Abstract
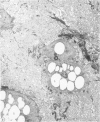
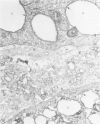
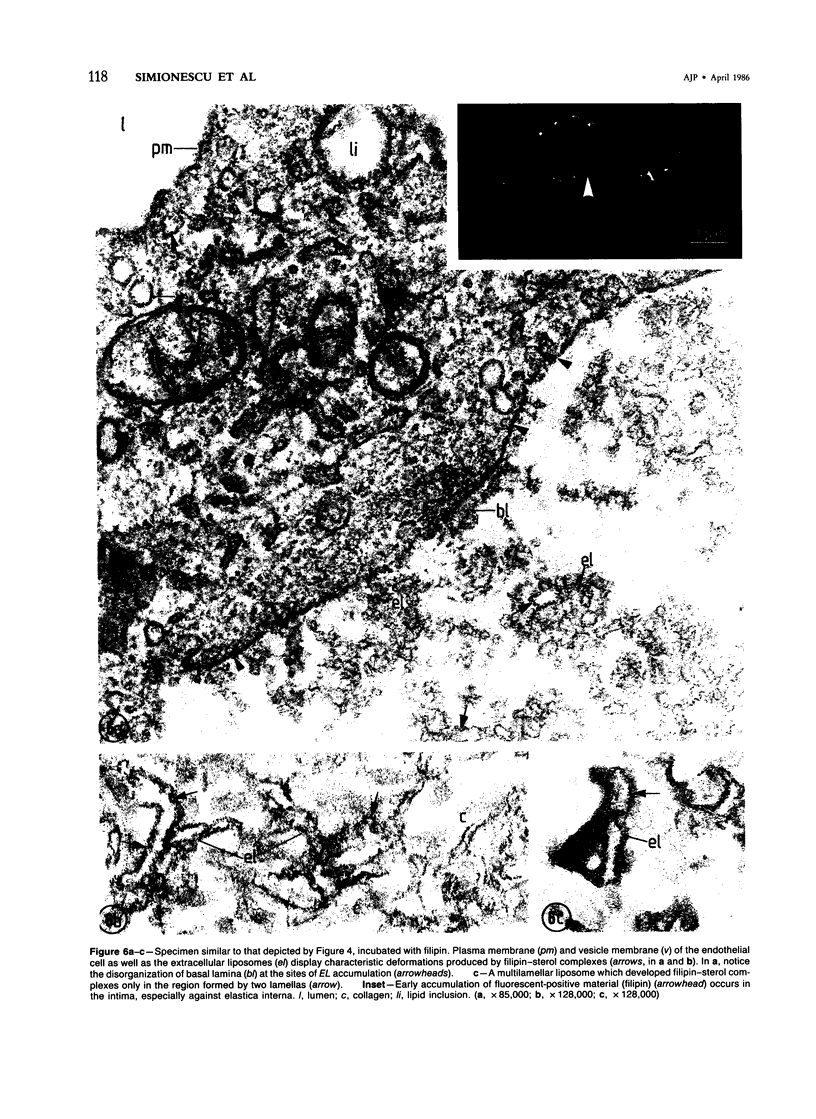
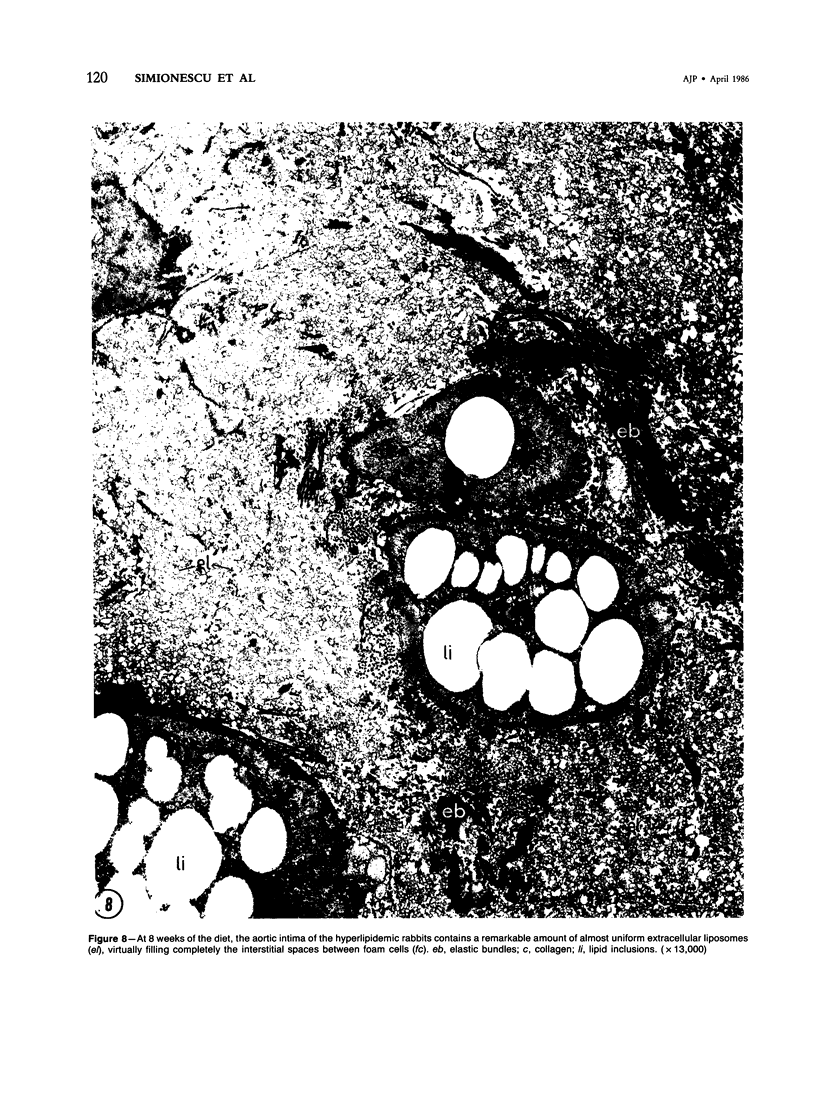
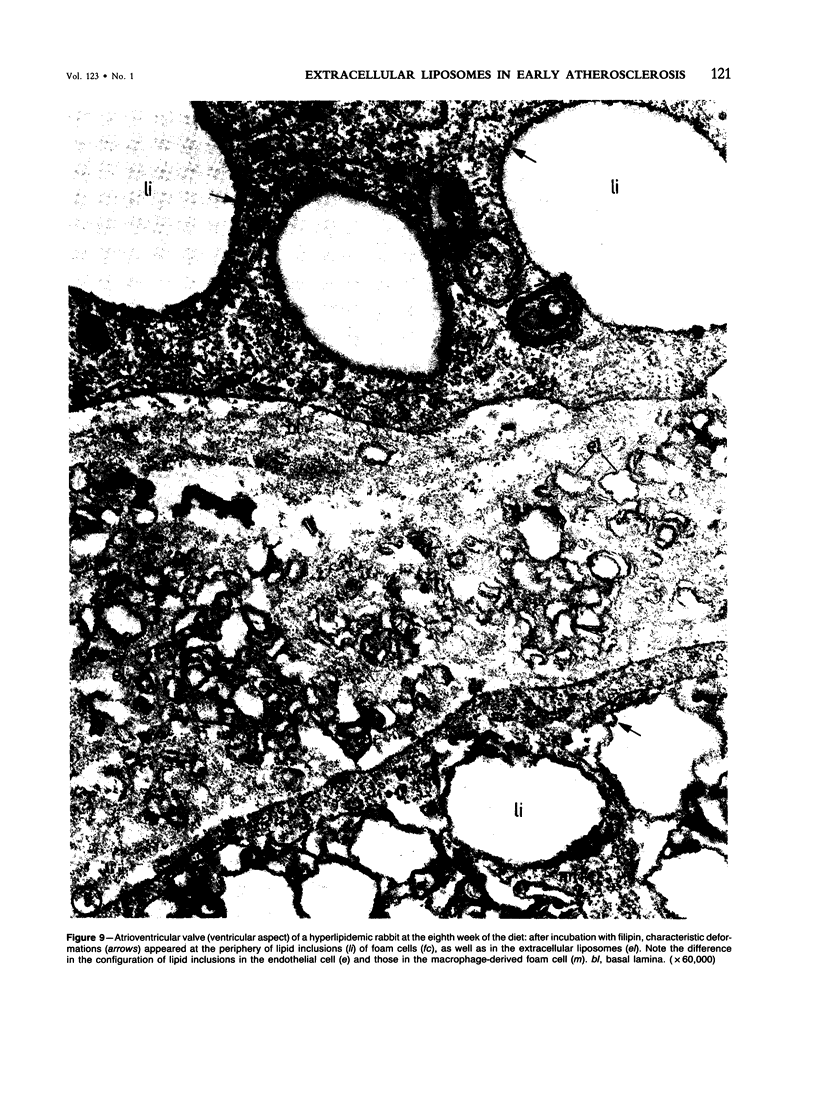
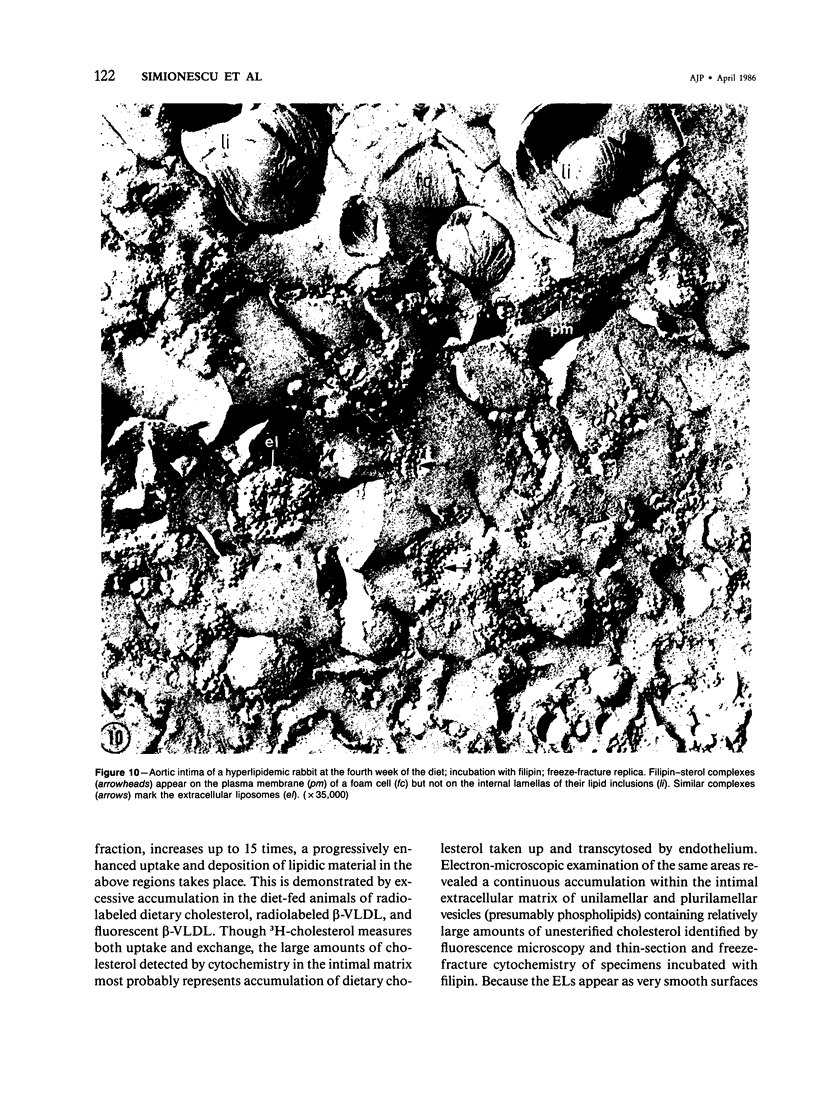
Biochemical, physiologic, and ultrastructural modifications which appear in the aortic intima and atrioventricular valves before monocyte diapedesis and foam cell formation were investigated in rabbits fed a cholesterol-rich diet. In the first 2 weeks of the diet, while plasma beta-VLDL cholesterol was increased up to 15-fold, the intima showed an enhanced uptake and deposition of dietary 3H-cholesterol, 125I-beta-VLDL, and the fluorescent beta-VLDL-1,1'-dioctadecyl-3,3,3',3'-tetramethylindocarbocyanine conjugate. beta-VLDL-gold complex perfused in situ was transcytosed across endothelium by plasmalemmal vesicles. Concomitantly, within the intima, a progressive accumulation of extracellular densely packed uni- or multilamellar vesicles took place. These commonly occurred in cell-free subendothelial spaces and were not associated with any sign of cytolysis. In freeze-fracture preparations, these vesicles appeared as smooth surfaces, suggesting the absence of translamellar proteins. Upon incubation with filipin, these extracellular liposomes (EL) displayed characteristic approximately 20 nm filipin-sterol complexes, revealing the presence of preparations unesterified cholesterol in the phospholipid lamellas. EL deposition was paralleled by proliferation of basal lamina-like material, microfibrils, and proteoglycans, and continued to increase during foam cell formation. For the entire period of our experiments, the endothelium was morphologically intact, and no platelet involvement was detected. The results show that an early prelesional ultrastructural change in lesion-prone aortic and valvular areas is the accumulation of extracellular phospholipid liposomes rich in unesterified cholesterol.
