Abstract
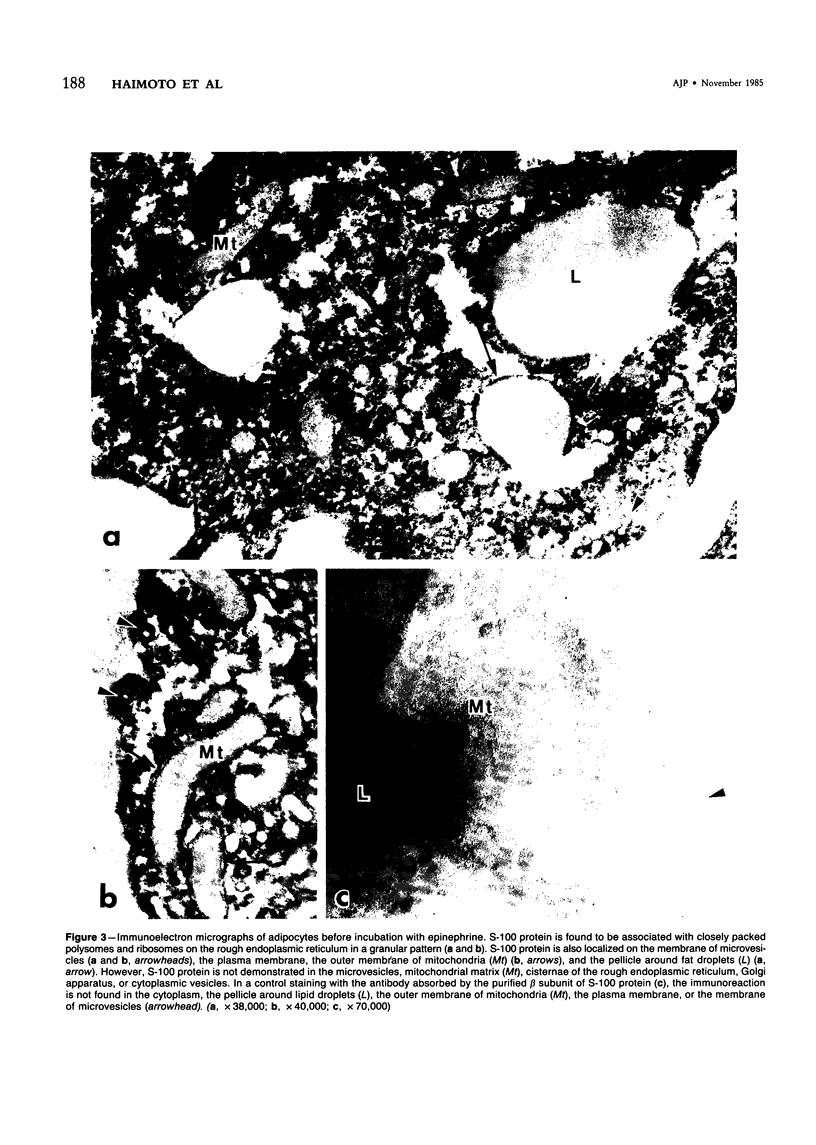
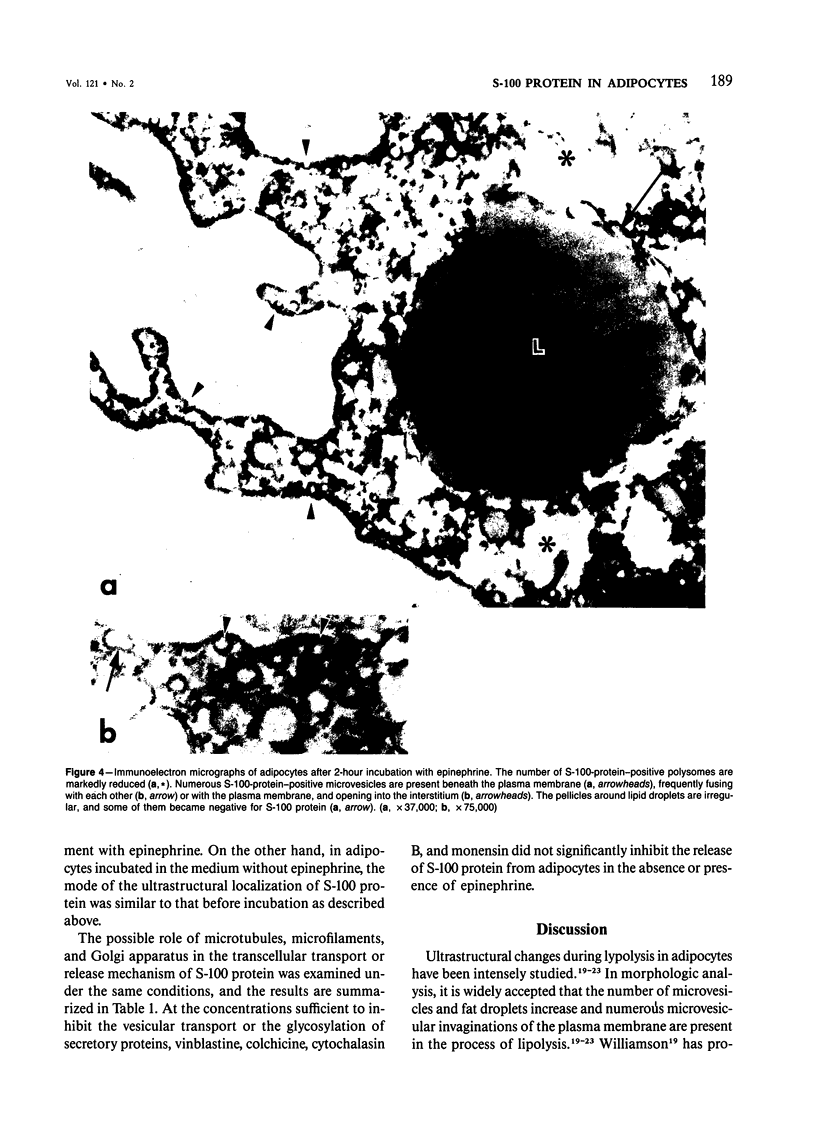
To elucidate the changes of ultrastructural localization of S-100 protein during lipolysis in adipocytes, an immunoelectron-microscopic study was performed. Epididymal fat pads from Wistar rats were incubated in the buffer with or without 10 microM epinephrine. Before incubation with epinephrine, S-100 protein was found to be associated with closely packed polysomes, the membrane of microvesicles, plasma membranes, the outer membrane of mitochondria, and the pellicle around fat droplets. In the epinephrine-treated tissues, however, S-100 protein-positive polysomes decreased drastically. S-100 protein-positive microvesicles increased in number, lined up below the plasma membranes, and fused with the plasma membrane, frequently opening into the interstitium. These microvesicles were also found around the lipid droplets. These findings, together with those of a previous report on ultrastructural changes of adipocytes during lipolysis, suggest that S-100 protein molecules interact with free fatty acids (FFAs) on their hydrophobic portions on the membrane of microvesicle and then are translocated through the cytoplasm and discharged from the surface of plasma membranes with FFAs into the interstitium. That is, S-100 protein might serve as one of carrier proteins of FFAs in adipocytes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calissano P., Alemà S., Fasella P. Interaction of S-100 protein with cations and liposomes. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 22;13(22):4553–4560. doi: 10.1021/bi00719a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Perrelet A., Orci L. Effects of insulin, glucagon, and epinephrine on the plasma membrane of the white adipose cell: a freeze-fracture study. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jul;17(4):335–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J., Perrelet A., Orci L. Morphological changes of the adipose cell plasma membrane during lipolysis. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jan;72(1):104–117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARLAND P. B., RANDLE P. J. A rapid enzymatic assay for glycerol. Nature. 1962 Dec 8;196:987–988. doi: 10.1038/196987a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglid K. G., Stavrou D. Water-soluble and pentanol-extractable proteins in human brain normal tissue and human brain tumours, with special reference to S-100 protein. J Neurochem. 1973 Jun;20(6):1523–1532. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimoto H., Nagura H., Imaizumi M., Watanabe K., Iijima S. Immunoelectronmicroscopic study on the transport of secretory IgA in the lower respiratory tract and alveoli. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1984;404(4):369–380. doi: 10.1007/BF00695221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hydén H., McEwen B. A glial protein specific for the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):354–358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe T., Okuyama T. The amino-acid sequence of S-100 protein (PAP I-b protein) and its relation to the calcium-binding proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 1;89(2):379–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Kimura S., Semba R., Suzuki F., Nakajima T. Increase in S-100 protein levels in blood plasma by epinephrine. J Biochem. 1983 Sep;94(3):1009–1011. