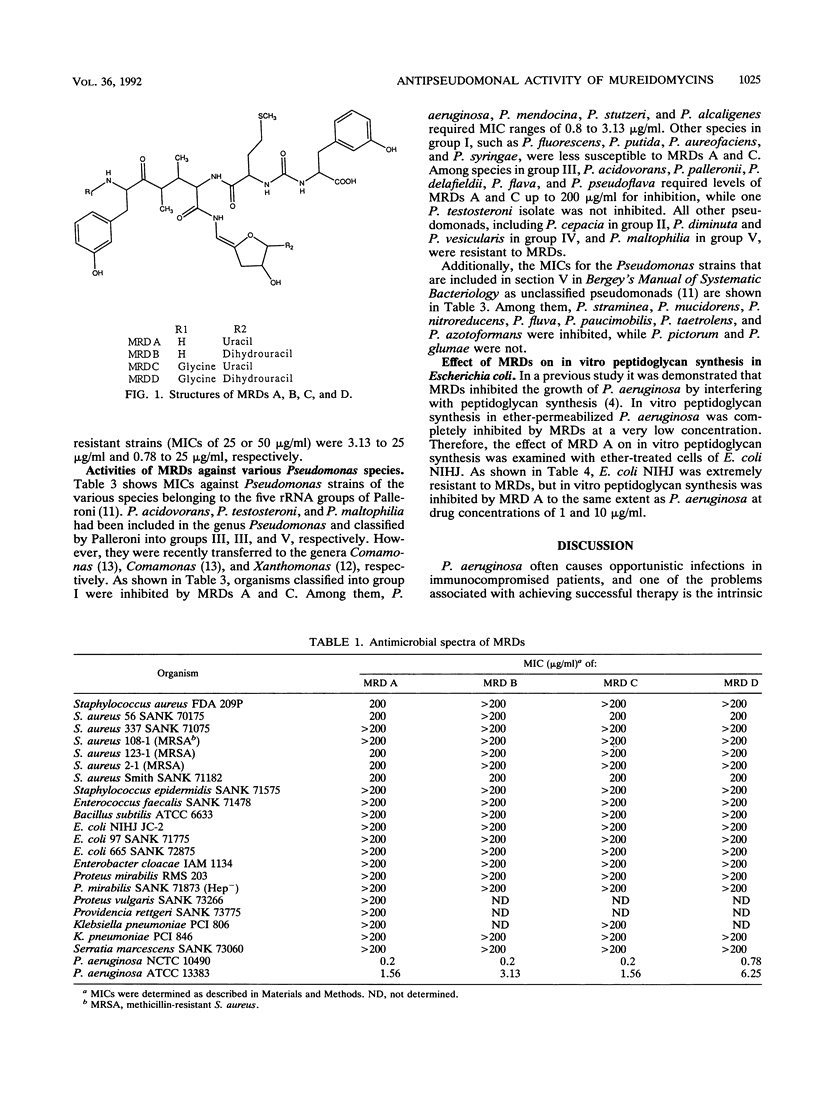
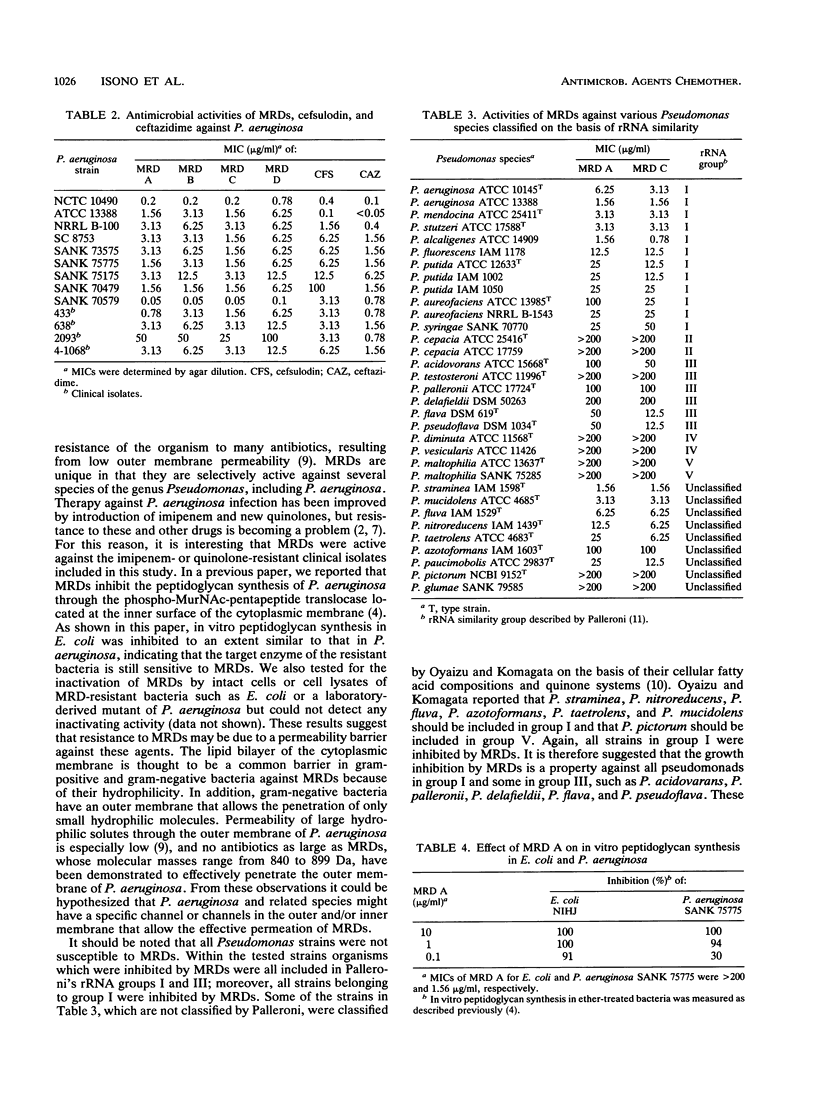
Abstract
Strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including imipenem- or ofloxacin-resistant clinical isolates, and some other species in the genus Pseudomonas were inhibited by novel antibiotics of the mureidomycin (MRD) group. On the other hand, almost all other gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria were resistant to MRDs, though the antibiotics potently inhibited the in vitro peptidoglycan synthesis of Escherichia coli and P. aeruginosa. All of the strains in the genus Pseudomonas that were inhibited by less than or equal to 200 micrograms of MRDs per ml were classified into the rRNA groups I and III, and none of the tested strains of rRNA group I were resistant to MRDs, suggesting that these two groups are closely related to each other evolutionary. Among group I strains, P. aeruginosa, P. mendocina, P. stutzeri, and P. alcaligenes were more susceptible than the others, suggesting a closer relationship among these species.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Giamarellou H., Galanakis N. Use of intravenous ciprofloxacin in difficult-to-treat infections. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):346–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inukai M., Isono F., Takahashi S., Enokita R., Sakaida Y., Haneishi T. Mureidomycins A-D, novel peptidylnucleoside antibiotics with spheroplast forming activity. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 May;42(5):662–666. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isono F., Inukai M. Mureidomycin A, a new inhibitor of bacterial peptidoglycan synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):234–236. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isono F., Inukai M., Takahashi S., Haneishi T., Kinoshita T., Kuwano H. Mureidomycins A-D, novel peptidylnucleoside antibiotics with spheroplast forming activity. II. Structural elucidation. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 May;42(5):667–673. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isono F., Katayama T., Inukai M., Haneishi T. Mureidomycins A-D, novel peptidylnucleoside antibiotics with spheroplast forming activity. III. Biological properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 May;42(5):674–679. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch M. J., Drusano G. L., Mobley H. L. Emergence of resistance to imipenem in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1892–1896. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Outer membrane barrier as a mechanism of antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosberg H. P., Hoffmann-Berling H. DNA synthesis in nucleotide-permeable Escherichia coli cells. I. Preparation and properties of ether-treated cells. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):739–753. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