Full text
PDF



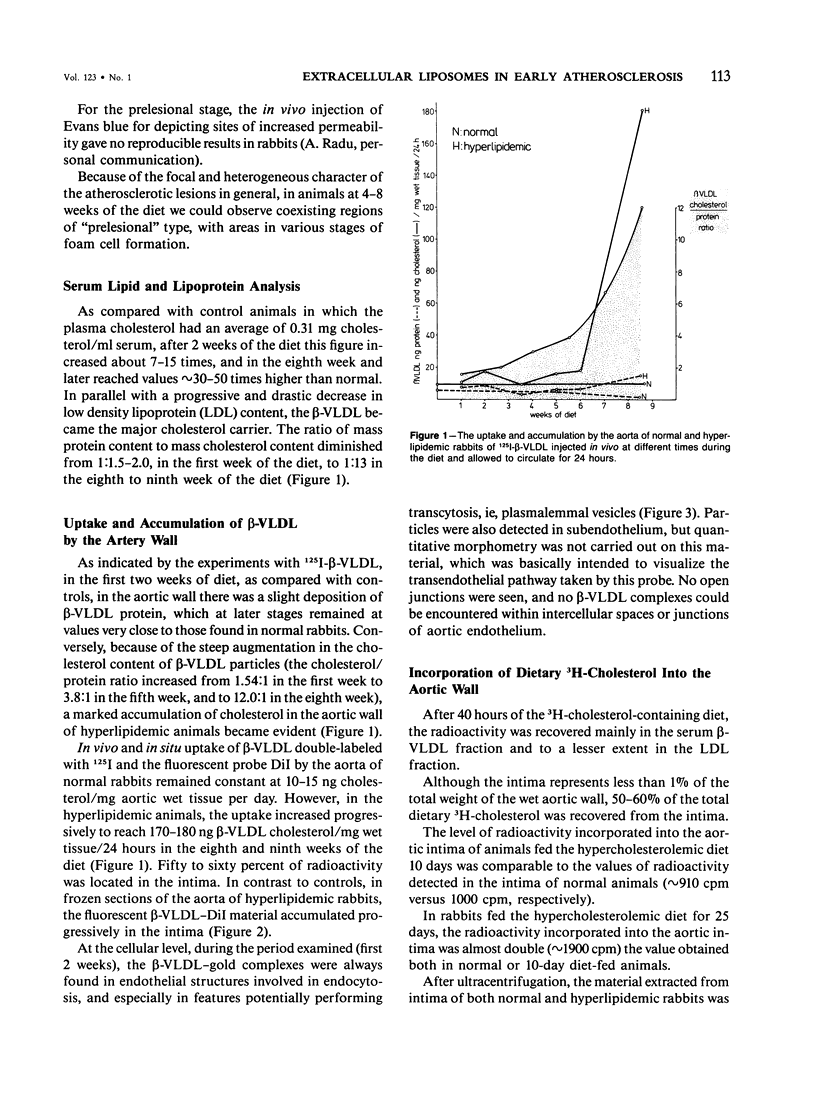
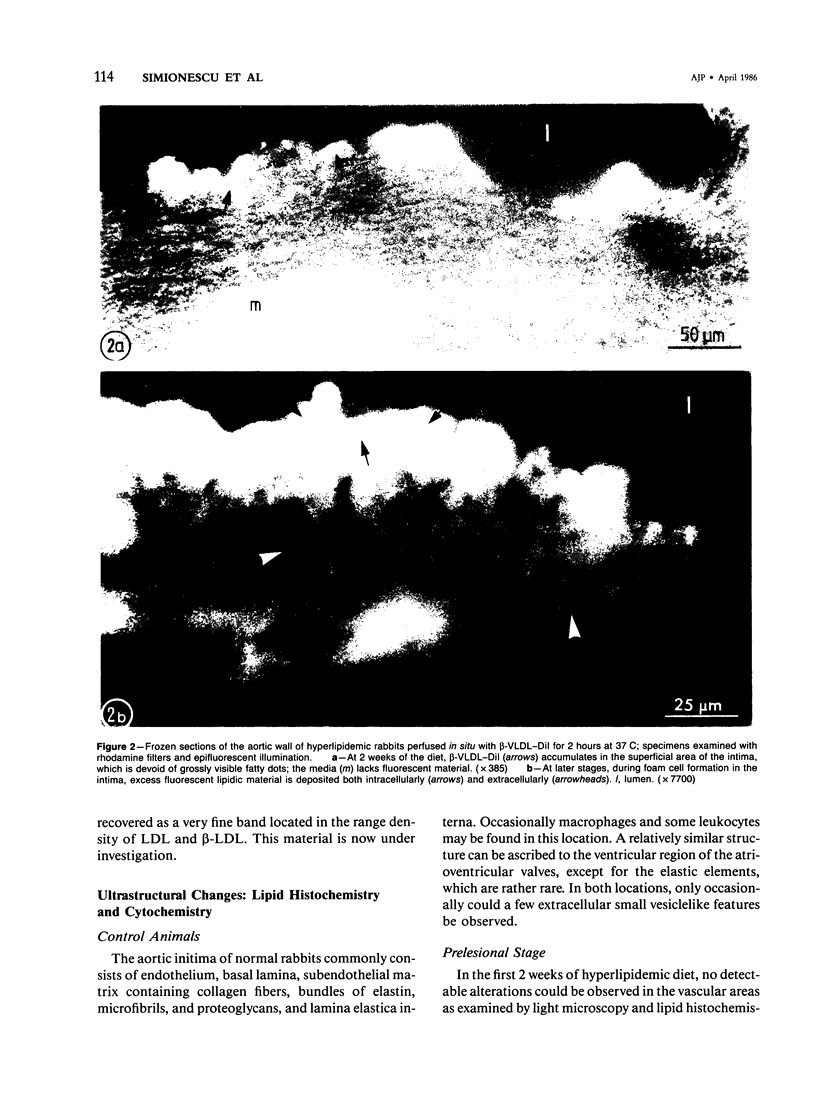
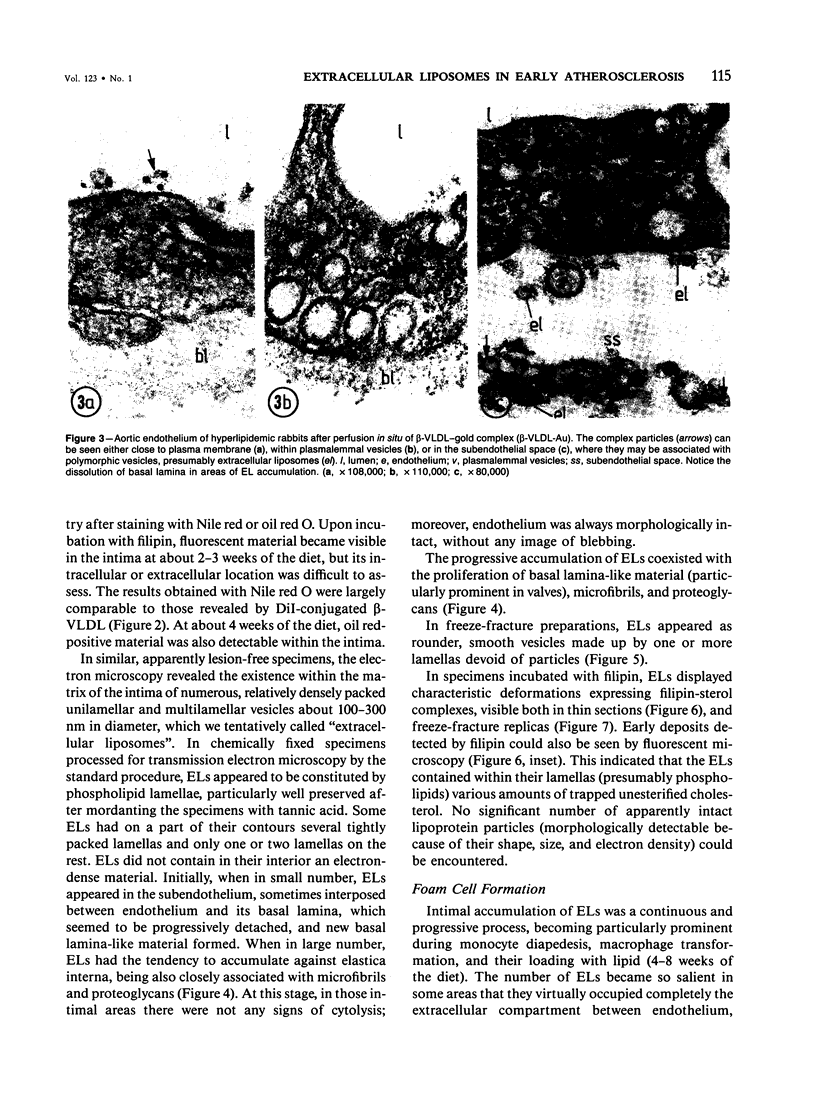
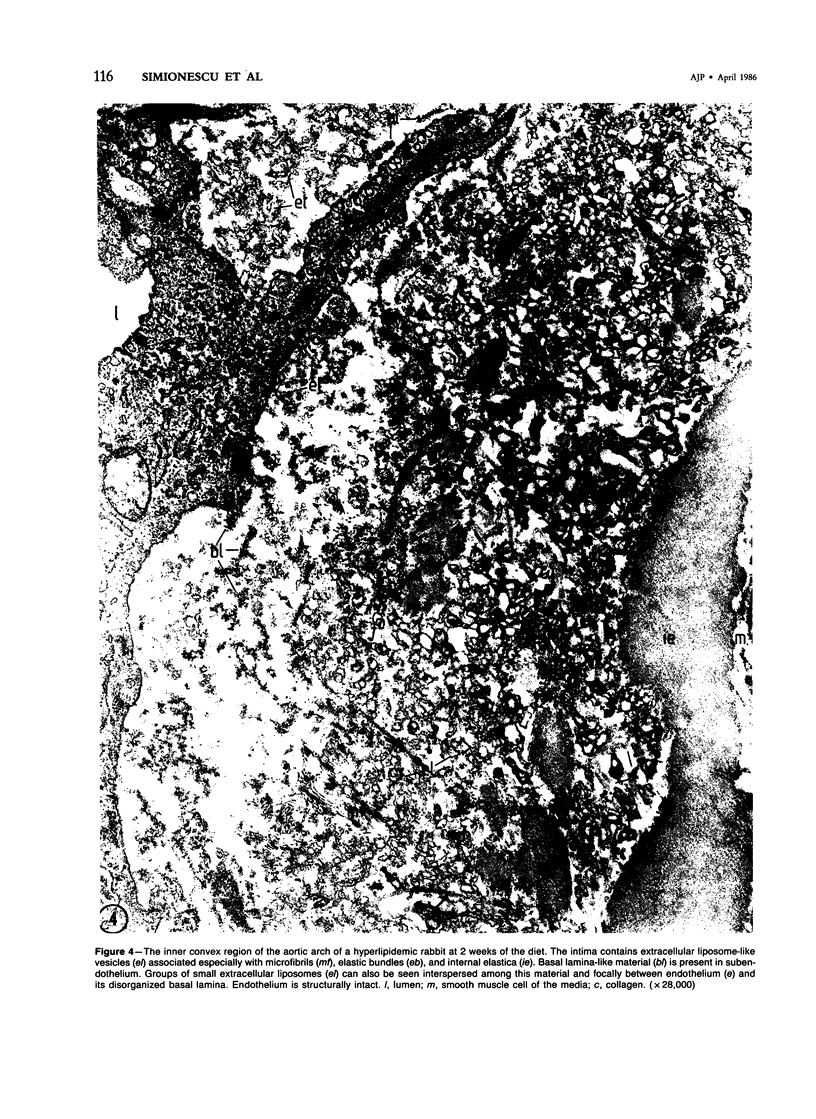





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS C. W., BAYLISS O. B., IBRAHIM M. Z. THE DISTRIBUTION OF LIPIDS AND ENZYMES IN THE AORTIC WALL IN DIETARY RABBIT ATHEROMA AND HUMAN ATHEROSCLEROSIS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:421–430. doi: 10.1002/path.1700860216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams C. W., Morgan R. S. The effect of saturated and polyunsaturated lecithins on the resorption of 4-14-C-cholesterol from subcutaneous implants. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):73–76. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell F. P., Adamson I. L., Schwartz C. J. Aortic endothelial permeability to albumin: focal and regional patterns of uptake and transmural distribution of 131I-albumin in the young pig. Exp Mol Pathol. 1974 Feb;20(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(74)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittman R., Fischkoff S. A. Fluorescence studies of the binding of the polyene antibiotics filipin 3, amphotericin B, nystatin, and lagosin to cholesterol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3795–3799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Börnig H., Geyer G. Staining of cholesterol with the fluorescent antibiotic "filipin". Acta Histochem. 1974;50(1):110–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevidence B. A., Morton R. E., West G., Dusek D. M., Hoff H. F. Cholesterol esterification in macrophages. Stimulation by lipoproteins containing apo B isolated from human aortas. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):196–207. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.3.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis H. R., Wissler R. W. Apoprotein B quantification in rhesus and cynomolgus monkey atherosclerotic lesions. Atherosclerosis. 1984 Mar;50(3):241–252. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(84)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskenasy M., Mora R., Simionescu N. In vitro study of low density lipoprotein--collagen interaction. Morphol Embryol (Bucur) 1984 Apr-Jun;30(2):147–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggiotto A., Ross R., Harker L. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. I. Changes that lead to fatty streak formation. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):323–340. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J. The origin and properties of free cholesterol potential gradients in plasma, and their relation to atherogenesis. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 15;25(13):1624–1628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florentin R. A., Nam S. C., Lee K. T., Lee K. J., Thomas W. A. Increased mitotic activity in aortas of swine after three days of cholesterol feeding. Arch Pathol. 