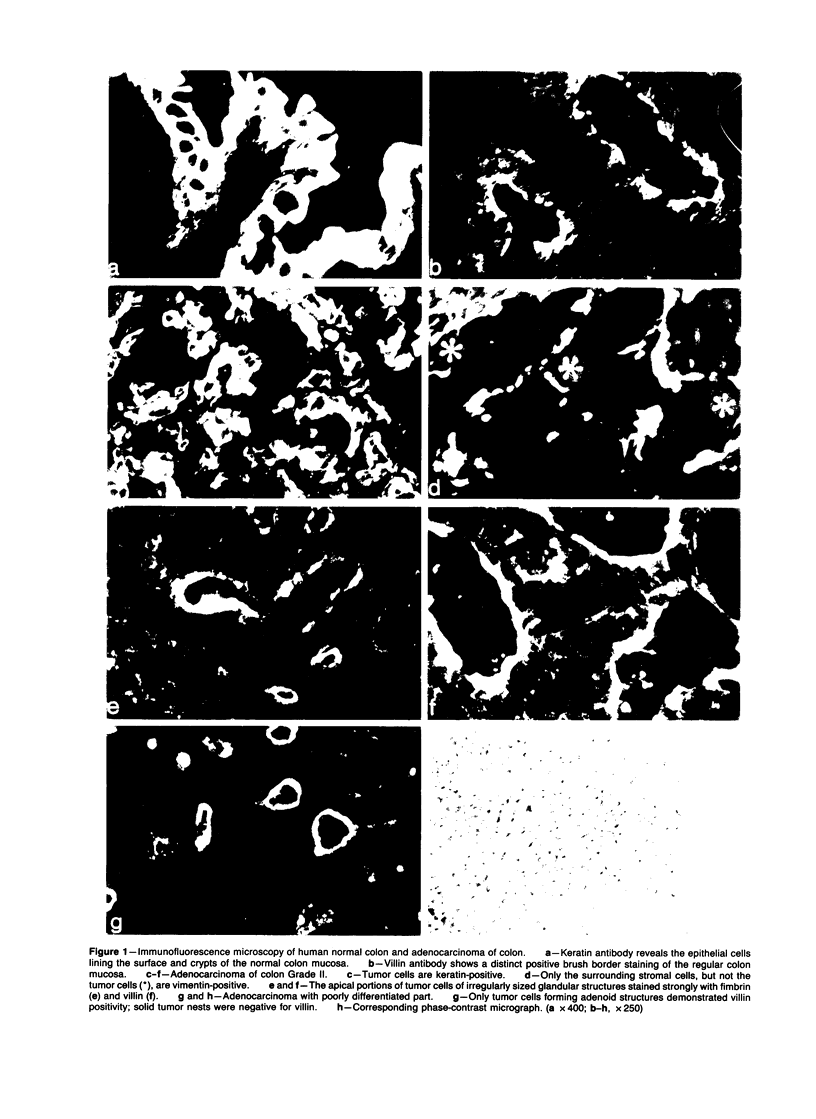
Abstract
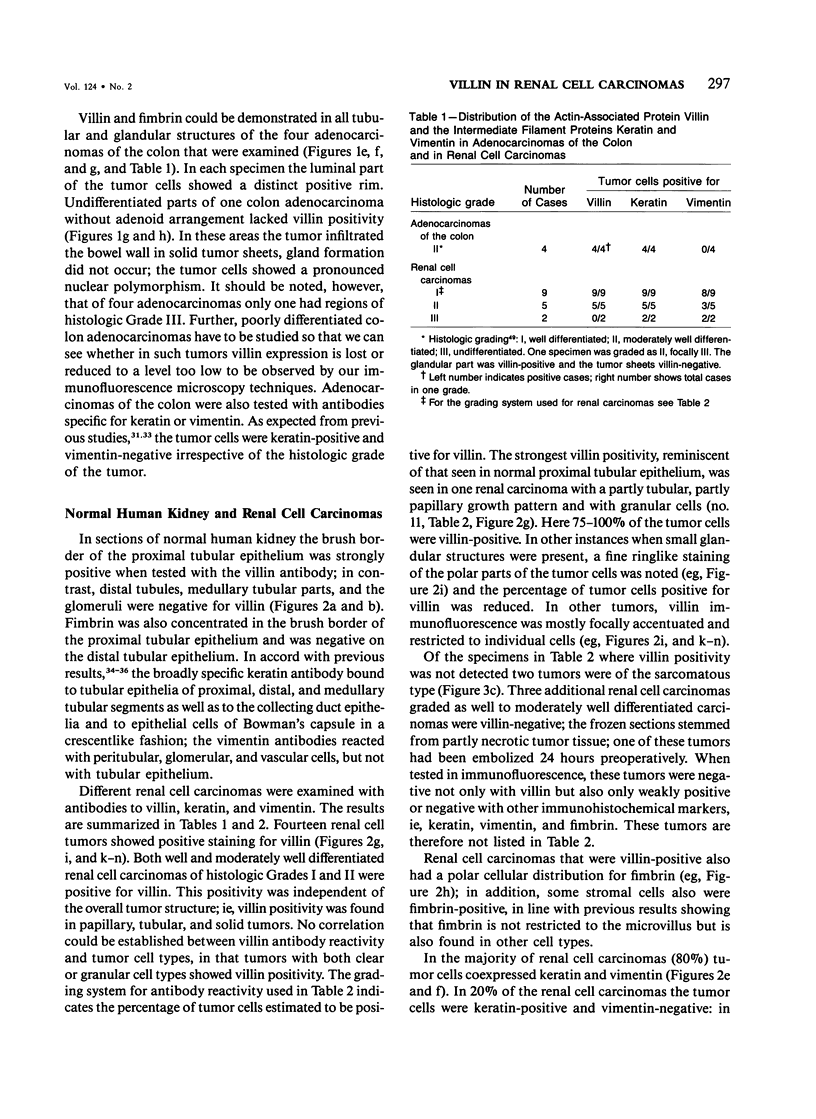
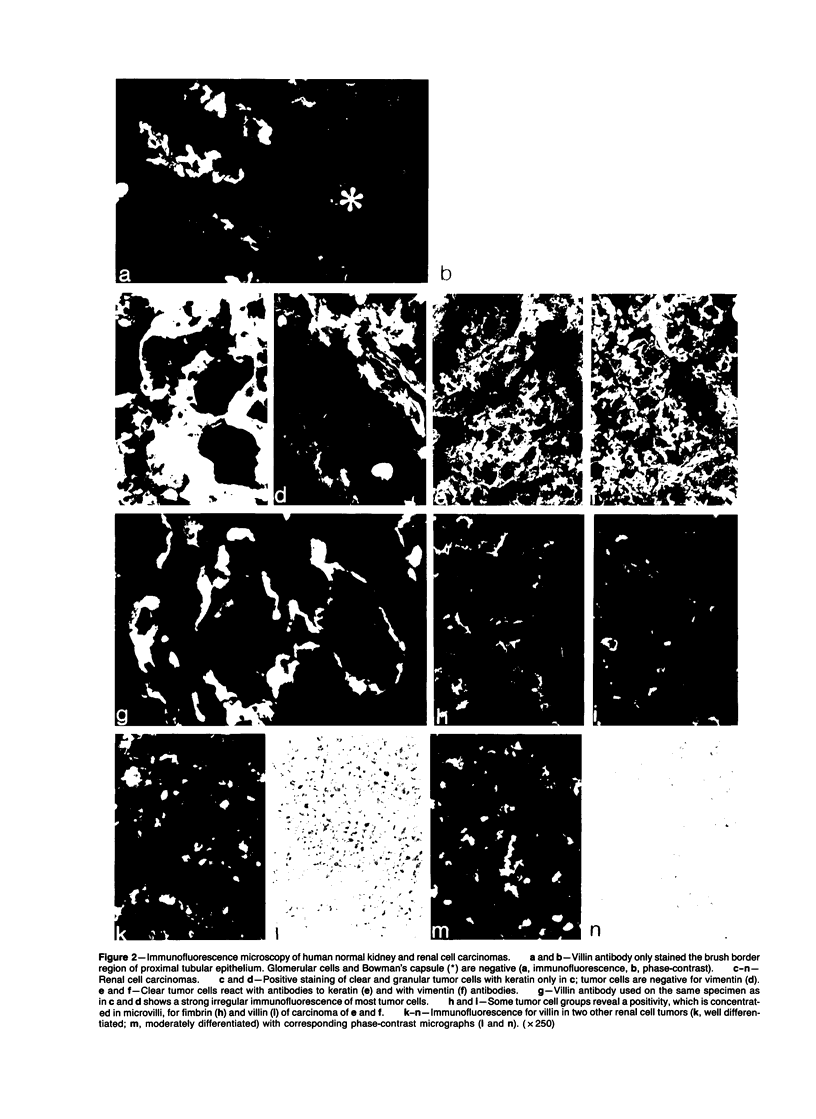
Expression of villin, a 95-kd F-actin bundling and severing protein, is restricted in animal tissues to epithelial cells with a brush border. Thus, the enterocytes of the intestine and epithelial cells of proximal but not distal tubules of the kidney are strongly positive. Here we report a similar staining pattern for human intestine and kidney. In four human colon adenocarcinomas villin expression was seen in tubular and glandular structures but not in the undifferentiated parts. Fourteen human renal carcinomas (9-Grade I and 5 Grade II) were villin-positive, and 2 sarcomatous renal carcinomas (Grade III) were villin-negative. The percentage of tumor cells that were villin-positive varied from 10-90% for the Grade I and II types. Our results indicate that villin may be a grading marker that deserves further study in renal carcinoma. They also raise the question whether the majority of renal carcinomas are derived from the proximal tubular epithelium rather than from the distal epithelium.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmannsberger M., Weber K., Hölscher A., Schauer A., Osborn M. Antibodies to intermediate filaments as diagnostic tools: human gastrointestinal carcinomas express prekeratin. Lab Invest. 1982 May;46(5):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arner O., Blanck C., von Schreeb T. Renal adenocarcinoma; morphology--grading of malignancy--prognosis. A study of 197 cases. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1965;346:1–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann S., Kriz W., Kuhn C., Franke W. W. Differentiation of cell types in the mammalian kidney by immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies to intermediate filament proteins and desmoplakins. Histochemistry. 1983;77(3):365–394. doi: 10.1007/BF00490899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannasch P., Krech R., Zerban H. Morphogenese und Mikromorphologie epithelialer Nierentumoren bei Nitrosomorpholin-vergifteten Ratten. IV. Tubuläre Läsionen und basophile Tumoren. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1980;98(3):243–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00410788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannayan G. A., Lamm D. L. Renal cell tumors. Pathol Annu. 1980;15(Pt 2):271–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein H., Adelman J. U. Histochemical study of the enzymatic activity of human neoplasms. II. Histogenesis of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 1966 Jul;19(7):935–938. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196607)19:7<935::aid-cncr2820190706>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Osborn M., Wehland J., Weber K. Villin associates with specific microfilamentous structures as seen by immunofluorescence microscopy on tissue sections and cells microinjected with villin. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Sep;135(1):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Fimbrin, a new microfilament-associated protein present in microvilli and other cell surface structures. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):335–340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin is a major protein of the microvillus cytoskeleton which binds both G and F actin in a calcium-dependent manner. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell N. D., Rheinwald J. G. Regulation of the cytoskeleton in mesothelial cells: reversible loss of keratin and increase in vimentin during rapid growth in culture. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUKES C. E., BUSSEY H. J. The spread of rectal cancer and its effect on prognosis. Br J Cancer. 1958 Sep;12(3):309–320. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1958.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Weber K., Osborn M. Monoclonal cytokeratin antibodies that distinguish simple from stratified squamous epithelia: characterization on human tissues. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1641–1647. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dees J. H., Heatfield B. M., Reuber M. D., Trump B. F. Adenocarcinoma of the kidney. III. Histogenesis of renal adenocarcinomas induced in rats by N-(4'-fluoro-4-biphenylyl)acetamide. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Jun;64(6):1537–1545. doi: 10.1093/jnci/64.6.1537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dees J. H., Reuber M. D., Trump B. F. Adenocarcinoma of the kidney. I. Ultrastructure of renal adenocarcinomas induced in rats by N-(4'-fluoro-4-biphenylyl)acetamide. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Oct;57(4):779–794. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.4.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohoe J. F., Venkatachalam M. A., Bernard D. B., Levinsky N. G. Tubular leakage and obstruction after renal ischemia: structural-functional correlations. Kidney Int. 1978 Mar;13(3):208–222. doi: 10.1038/ki.1978.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOOT N. C., HUMPHREYS G. A., WHITMORE W. F. Renal tumors: pathology and prognosis in 295 cases. J Urol. 1951 Aug;66(2):190–200. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)74326-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finstad C. L., Cordon-Cardo C., Bander N. H., Whitmore W. F., Melamed M. R., Old L. J. Specificity analysis of mouse monoclonal antibodies defining cell surface antigens of human renal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2955–2959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming S., Lindop G. B., Gibson A. A. The distribution of epithelial membrane antigen in the kidney and its tumours. Histopathology. 1985 Jul;9(7):729–739. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1985.tb02859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Weber K. Identity of p36K phosphorylated upon Rous sarcoma virus transformation with a protein purified from brush borders; calcium-dependent binding to non-erythroid spectrin and F-actin. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):227–233. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaumann B., Trump B. F. Studies on the pathogenesis of ischemic cell injury. III. Morphological changes of the proximal pars recta tubules (P3) of the rat kidney made ischemic in vivo. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1975 Dec 19;19(4):303–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Weber K. Calcium control of microfilaments: uncoupling of the F-actin-severing and -bundling activity of villin by limited proteolysis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2810–2814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman C. J., Moesker O., Kant A., Huysmans A., Vooijs G. P., Ramaekers F. C. Is renal cell (Grawitz) tumor a carcinosarcoma? Evidence from analysis of intermediate filament types. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1983;44(1):73–83. doi: 10.1007/BF02890161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthöfer H., Miettinen A., Lehto V. P., Lehtonen E., Virtanen I. Expression of vimentin and cytokeratin types of intermediate filament proteins in developing and adult human kidneys. Lab Invest. 1984 May;50(5):552–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthöfer H., Miettinen A., Paasivuo R., Lehto V. P., Linder E., Alfthan O., Virtanen I. Cellular origin and differentiation of renal carcinomas. A fluorescence microscopic study with kidney-specific antibodies, antiintermediate filament antibodies, and lectins. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):317–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie A. J. Epithelial membrane antigen in normal and proteinuric glomeruli and in damaged proximal tubules. J Pathol. 1986 Jan;148(1):55–60. doi: 10.1002/path.1711480109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. B. Ultrastructure of human acute renal failure. Lab Invest. 1982 Mar;46(3):254–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen A., Linder E. Membrane antigens shared by renal proximal tubules and other epithelia associated with absorption and excretion. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Mar;23(3):568–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moeremans M., Daneels G., Van Dijck A., Langanger G., De Mey J. Sensitive visualization of antigen-antibody reactions in dot and blot immune overlay assays with immunogold and immunogold/silver staining. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 30;74(2):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90303-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OBERLING C., RIVIERE M., HAGUENAU F. Ultrastructure of the clear cells in renal carcinomas and its importance for the demonstration of their renal origin. Nature. 