Abstract
Acute lung injury has been produced in mice by the intravenous injection of cobra venom factor. The marked attenuation of lung injury in C5-deficient mice indicates an absolute requirement for C5 in the development of lung injury. Similar studies carried out in beige mice suggest that leukocytic proteinases play, at best, a limited role in the injury. Neutrophil or platelet depletion resulted in a marked reduction in the extent of lung injury, suggesting that both platelets as well as neutrophils contribute to the injury. Treatment of mice with catalase provided a marked degree of protection from the lung injury, while treatment with superoxide dismutase produced limited protection, which suggests that H2O2 or its derivatives are involved in the induction of acute lung injury. By the use of transmission electron microscopy, areas of lung vascular injury, as manifested by extensive blebbing of endothelial cells, were associated with intravascular aggregates of platelets, neutrophils, and fibrin. Finally, lipoxygenase and thromboxane synthetase inhibitors afforded some protection against cobra venom factor-induced acute lung injury, while cyclooxygenase inhibitors gave variable results. These data suggest that acute lung injury in mice following systemic activation of complement has an absolute requirement for C5, is dependent on a role of both neutrophils as well as platelets, and can be linked to the generation of toxic oxygen products by neutrophils.
Full text
PDF

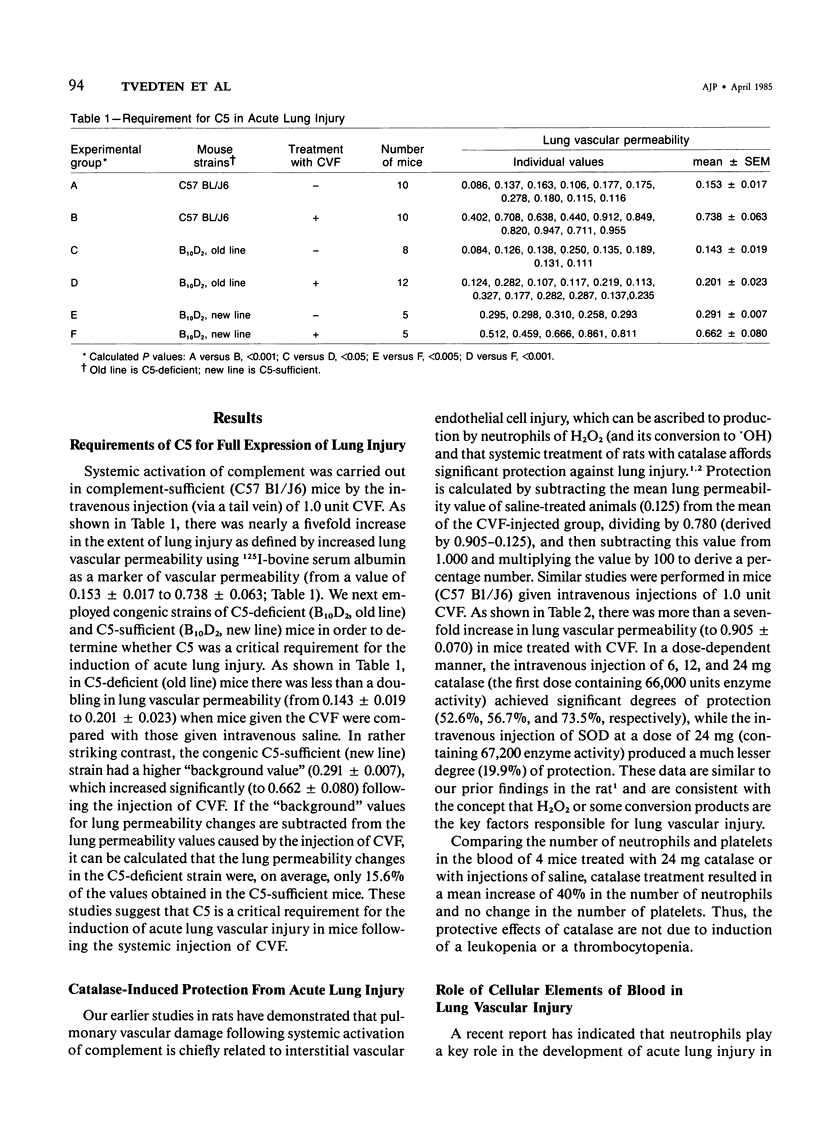
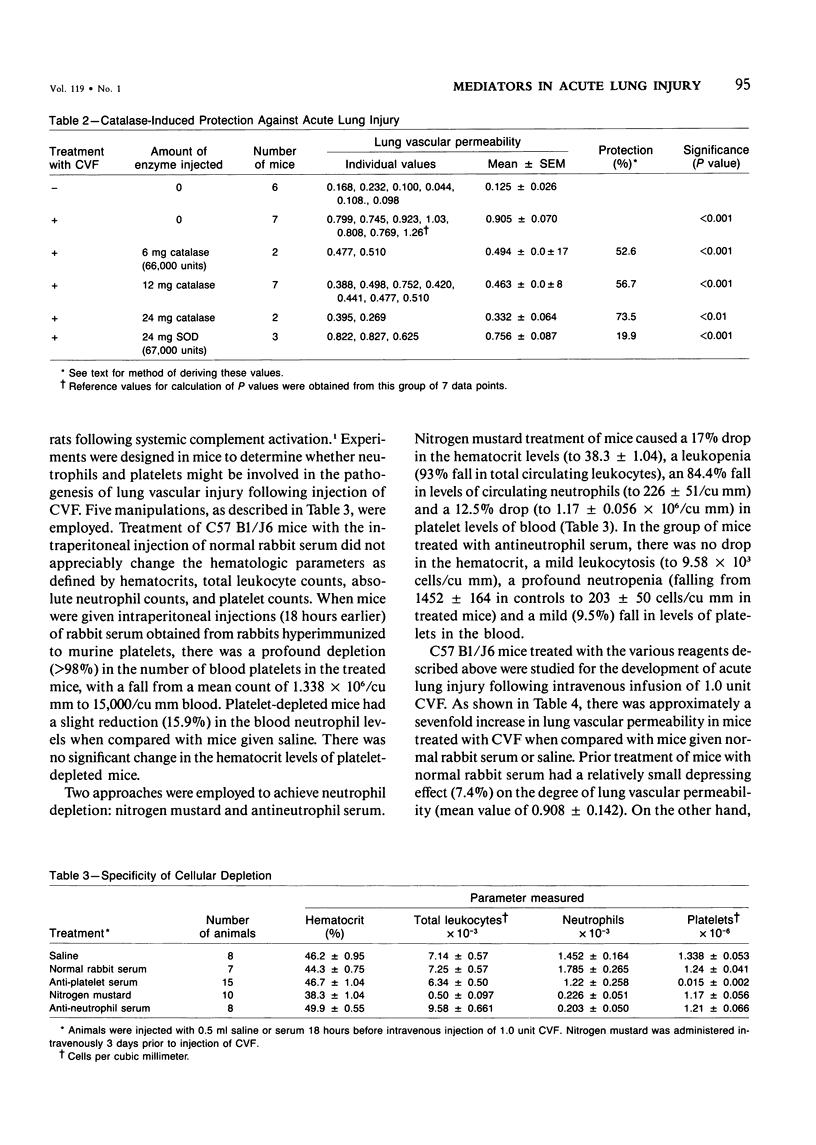
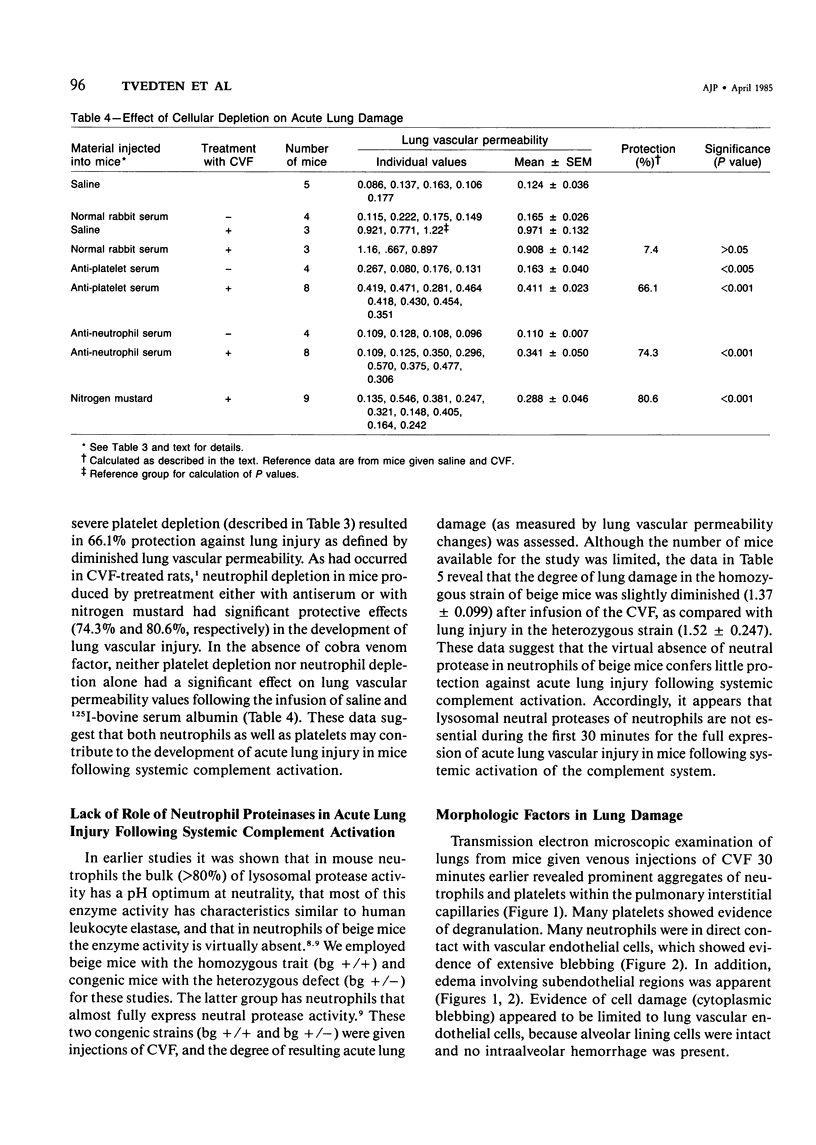

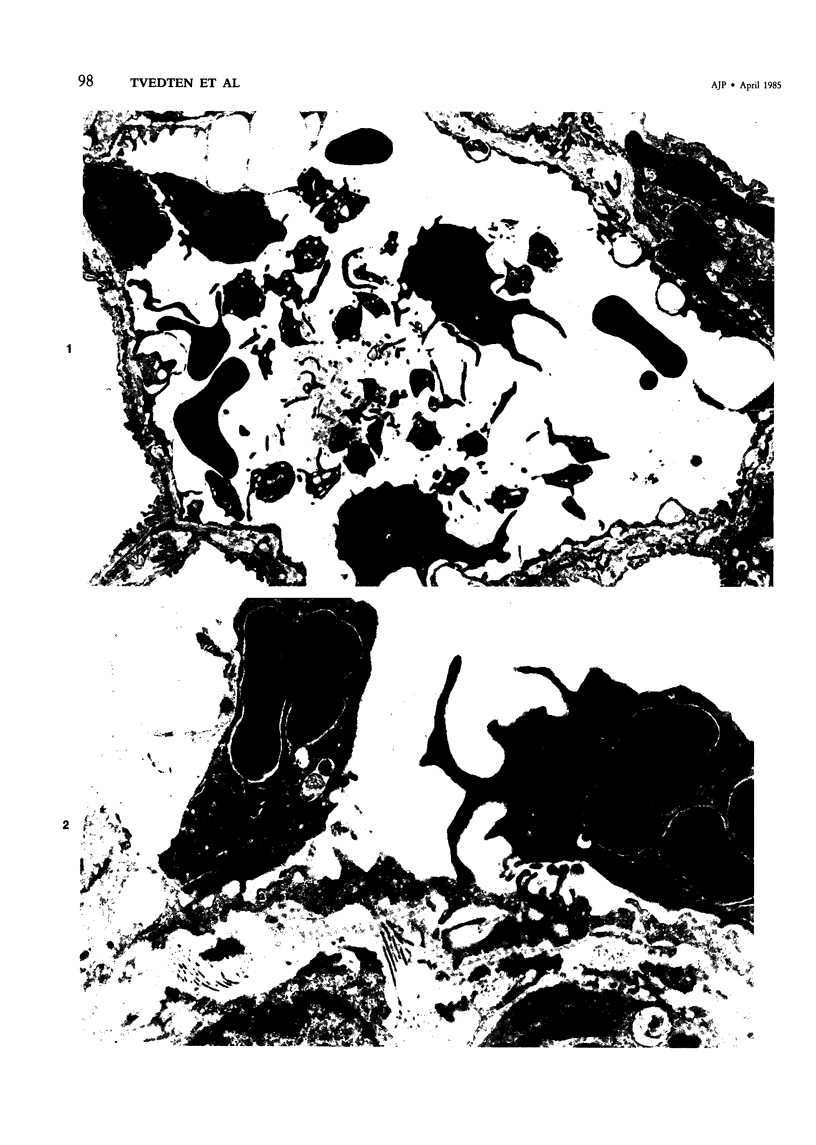
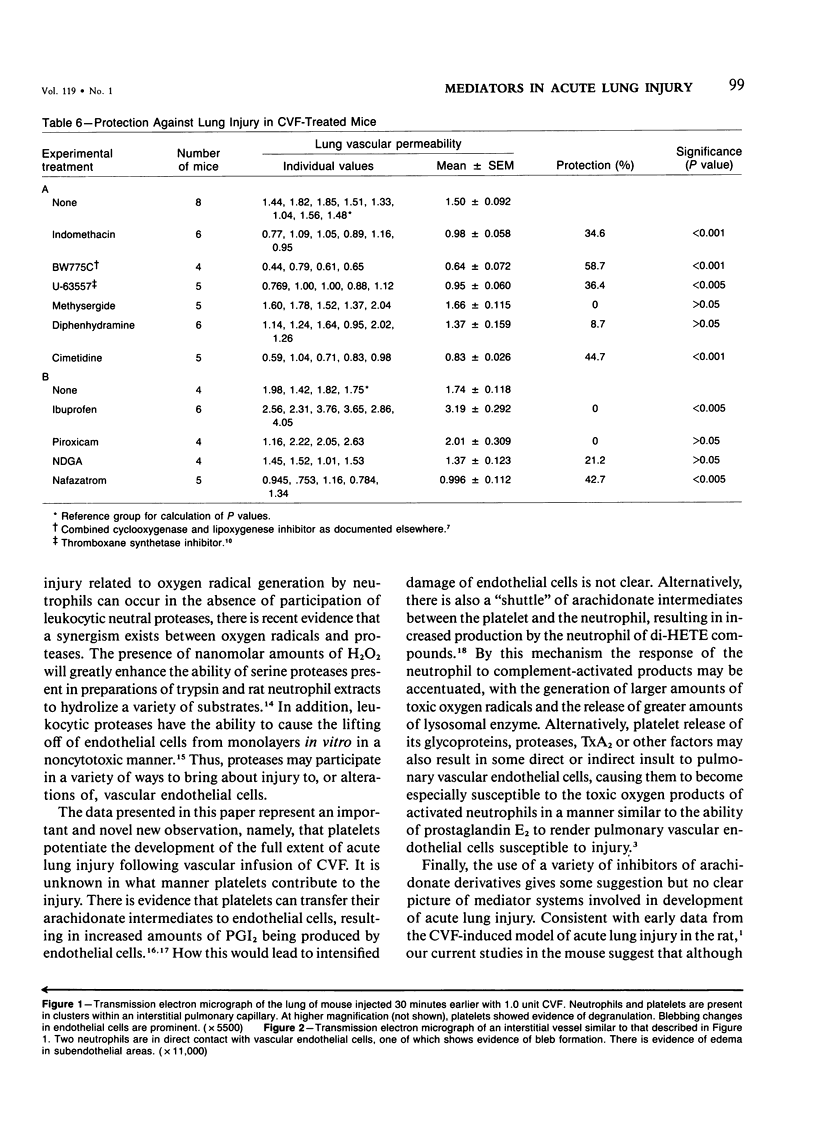

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fligiel S. E., Lee E. C., McCoy J. P., Johnson K. J., Varani J. Protein degradation following treatment with hydrogen peroxide. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jun;115(3):418–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fligiel S. E., Ward P. A., Johnson K. J., Till G. O. Evidence for a role of hydroxyl radical in immune-complex-induced vasculitis. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jun;115(3):375–382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Killen P. D., Harker L. A., Striker G. E., Wright D. G. Neutrophil-mediated endothelial injury in vitro mechanisms of cell detachment. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1394–1403. doi: 10.1172/JCI110390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Larsen G. L., Webster R. O., Mitchell B. C., Goins A. J., Henson J. E. Pulmonary microvascular alterations and injury induced by complement fragments: synergistic effect of complement activation, neutrophil sequestration, and prostaglandins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;384:287–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb21379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn D. C., Meyers A. J., Gherini S. T., Beckmann A., Markison R. E., Churg A. M. Production of acute pulmonary injury by leukocytes and activated complement. Surgery. 1980 Jul;88(1):48–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Varani J., Oliver J., Ward P. A. Immunologic vasculitis in beige mice with deficiency of leukocytic neutral protease. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1807–1811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Mouton C., Higashi G. I. Role of lipoxygenase products in murine pulmonary granuloma formation. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):514–524. doi: 10.1172/JCI111449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Broekman M. J., Safier L. B., Ullman H. L., Islam N., Sherhan C. N., Rutherford L. E., Korchak H. M., Weissmann G. Formation of leukotrienes and other hydroxy acids during platelet-neutrophil interactions in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Weksler B. B., Jaffe E. A., Broekman M. J. Synthesis of prostacyclin from platelet-derived endoperoxides by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):979–986. doi: 10.1172/JCI109967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Bryan B., Wyche A., Bronson S. D., Eakins K., Ferrendelli J. A., Minkes M. Thromboxane synthetase inhibitors as pharmacological tools: differential biochemical and biological effects on platelet suspensions. Prostaglandins. 1977 Nov;14(5):897–907. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer A. I., Crawford D. D., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Unidirectional transfer of prostaglandin endoperoxides between platelets and endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1105–1112. doi: 10.1172/JCI111296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schraufstätter I. U., Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G. Proteases and oxidants in experimental pulmonary inflammatory injury. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1175–1184. doi: 10.1172/JCI111303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spagnuolo P. J., Ellner J. J., Hassid A., Dunn M. J. Thromboxane A2 mediates augmented polymorphonuclear leukocyte adhesiveness. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):406–414. doi: 10.1172/JCI109870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G. O., Johnson K. J., Kunkel R., Ward P. A. Intravascular activation of complement and acute lung injury. Dependency on neutrophils and toxic oxygen metabolites. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1126–1135. doi: 10.1172/JCI110548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Granelli-Piperno A., Griscelli C., Reich E. Specific protease deficiency in polymorphonuclear leukocytes of Chédiak-Higashi syndrome and beige mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1285–1290. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Sulavik M. C., Johnson K. J. Rat neutrophil activation and effects of lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Am J Pathol. 1984 Aug;116(2):223–233. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Till G. O., Kunkel R., Beauchamp C. Evidence for role of hydroxyl radical in complement and neutrophil-dependent tissue injury. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):789–801. doi: 10.1172/JCI111050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]