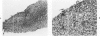Abstract
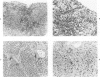
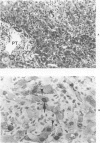
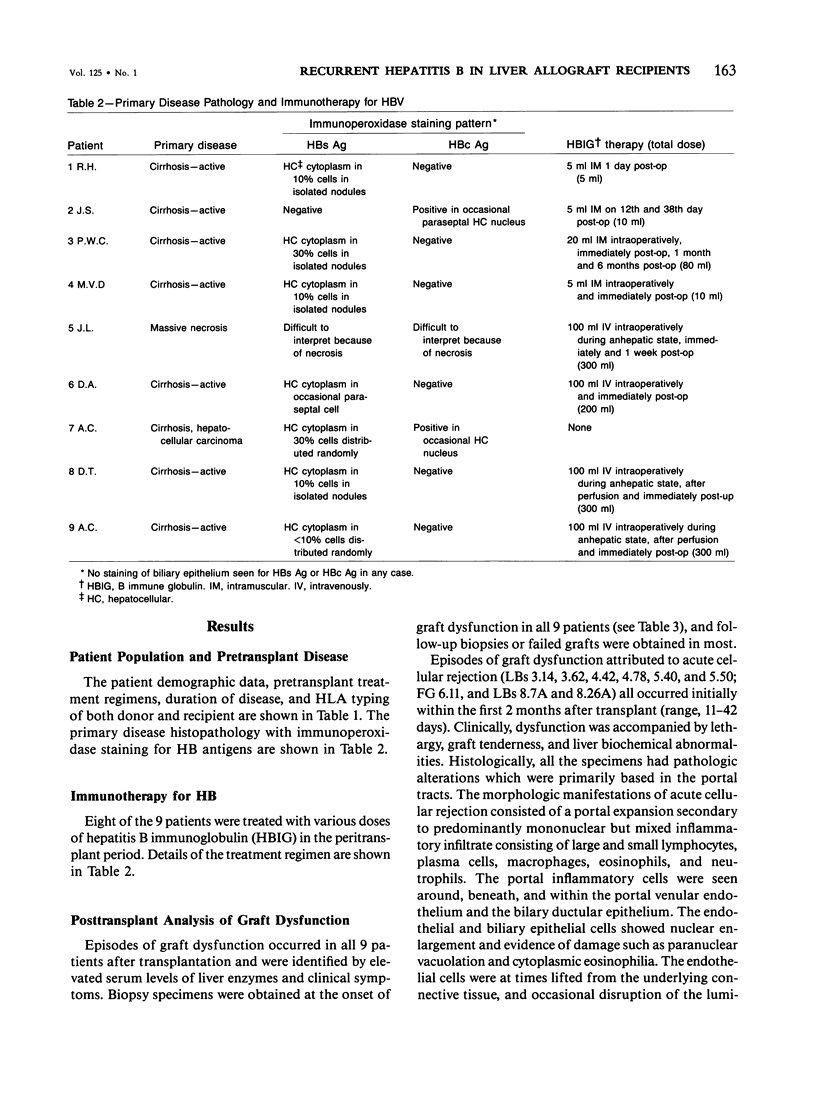
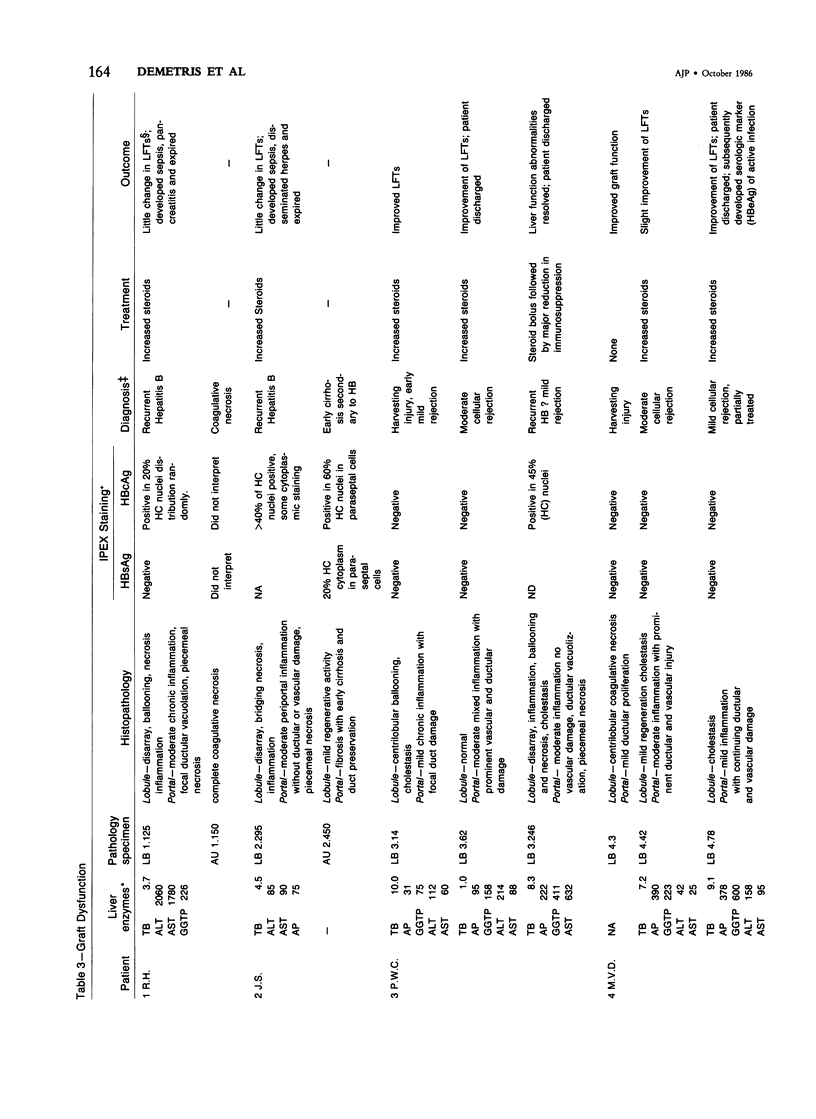
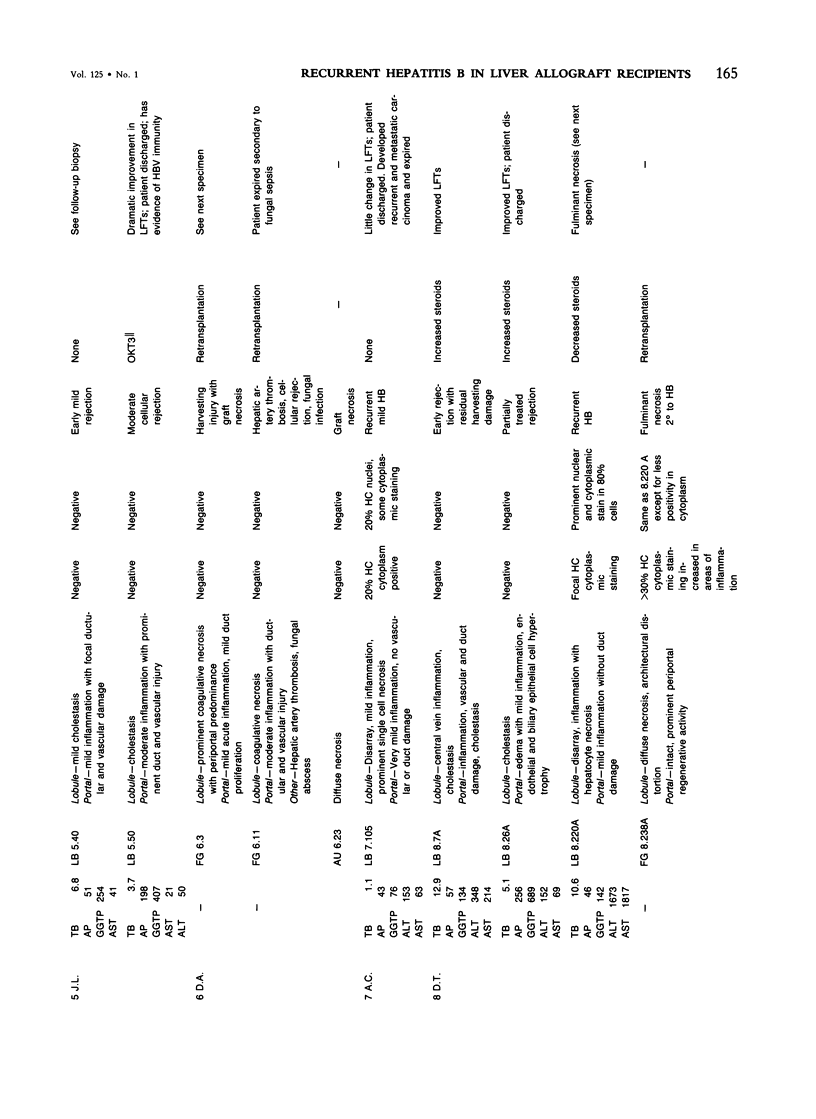
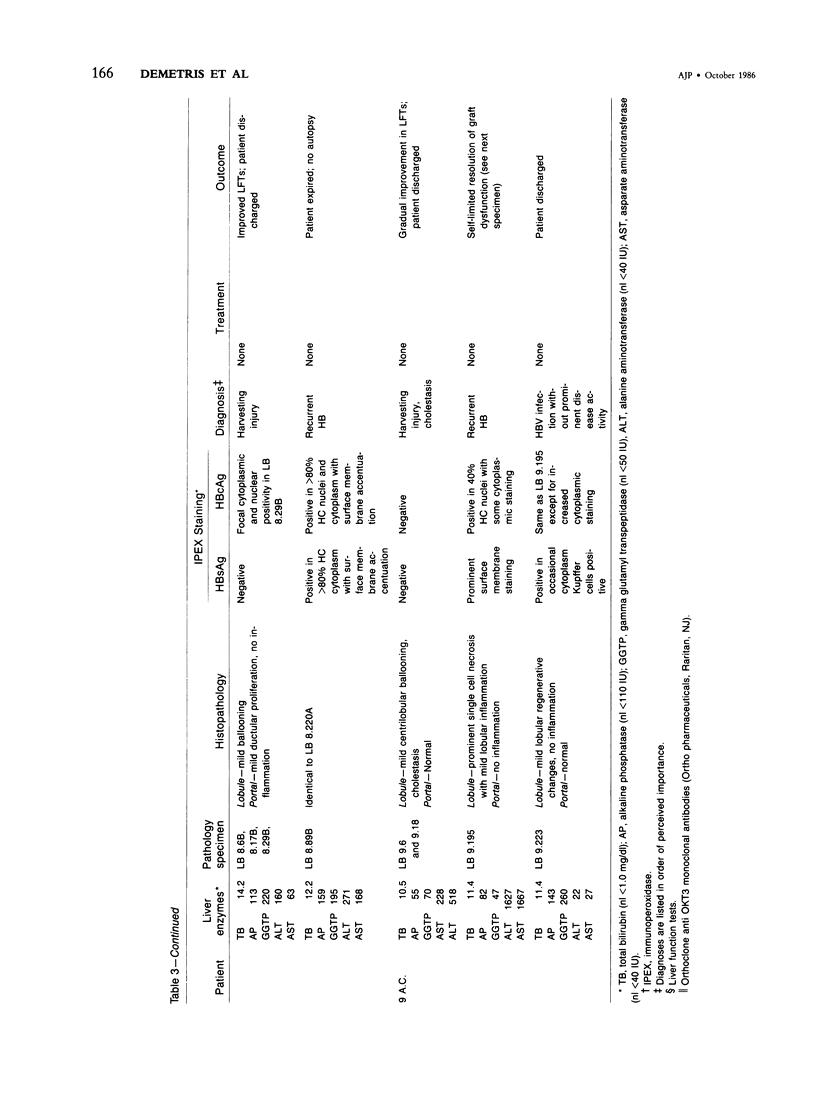
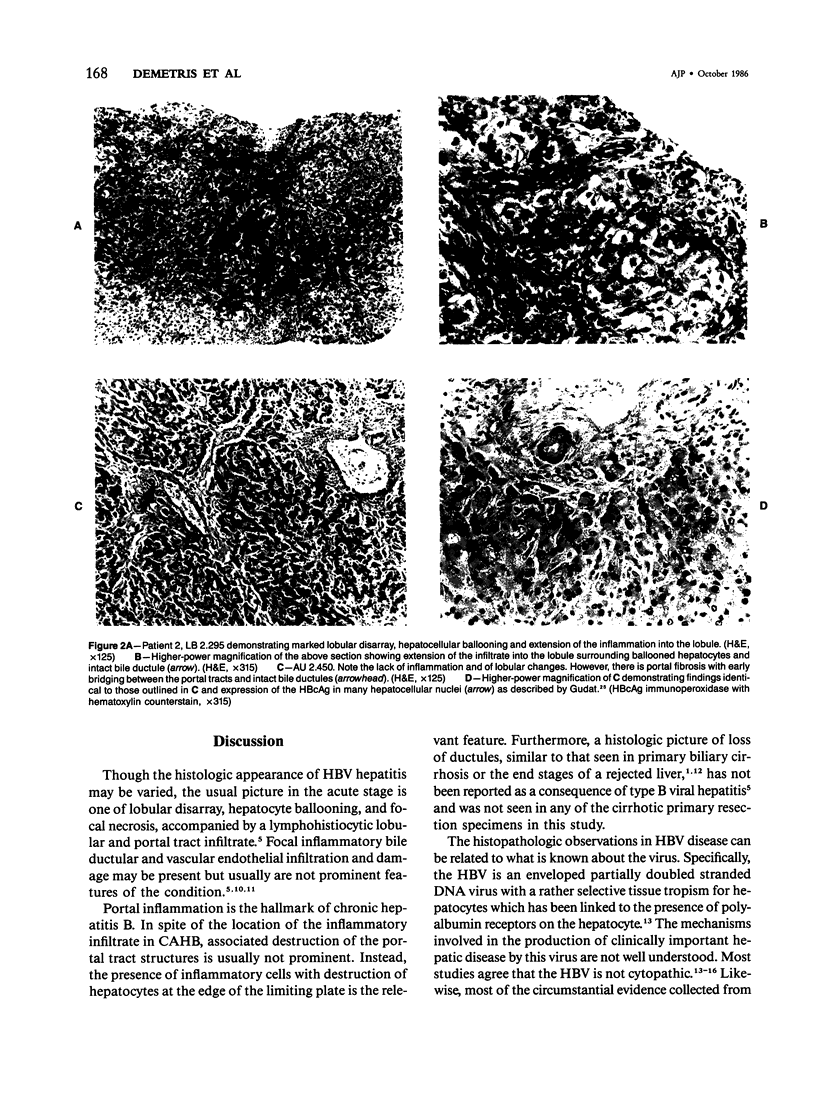
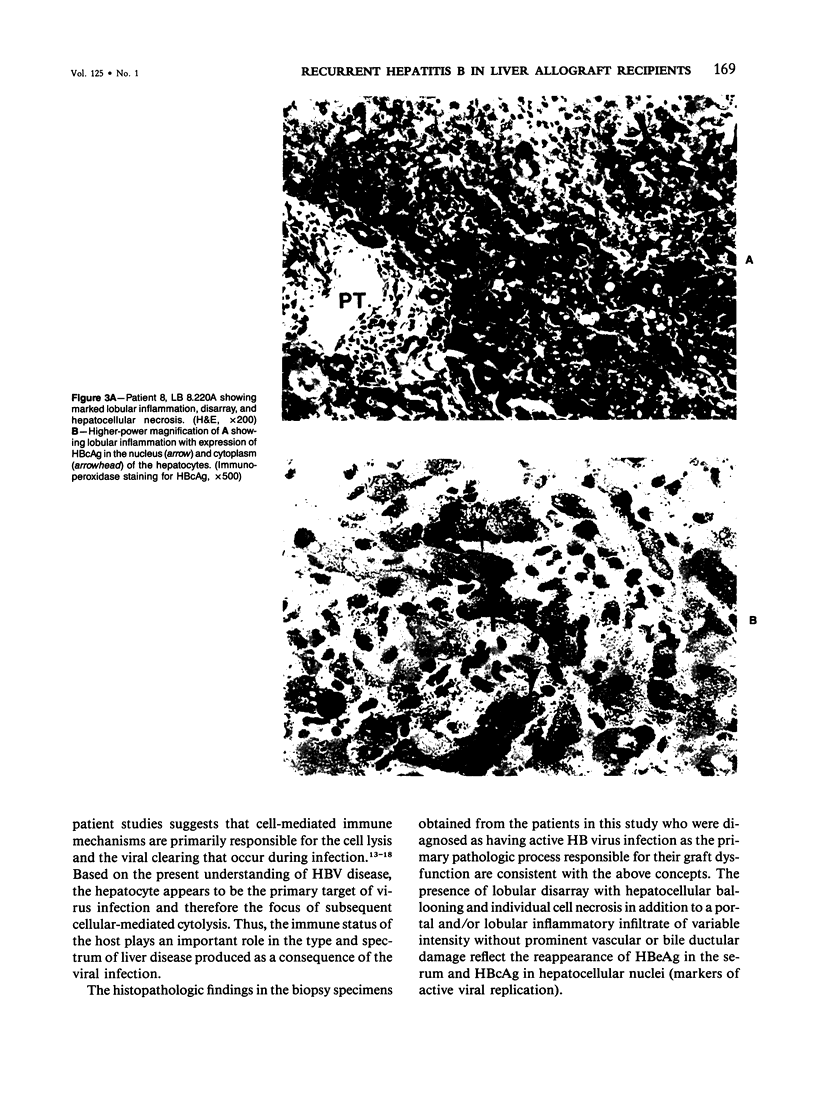
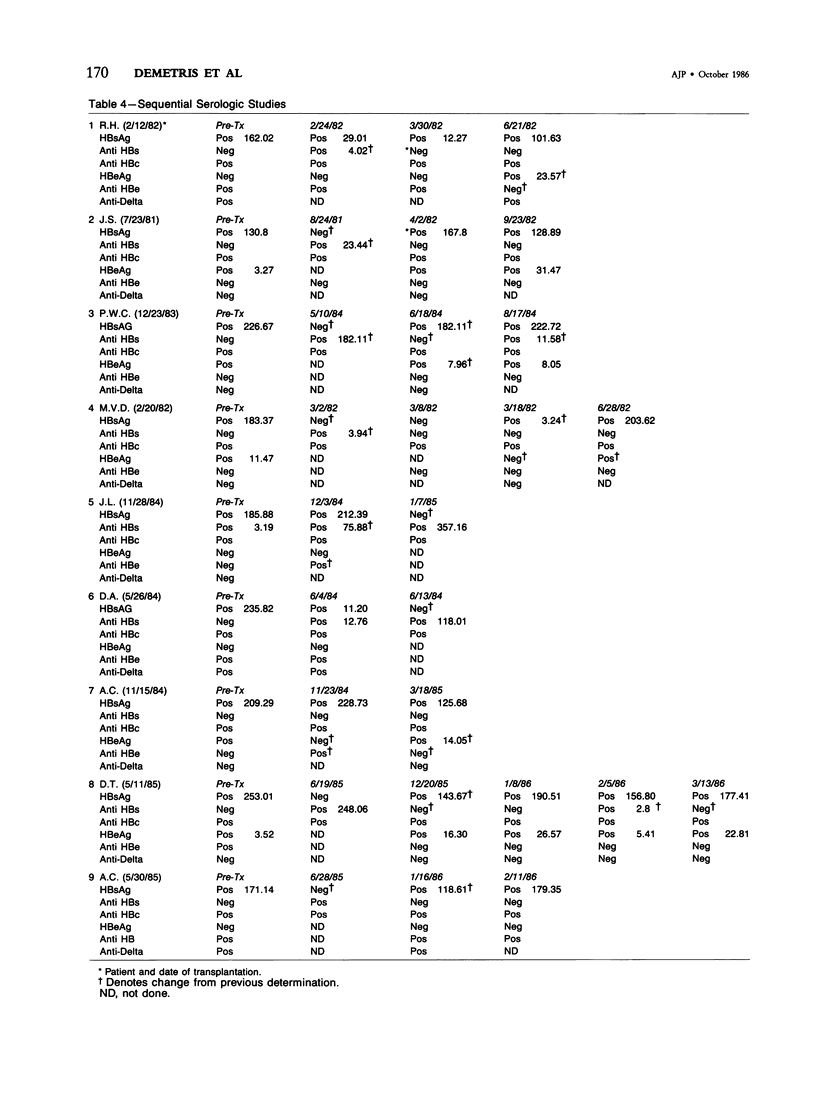
The histologic findings in the original liver obtained from 9 liver allograft patients with active B virus hepatitis were compared with 28 posttransplant pathology specimens. All specimens were studied with the use of light and immunohistochemical microscopy in conjunction with pertinent clinical data. Eight of the 9 patients had chronic active hepatitis B (HB) with cirrhosis, prior to transplant, one of which had coexistent hepatocellular carcinoma. The ninth patient had fulminant hepatic necrosis secondary to acute HB prior to transplantation. In all of the patients with chronic HB prior to transplantation who survived more than 2 months after transplantation recurrent infection of the graft developed despite perioperative HB