1969 Nov;88(5):463–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Bearer E. L. beta-Hydroxysterol distribution as determined by freeze-fracture cytochemistry. Histochem J. 1981 Jul;13(4):535–546. doi: 10.1007/BF01002709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G., Schwartz C. J. Endothelial cell injury in early mild hypercholesterolemia. Prog Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;13:213–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G. The role of the monocyte in atherogenesis: I. Transition of blood-borne monocytes into foam cells in fatty lesions. Am J Pathol. 1981 May;103(2):181–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghidoni J. J., O'Neal R. M. Recent advances in molecular pathology: a review ultrastructure of human atheroma. Exp Mol Pathol. 1967 Dec;7(3):378–400. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(67)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan P., Mayer E. P., Fowler S. D. Nile red: a selective fluorescent stain for intracellular lipid droplets. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):965–973. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar D. P., Wight T. N., Smith S. C. Lipid accumulation and ultrastructural change within the aortic wall during early spontaneous atherogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1980 Sep;100(3):683–705. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Bondjers G., Bylock A., Hjalmarsson L. Ultrastructural studies on the localization of IgG in the aortic endothelium and subendothelial intima of atherosclerotic and nonatherosclerotic rabbits. Exp Mol Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(3):302–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(80)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff H. F., Gaubatz J. W. Isolation, purification, and characterization of a lipoprotein containing Apo B from the human aorta. Atherosclerosis. 1982 Apr;42(2-3):273–297. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(82)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff H. F., Heideman C. L., Gotto A. M., Jr, Gaubatz J. W. Apolipoprotein B retention in the grossly normal and atherosclerotic human aorta. Circ Res. 1977 Nov;41(5):684–690. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.5.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingerman-Wojenski C. M., Sedar A. W., Nissenbaum M., Silver M. J., Klurfeld D. M., Kritchevsky D. Early morphological changes in the endothelium of a peripheral artery of rabbits fed an atherogenic diet. Exp Mol Pathol. 1983 Feb;38(1):48–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(83)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insull W., Jr, Bartsch G. E. Cholesterol, triglyceride, and phospholipid content of intima, media, and atherosclerotic fatty streak in human thoracic aorta. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):513–523. doi: 10.1172/JCI105365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris I., Majno G. Cellular breakdown within the arterial wall. An ultrastructural study of the coronary artery in young and aging rats. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1974;364(1):111–127. doi: 10.1007/BF01230861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris I., Zand T., Nunnari J. J., Krolikowski F. J., Majno G. Studies on the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. I. Adhesion and emigration of mononuclear cells in the aorta of hypercholesterolemic rats. Am J Pathol. 1983 Dec;113(3):341–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. S., Small D. M. Isolation and and partial characterization of the lipid phases of human atherosclerotic plaques. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9753–9759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. S., Small D. M., Smith F. R., Dell R. B., Goodman D. S. Cholesterol turnover in lipid phases of human atherosclerotic plaque. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jul;23(5):733–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruth H. S. Filipin-positive, oil red O-negative particles in atherosclerotic lesions induced by cholesterol feeding. Lab Invest. 1984 Jan;50(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruth H. S., Fry D. L. Histochemical detection and differentiation of free and esterified cholesterol in swine atherosclerosis using filipin. Exp Mol Pathol. 1984 Jun;40(3):288–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(84)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruth H. S. Histochemical detection of esterified cholesterol within human atherosclerotic lesions using the fluorescent probe filipin. Atherosclerosis. 1984 May-Jun;51(2-3):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(84)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C., Taylor R. G., Jones N. D., St Clair R. W., Cornhill J. F. Endothelial surface characteristics in pigeon coronary artery atherosclerosis. I. Cellular alterations during the initial stages of dietary cholesterol challenge. Lab Invest. 1982 Feb;46(2):123–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. Cholesteryl ester synthesis in macrophages: stimulation by beta-very low density lipoproteins from cholesterol-fed animals of several species. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):970–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majno G., Joris I., Zand T. Atherosclerosis: new horizons. Hum Pathol. 1985 Jan;16(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone T., Jensen M., Chait A. Human arterial wall cells secrete factors that are chemotactic for monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5094–5097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill H. C., Jr Fatty streaks in the coronary arteries and aorta. Lab Invest. 1968 May;18(5):560–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Weinstein J. N., Mahley R. W. Acetoacetylated lipoproteins used to distinguish fibroblasts from macrophages in vitro by fluorescence microscopy. Arteriosclerosis. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):177–185. