. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(83)90080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. L., Grove D. I., Warren K. S. The Schistosoma mansoni egg granuloma: quantitation of cell populations. J Pathol. 1977 Jan;121(1):41–50. doi: 10.1002/path.1711210107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Cheever A. W., Ottesen E. A., Cook J. A. Schistosome infections in humans: perspectives and recent findings. NIH conference. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Nov;97(5):740–754. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-5-740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto M., Dannenberg A. M., Jr, Wahl L. M., Ettinger W. H., Jr, Hastie A. T., Daniels D. C., Thomas C. R., Demoulin-Brahy L. Extracellular hydrolytic enzymes of rabbit dermal tuberculous lesions and tuberculin reactions collected in skin chambers. Am J Pathol. 1978 Mar;90(3):583–607. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Dunn M. A., Seifter S. Liver collagenase in murine schistosomiasis. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jun;78(6):1425–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Simpser E. Granuloma collagenase and EDTA-sensitive neutral protease production in hepatic murine schistosomiasis. Hepatology. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):211–220. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S. Hepatosplenic schistosomiasis: a great neglected disease of the liver. Gut. 1978 Jun;19(6):572–577. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.6.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S. The secret of the immunopathogenesis of schistosomiasis: in vivo models. Immunol Rev. 1982;61:189–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock J. V., Boros D. L. Organ-dependent differences in composition and function observed in hepatic and intestinal granulomas isolated from mice with Schistosomiasis mansoni. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):418–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock J. V., Ehrinpreis M. N., Boros D. L., Gee J. B. Effect of SQ 14225, an inhibitor of angiotensin I-converting enzyme, on the granulomatous response to Schistosoma mansoni eggs in mice. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):931–936. doi: 10.1172/JCI110142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellhausen S. R., Boros D. L. Comparison of Fc, C3 receptors and Ia antigens on the inflammatory macrophage isolated from vigorous or immunomodulated liver granulomas of schistosome-infected mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Sep;30(3):191–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T., Williams W. J. Granulomatous inflammation--a review. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jul;36(7):723–733. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.7.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler D. J., Tracy J. W. Direct and indirect effects of soluble extracts of Schistosoma mansoni eggs on fibroblast proliferation in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):103–108. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.103-108.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler D. J., Wahl S. M., Wahl L. M. Hepatic fibrosis in schistosomiasis: egg granulomas secrete fibroblast stimulating factor in vitro. Science. 1978 Oct 27;202(4366):438–440. doi: 10.1126/science.705337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