immunoglobulin therapy. The patient with acute fulminant hepatitis B pretransplant has done well postoperatively and has evidence of HB virus immunity (positive anti-HBs) 15 months after transplantation. Examination of tissue specimens obtained during episodes of allograft dysfunction in these 9 patients indicate that pathologic alterations of active HB infection of the allograft are associated with a preferential lobular insult, whereas those occurring in rejection preferentially involve portal tract structures. Serologic data combined with biopsy histopathologic data are essential in distinguishing between the two quite different events.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Corman J. L., Putnam C. W., Iwatsuki S., Redeker A. G., Porter K. A., Peters R. L., Schröter G., Starzl T. E. Liver allograft. Its use in chronic active hepatitis with macronodular cirrhosis, hepatitis B surface antigen. Arch Surg. 1979 Jan;114(1):75–78. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1979.01370250077016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fuggle S. V., Fabre J. W., Ting A., Morris P. J. The detailed distribution of HLA-A, B, C antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation. 1984 Sep;38(3):287–292. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198409000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fuggle S. V., Fabre J. W., Ting A., Morris P. J. The detailed distribution of MHC Class II antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation. 1984 Sep;38(3):293–298. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198409000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demetris A. J., Lasky S., Van Thiel D. H., Starzl T. E., Dekker A. Pathology of hepatic transplantation: A review of 62 adult allograft recipients immunosuppressed with a cyclosporine/steroid regimen. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jan;118(1):151–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demetris A. J., Lasky S., Van Thiel D. H., Starzl T. E., Whiteside T. Induction of DR/IA antigens in human liver allografts. An immunocytochemical and clinicopathologic analysis of twenty failed grafts. Transplantation. 1985 Nov;40(5):504–509. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198511000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eron L., Kosinski K., Hirsch M. S. Hepatitis in an adult caused by Herpes simplex virus type I. Gastroenterology. 1976 Sep;71(3):500–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennell R. H., Jr, Shikes R. H., Vierling J. M. Relationship of pretransplant hepatobiliary disease to bile duct damage occurring in the liver allograft. Hepatology. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):84–89. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Thung S. N. Molecular and cellular pathology of hepatitis B. Lab Invest. 1985 Jun;52(6):572–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudat F., Bianchi L., Sonnabend W., Thiel G., Aenishaenslin W., Stalder G. A. Pattern of core and surface expression in liver tissue reflects state of specific immune response in hepatitis B. Lab Invest. 1975 Jan;32(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. N., Neurath A. R. Immunohistologic demonstration of hepatitis B viral antigens in liver with reference to its significance in liver injury. Lab Invest. 1979 Jan;40(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfrey P. S., Forbes R. D., Hutchinson T. A., Kenick S., Farge D., Dauphinee W. D., Seely J. F., Guttmann R. D. The impact of renal transplantation on the course of hepatitis B liver disease. Transplantation. 1985 Jun;39(6):610–615. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198506000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter K. A. Pathology of liver transplantation. Transplant Rev. 1969;2:129–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1969.tb00209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen H., Christoffersen P. Abnormal bile duct epithelium in chronic aggressive hepatitis and cirrhosis. A review of morphology and clinical, biochemical, and immunologic features. Hum Pathol. 1972 Jun;3(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(72)80075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snover D. C., Sibley R. K., Freese D. K., Sharp H. L., Bloomer J. R., Najarian J. S., Ascher N. L. Orthotopic liver transplantation: a pathological study of 63 serial liver biopsies from 17 patients with special reference to the diagnostic features and natural history of rejection. Hepatology. 1984 Nov-Dec;4(6):1212–1222. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Koep L. J., Halgrimson C. G., Hood J., Schroter G. P., Porter K. A., Weil R., 3rd Fifteen years of clinical liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 1979 Aug;77(2):375–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten Napel C. H., Houthoff H. J., The T. H. Cytomegalovirus hepatitis in normal and immune compromised hosts. Liver. 1984 Jun;4(3):184–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1984.tb00926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vento S., Hegarty J. E., Alberti A., O'Brien C. J., Alexander G. J., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. T lymphocyte sensitization to HBcAg and T cell-mediated unresponsiveness to HBsAg in hepatitis B virus-related chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):192–197. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada G., Feinberg L. E., Nakane P. K. Hepatitis B. Cytologic localization of virus antigens and the role of the immune response. Hum Pathol. 1978 Jan;9(1):93–109. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(78)80011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]