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.1.3.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. H., Connor W. E., Lin D. S., Inahara T., Porter J. M. Lipids of human atherosclerotic plaques and xanthomas: clues to the mechanism of plaque progression. J Lipid Res. 1983 Oct;24(10):1329–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G., Roberts D. C., West C. E. Separation of plasma lipoproteins by density-gradient ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):42–49. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90488-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson C. S., Wagner R. C. Differential endocytosis of lipoproteins by capillary endothelial vesicles. Microcirc Endothelium Lymphatics. 1985 Jun;2(3):313–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Bowen-Pope D., Raines E. W., Faggiotto A. Endothelial injury: blood-vessel wall interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;401:260–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. George Lyman Duff Memorial Lecture. Atherosclerosis: a problem of the biology of arterial wall cells and their interactions with blood components. Arteriosclerosis. 1981 Sep-Oct;1(5):293–311. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.1.5.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Harker L. Hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Science. 1976 Sep 17;193(4258):1094–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.822515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE M. L., ZILVERSMIT D. B., ACKERMAN R. F. Plasma phospholipide deposition and aortic phospholipide synthesis in experimental atherosclerosis. Am J Physiol. 1955 Jun;181(3):527–531. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.181.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury B. G., Falcone D. J., Minick C. R. Insoluble low-density lipoprotein-proteoglycan complexes enhance cholesteryl ester accumulation in macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jul;120(1):6–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard N., Mitchell N. The localization of proteoglycan by light and electron microscopy using safranin O. A study of epiphyseal cartilage. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Mar;54(3):451–460. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shio H., Haley N. J., Fowler S. Characterization of lipid-laden aortic cells from cholesterol-fed rabbits. III. Intracellular localization of cholesterol and cholesteryl ester. Lab Invest. 1979 Aug;41(2):160–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu N., Simionescu M. Galloylglucoses of low molecular weight as mordant in electron microscopy. I. Procedure, and evidence for mordanting effect. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):608–621. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu N., Simionescu M., Palade G. E. Permeability of intestinal capillaries. Pathway followed by dextrans and glycogens. J Cell Biol. 1972 May;53(2):365–392. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M. Cellular mechanisms for lipid deposition in atherosclerosis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1977 Oct 20;297(16):873–877. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197710202971608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Physical-chemical basis of lipid deposition in atherosclerosis. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):222–229. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. B., Staples E. M. Distribution of plasma proteins across the human aortic wall--barrier functions of endothelium and internal elastic lamina. Atherosclerosis. 1980 Dec;37(4):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(80)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan S. R., Vijayagopal P., Dalferes E. R., Jr, Abbate B., Radhakrishnamurthy B., Berenson G. S. Dynamics of lipoprotein-glycosaminoglycan interactions in the atherosclerotic rabbit aorta in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 18;793(2):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90317-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stary H. C. Coronary artery fine structure in rhesus monkeys: the early atherosclerotic lesion and its progression. Primates Med. 1976;9:359–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehbens W. E. Cerebral atherosclerosis. Intimal proliferation and atherosclerosis in the cerebral arteries. Arch Pathol. 1975 Nov;99(11):582–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trillo A. A., Prichard R. W. Early endothelial changes in experimental primate atherosclerosis. Lab Invest. 1979 Oct;41(4):294–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasile E., Simionescu M., Simionescu N. Visualization of the binding, endocytosis, and transcytosis of low-density lipoprotein in the arterial endothelium in situ. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1677–1689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Fabbrini P., Resi L. On the presence of a concanavalin-A reactive coat over the endothelial aortic surface and its modifications during early experimental cholesterol atherogenesis in rabbits. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1973 Jun 29;359(4):299–307. doi: 10.1007/BF00548601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund O., Carew T. E., Steinberg D. Role of the low density lipoprotein receptor in penetration of low density lipoprotein into rabbit aortic wall. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):135–141. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilversmit D. B. Mechanisms of cholesterol accumulation in the arterial wall. Am J Cardiol. 1975 Apr;35(4):559–566. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(75)90840-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent C. M., Emeis J. J. Histochemistry of free and esterified cholesterol in human atherosclerotic arteries. Prog Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;13:262–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]