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Suzuki F., Nakajima T. Decrease in adipose S-100 protein levels by epinephrine in rat. J Biochem. 1983 Jan;93(1):311–313. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Suzuki F., Nakajima T. S-100 protein in adipose tissue. Int J Biochem. 1983;15(5):609–613. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(83)90183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Hashimoto K., Saraste J., Virtanen I., Penttinen K. Monensin and FCCP inhibit the intracellular transport of alphavirus membrane glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):783–791. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michetti F., Dell'Anna E., Tiberio G., Cocchia D. Immunochemical and immunocytochemical study of S-100 protein in rat adipocytes. Brain Res. 1983 Mar 7;262(2):352–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Toyosato M., Yabumoto S., Tanimizu I., Hirakawa H. A new enzymatic method for colorimetric determination of free fatty acids. Anal Biochem. 1980 Oct;108(1):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90686-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy S. K. Microscopic studies of the effect of epinephrine on the isolated fat cells of the rat epididymal fat pads. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Apr;46(1):155–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90417-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Yoshida T., Hamaguchi M., Nagura H., Hasegawa H., Yoshimura S., Watanabe K. Subcellular location of the major protein antigens of paramyxoviruses revealed by immunoperoxidase cytochemistry. Microbiol Immunol. 1983;27(6):531–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1983.tb00614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Jarett L. Surface structure changes of rat adipocytes during lipolysis stimulated by various lipolytic agents. A scanning electron microscopic study. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):57–65. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki F., Kato K., Nakajima T. Enhancement of adipose S-100 protein release by catecholamines. J Biochem. 1983 Nov;94(5):1707–1710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki F., Kato K., Nakajima T. Hormonal regulation of adipose S-100 protein release. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1336–1341. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki F., Kato K., Nakajima T. Regulation of nervous system-specific S-100 protein and enolase levels in adipose tissue by catecholamines. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):130–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON J. R. ADIPOSE TISSUE. MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES ASSOCIATED WITH LIPID MOBILIZATION. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jan;20:57–74. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Spooner B. S., Ash J. F., Bradley M. O., Luduena M. A., Taylor E. L., Wrenn J. T., Yamada K. Microfilaments in cellular and developmental processes. Science. 1971 Jan 15;171(3967):135–143. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3967.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitake S., Imagawa M., Ishikawa E., Niitsu Y., Urushizaki I., Nishiura M., Kanazawa R., Kurosaki H., Tachibana S., Nakazawa N. Mild and efficient conjugation of rabbit Fab' and horseradish peroxidase using a maleimide compound and its use for enzyme immunoassay. J Biochem. 1982 Nov;92(5):1413–1424. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]