1960 Apr 30;186:402–403. doi: 10.1038/186402a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada K., Nagamatsu G. R. The significance of electron microscopy in urological kidney diseases. Urol Int. 1971;26(2):112–121. doi: 10.1159/000279721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Debus E., Weber K. Monoclonal antibodies specific for vimentin. Eur J Cell Biol. 1984 May;34(1):137–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robine S., Huet C., Moll R., Sahuquillo-Merino C., Coudrier E., Zweibaum A., Louvard D. Can villin be used to identify malignant and undifferentiated normal digestive epithelial cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8488–8492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELJELID R., ERICSSON J. L. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS ON SPECIALIZATIONS OF THE CELL SURFACE IN RENAL CLEAR CELL CARCINOMA. Lab Invest. 1965 Apr;14:435–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner D. G., Colvin R. B., Vermillion C. D., Pfister R. C., Leadbetter W. F. Diagnosis and management of renal cell carcinoma. A clinical and pathologic study of 309 cases. Cancer. 1971 Nov;28(5):1165–1177. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1971)28:5<1165::aid-cncr2820280513>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjänen K., Hjelt L. Grading of human renal adenocarcinoma. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1978;12(1):49–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjänen K., Hjelt L. Ultrastructural characteristics of human renal cell carcinoma in relation to the light microscopic grading. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1978;12(1):57–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum M. Ultrastructural pathology of human renal cell tumors. Pathol Annu. 1971;6:249–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace A. C., Nairn R. C. Renal tubular antigens in kidney tumors. Cancer. 1972 Apr;29(4):977–981. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197204)29:4<977::aid-cncr2820290444>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Glenney J. R., Jr Microfilament-membrane interaction: the brush border of intestinal epithelial cells as a model. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Nov 4;299(1095):207–214. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama M. Ultracytochemical and morphological studies of human renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 1972 Jul;108(1):62–70. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)60642-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Overbeck J., Stähli C., Gudat F., Carmann H., Lautenschlager C., Dürmüller U., Takacs B., Miggiano V., Staehelin T., Heitz P. U. Immunohistochemical characterization of an anti-epithelial monoclonal antibody (mAB lu-5). Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1985;407(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00701324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]