Abstract
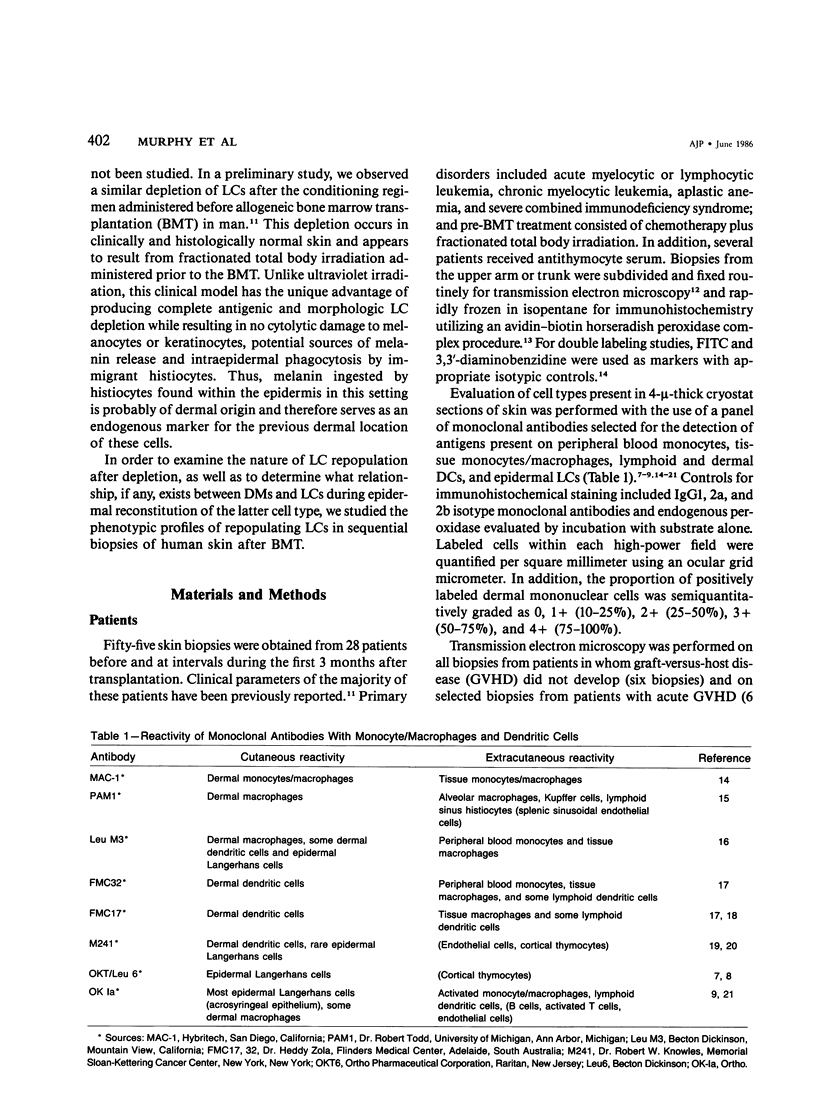
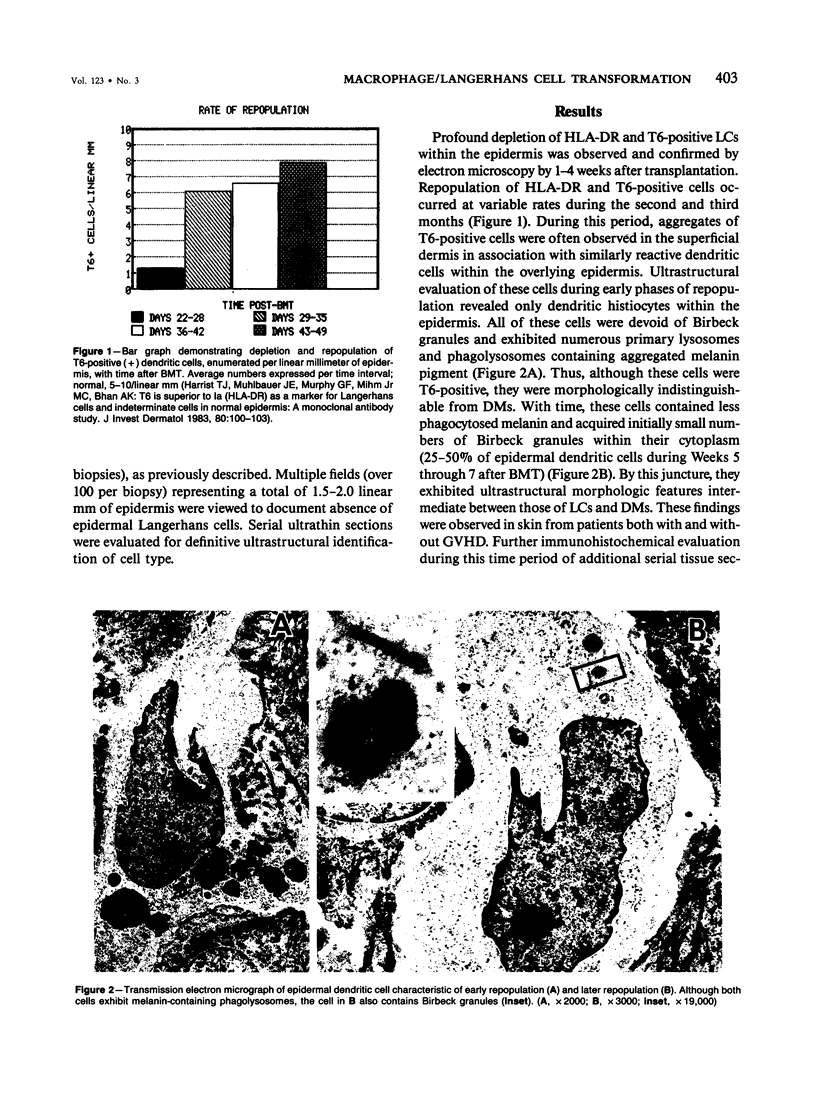
Langerhans cells, important participants in the cutaneous cellular immune response, are markedly diminished in skin of patients undergoing allogeneic bone marrow transplantation during the first 4 weeks after this procedure. To determine the mechanism responsible for the subsequent repopulation of these cells, the authors studied the immunophenotypic and morphologic profiles of sequential skin biopsies during the posttransplantation period. Cells with surface antigens of monocytes/macrophages within the superficial dermis were gradually replaced by dermal and epidermal dendritic cells exhibiting coexpression of monocyte/macrophage and Langerhans cell surface antigens. Ultrastructural examination revealed that many of these cells contained both prominent phagolysosomes and Birbeck granules. Antigenically and structurally mature Langerhans cells were observed within the epidermis by the end of the second month after transplantation. Phenotypic transformation of phagocytic dermal macrophages to Langerhans cells appears to represent a mechanism for repopulation of Langerhans cells during the period of immunologic reconstitution in this patient population.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benacerraf B. Role of MHC gene products in immune regulation. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1229–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.6165083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biondi A., Rossing T. H., Bennett J., Todd R. F., 3rd Surface membrane heterogeneity among human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1237–1243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. A., Zola H., McNamara P. J., Bradley J., Bradstock K. F., Hancock W. W., Atkins R. C. Membrane antigens of human cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage studied with monoclonal antibodies. Pathology. 1983 Jan;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.3109/00313028309061401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. D., Fox P., Neises G., Katz S. I. Effects of ultraviolet radiation on human epidermal cell alloantigen presentation: initial depression of Langerhans cell-dependent function is followed by the appearance of T6- Dr+ cells that enhance epidermal alloantigen presentation. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):129–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fithian E., Kung P., Goldstein G., Rubenfeld M., Fenoglio C., Edelson R. Reactivity of Langerhans cells with hybridoma antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2541–2544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flotte T. J., Springer T. A., Thorbecke G. J. Dendritic cell and macrophage staining by monoclonal antibodies in tissue sections and epidermal sheets. Am J Pathol. 1983 Apr;111(1):112–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock W. W., Zola H., Atkins R. C. Antigenic heterogeneity of human mononuclear phagocytes: immunohistologic analysis using monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1983 Dec;62(6):1271–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. A comparative study of the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method and an avidin-biotin complex method for studying polypeptide hormones with radioimmunoassay antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 May;75(5):734–738. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.5.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Robinson A. P., MacPherson G. G., Gordon S. The mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80. Relationship between macrophages, Langerhans cells, reticular cells, and dendritic cells in lymphoid and hematopoietic organs. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1522–1536. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii M., Terao Y., Kitajima J., Hamada T. Sequential production of Birbeck granules through adsorptive pinocytosis. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jan;82(1):28–29. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12259049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J. The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):213–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. W., Bodmer W. F. A monoclonal antibody recognizing a human thymus leukemia-like antigen associated with beta 2-microglobulin. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Aug;12(8):676–681. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. F., Bhan A. K., Sato S., Harrist T. J., Mihm M. C., Jr Characterization of Langerhans cells by the use of monoclonal antibodies. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):465–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. F., Bronstein B. R., Knowles R. W., Bhan A. K. Ultrastructural documentation of M241 glycoprotein on dendritic and endothelial cells in normal human skin. Lab Invest. 1985 Mar;52(3):264–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. F., Merot Y., Tong A. K., Smith B., Mihm M. C., Jr Depletion and repopulation of epidermal dendritic cells after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in humans. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Mar;84(3):210–214. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12265149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Lewis M. G., Sullivan A. K. Ia antigen expression on human epidermal Langerhans cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):247–248. doi: 10.1038/268247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schamburg-Lever G., Lever W. F. Electron microscopy of incontinentia pigmenti. J Invest Dermatol. 1973 Sep;61(3):151–158. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12676208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G., Steinman R. M. Murine epidermal Langerhans cells mature into potent immunostimulatory dendritic cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):526–546. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda Y., Asano S., Miyazaki T., Sagami S. Electron microscopic study on Langerhans cells and related cells in lymph nodes of DNCB-sensitive mice. Arch Dermatol Res. 1985;277(1):44–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00406480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Katz S. I., Clement L., Green I., Shevach E. M. Immunologic functions of Ia-bearing epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2005–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Beller D. I., Lu C. Y., Allen P. M. Antigen presentation: comments on its regulation and mechanism. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhis W. C., Valinsky J., Hoffman E., Luban J., Hair L. S., Steinman R. M. Relative efficacy of human monocytes and dendritic cells as accessory cells for T cell replication. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):174–191. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. S., Turner R. R., Shiurba R. A., Eng L., Warnke R. A. Human dendritic cells and macrophages. In situ immunophenotypic definition of subsets that exhibit specific morphologic and microenvironmental characteristics. Am J Pathol. 1985 Apr;119(1):73–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]