Abstract
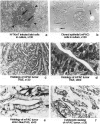
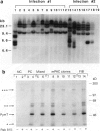
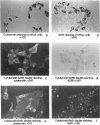
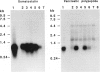
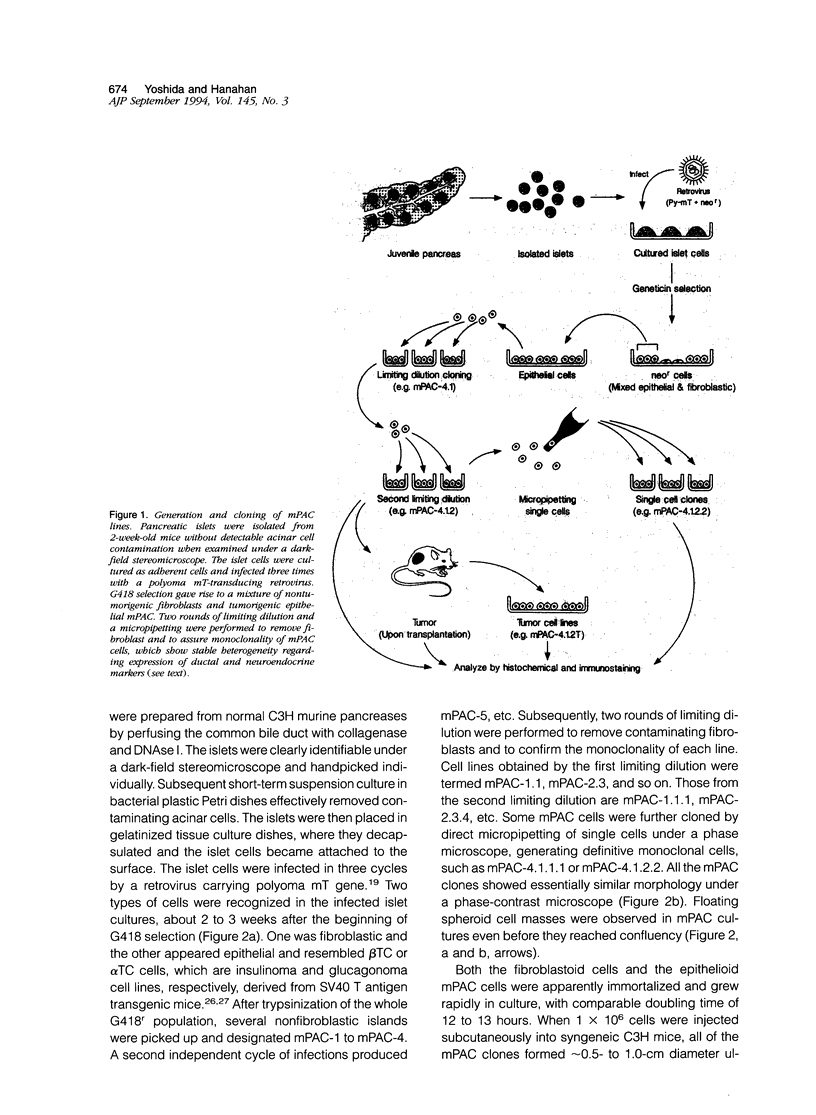
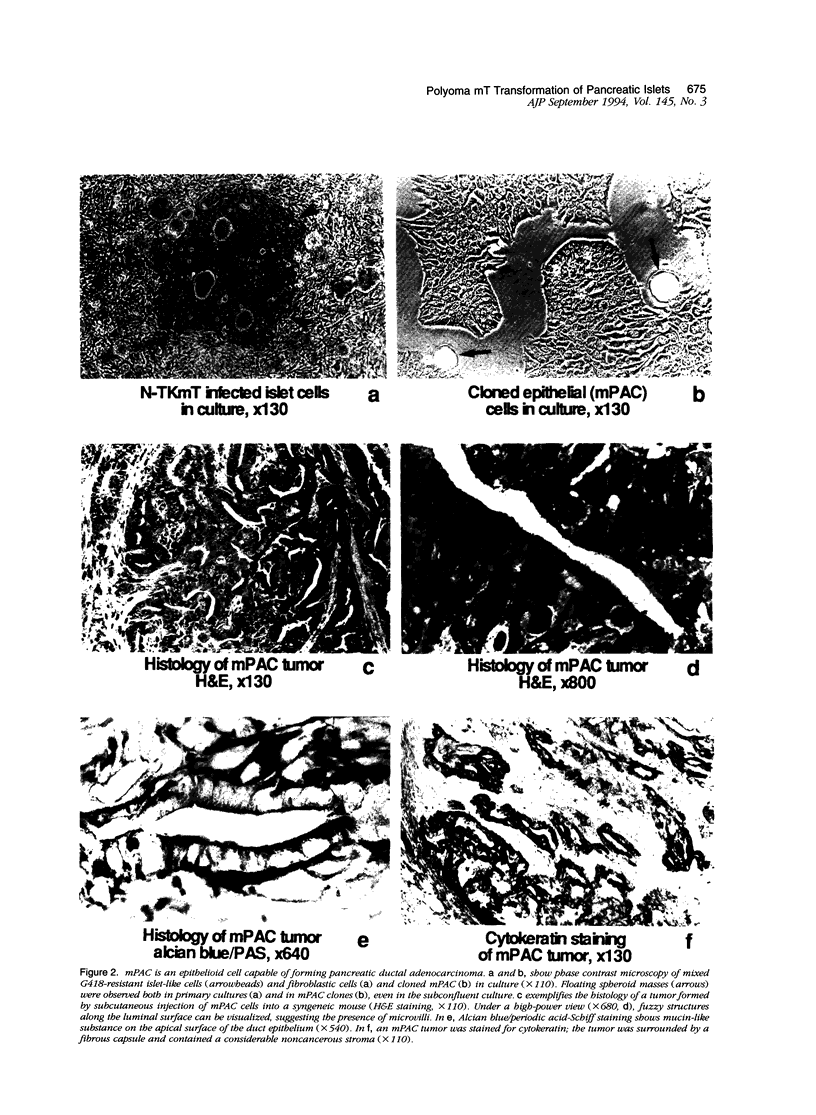
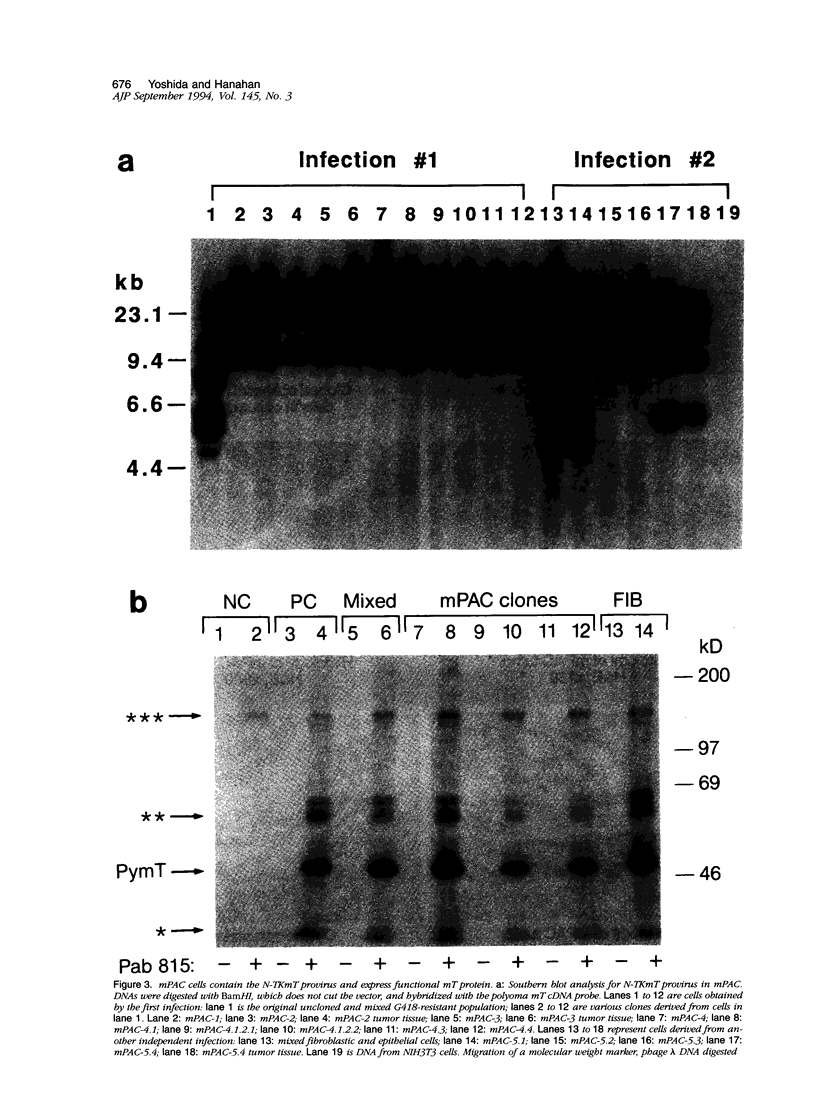
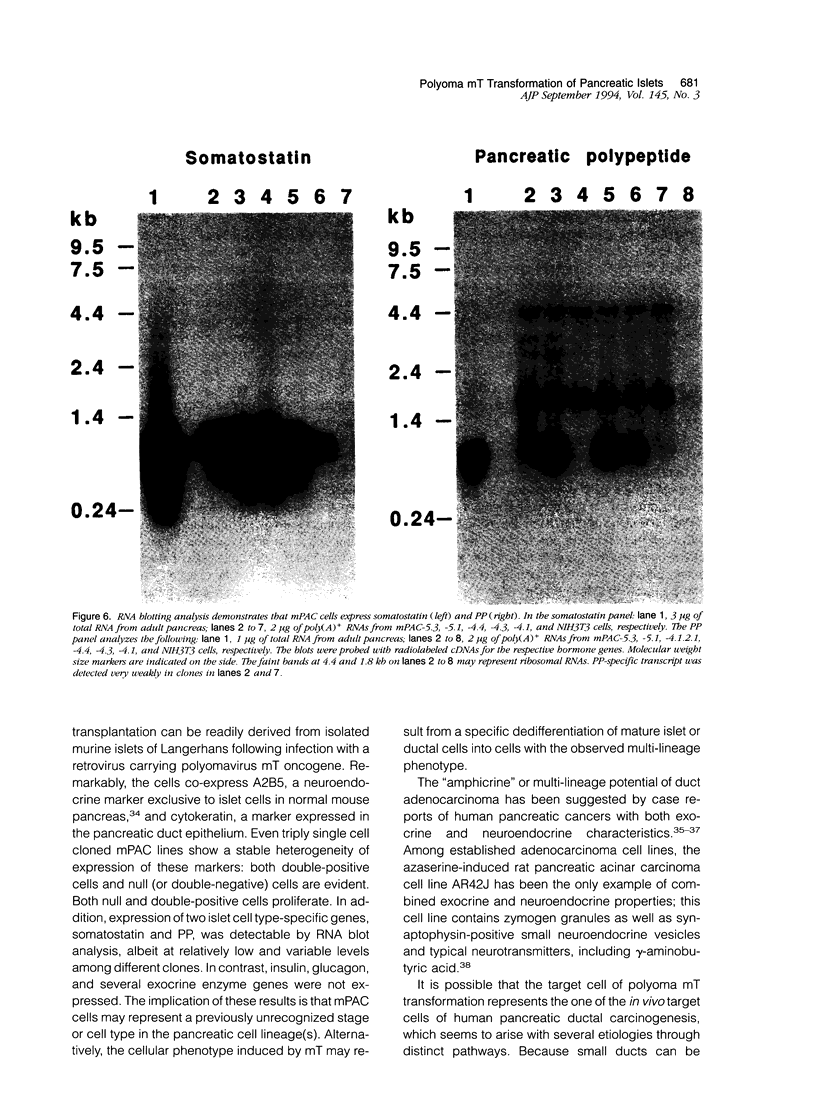
Pancreatic islets isolated from juvenile but not aging adult mice, when infected with a retrovirus carrying polyomavirus middle T oncogene, produced cell lines, mPAC, with characteristics both of pancreatic ductal epithelium and neuroendocrine cells of the islets. Following three cycles of single cell cloning, mPAC cells consisted of two subtypes, a null cell, and a double-positive cell that co-expressed cytokeratin, a marker of ductal epithelium, and A2B5, a neuroendocrine ganglioside expressed in developing islet cells. Two islet cell genes, encoding somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide, were transcribed at low levels in most mPAC clones, whereas the insulin and glucagon genes were not. Upon inoculation of mice, mPAC cells rapidly formed well-differentiated ductal adenocarcinomas that expressed cytokeratin but not the islet cell markers. The mPAC phenotype may result from a specific dedifferentiation of juvenile islet cells or ductal epithelium induced by middle T protein. Alternatively, mPAC cells may arise by transformation of a multipotential progenitor present within or in juxtaposition to juvenile islets. This cell type could therefore represent one of the targets in human cancers of the pancreatic duct. Moreover, signal transduction systems modulated by middle T, including src-related kinases, phosphatidylinositol kinase, and protein phosphatase 2A, may be involved in pancreatic carcinogenesis.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J., Novotný J., Martin J., Heinrich G. Molecular structure of mammalian neuropeptide Y: analysis by molecular cloning and computer-aided comparison with crystal structure of avian homologue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2532–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almoguera C., Shibata D., Forrester K., Martin J., Arnheim N., Perucho M. Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90571-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomeusz R. K., Campbell I. L., Harrison L. C. Pancreatic islet A2B5- and 3G5-reactive gangliosides are markers of differentiation in rat insulinoma cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Jun;124(6):2680–2685. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-6-2680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautch V. L., Toda S., Hassell J. A., Hanahan D. Endothelial cell tumors develop in transgenic mice carrying polyoma virus middle T oncogene. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):529–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., DeSeau V., O'Shaughnessy J., Amini S. Analysis of middle tumor antigen and pp60c-src interactions in polyomavirus-transformed rat cells. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3299–3305. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3299-3305.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Baxter L. A., Schuppin G. T., Smith F. E. A second pathway for regeneration of adult exocrine and endocrine pancreas. A possible recapitulation of embryonic development. Diabetes. 1993 Dec;42(12):1715–1720. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.12.1715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Baithun S. I., Pollock D. J., Berry C. L. Argyrophilic and hormone immunoreactive cells in normal and hyperplastic pancreatic ducts and exocrine pancreatic carcinoma. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1988;413(5):399–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00716988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Harvey R., Espino P. C., Semba K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K., Smith A. E. Peptide antibodies to the human c-fyn gene product demonstrate pp59c-fyn is capable of complex formation with the middle-T antigen of polyomavirus. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3845–3855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Heber A. An 81 kd protein complexed with middle T antigen and pp60c-src: a possible phosphatidylinositol kinase. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):435–439. doi: 10.1038/303435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Linde S., Kofod H., Spector D., Delannoy M., Grant S., Hanahan D., Baekkeskov S. Beta-cell lines derived from transgenic mice expressing a hybrid insulin gene-oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9037–9041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Githens S., Pictet R., Phelps P., Rutter W. J. 5-bromodeoxyuridine may alter the differentiative program of the embryonic pancreas. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):341–356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittes G. K., Rutter W. J. Onset of cell-specific gene expression in the developing mouse pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1128–1132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn G. M., Eckhart W. Mutation of a cysteine residue in polyomavirus middle T antigen abolishes interactions with protein phosphatase 2A, pp60c-src, and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase, activation of c-fos expression, and cellular transformation. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1945–1952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1945-1952.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh M., Maki T., Kiyoizumi T., Satomi S., Monaco A. P. An improved method for isolation of mouse pancreatic islets. Transplantation. 1985 Oct;40(4):437–438. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198510000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., Hughes C. M., Staddon S. L., Richman P. I., Gullick W. J., Lemoine N. R. The c-erb B-2 proto-oncogene in human pancreatic cancer. J Pathol. 1990 Jul;161(3):195–200. doi: 10.1002/path.1711610305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen W. A., Christie M. R., Kahn R., Norgaard A., Abel I., Petersen A. M., Jorgensen D. W., Baekkeskov S., Nielsen J. H., Lernmark A. Supravital dithizone staining in the isolation of human and rat pancreatic islets. Diabetes Res. 1989 Feb;10(2):53–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. D., Ingber D. E., Muresan V., Hull B. E., Sarras M. P., Jr, Maylié-Pfenninger M. F., Iwanij V. Cell surface properties of normal, differentiating, and neoplastic pancreatic acinar cells. Cancer. 1981 Mar 15;47(6 Suppl):1516–1527. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810315)47:6+<1516::aid-cncr2820471413>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Hanafusa H. The effects of reciprocal changes in temperature on the transformed state of cells infected with a rous sarcoma virus mutant. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):470–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G., Paige C., Gilboa E., Wagner E. F. Expression of a foreign gene in myeloid and lymphoid cells derived from multipotent haematopoietic precursors. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):149–154. doi: 10.1038/318149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. H., Ho S. B., Montgomery C. K., Kim Y. S. Cell lineage markers in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 1990 Nov 15;66(10):2134–2143. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19901115)66:10<2134::aid-cncr2820661016>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi Y., Mizumoto K., Kitazawa S., Tsujiuchi T., Tsutsumi M., Kamano T. Early ductal lesions of pancreatic carcinogenesis in animals and humans. Int J Pancreatol. 1990 Aug-Nov;7(1-3):83–89. doi: 10.1007/BF02924223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Sudol M., Hanafusa H. Association of the polyomavirus middle-T antigen with c-yes protein. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):171–173. doi: 10.1038/325171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusielewicz D., Houry S., Sabourin J. C., Georges O., Roland J., Huguier M., Bodin F. Composante endocrine des tumeurs excréto-pancréatiques. A propos de deux observations. Ann Gastroenterol Hepatol (Paris) 1992 Jan-Feb;28(1):12–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Hemming A., Courtneidge S. A. Identification and characterization of p59fyn (a src-like protein tyrosine kinase) in normal and polyoma virus transformed cells. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3837–3844. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter A. B., Toder A., Wolfe H. J., Taylor I. L., Cooperman S., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Peptide YY. Structure of the precursor and expression in exocrine pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):12984–12988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino T., Usuda N., Rao S., Reddy J. K., Scarpelli D. G. Transdifferentiation of ductular cells into hepatocytes in regenerating hamster pancreas. Lab Invest. 1990 May;62(5):552–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markland W., Smith A. E. Mutants of polyomavirus middle-T antigen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 25;907(3):299–321. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Shahrik L. K., Martin B. L., Jaspers S., Miller T. B., Brautigan D. L., Roberts T. M. Polyoma small and middle T antigens and SV40 small t antigen form stable complexes with protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90726-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsa I., Longnecker D. S., Scarpelli D. G., Pour P., Reddy J. K., Lefkowitz M. Ductal metaplasia of human exocrine pancreas and its association with carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1985 Mar;45(3):1285–1290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pour P., Krüger F. W., Althoff J., Cardesa A., Mohr U. Cancer of the pancreas induced in the Syrian golden hamster. Am J Pathol. 1974 Aug;76(2):349–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers A. C., Efrat S., Mojsov S., Spector D., Habener J. F., Hanahan D. Proglucagon processing similar to normal islets in pancreatic alpha-like cell line derived from transgenic mouse tumor. Diabetes. 1990 Apr;39(4):406–414. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.4.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Courtneidge S. A., Loubière R., el Baze P., Cuzin F. A variety of tumours induced by the middle T antigen of polyoma virus in a transgenic mouse family. Oncogene. 1990 Oct;5(10):1507–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renfranz P. J., Cunningham M. G., McKay R. D. Region-specific differentiation of the hippocampal stem cell line HiB5 upon implantation into the developing mammalian brain. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):713–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90116-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosewicz S., Vogt D., Harth N., Grund C., Franke W. W., Ruppert S., Schweitzer E., Riecken E. O., Wiedenmann B. An amphicrine pancreatic cell line: AR42J cells combine exocrine and neuroendocrine properties. Eur J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;59(1):80–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri B., Zhang S. Y., Caamano J., DiRado M., Flynn S. D., Klein-Szanto A. J. Human pancreatic carcinomas and cell lines reveal frequent and multiple alterations in the p53 and Rb-1 tumor-suppressor genes. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1503–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandgren E. P., Quaife C. J., Paulovich A. G., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Pancreatic tumor pathogenesis reflects the causative genetic lesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):93–97. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvetnick N. E., Gu D. Regeneration of pancreatic endocrine cells in interferon-gamma transgenic mice. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;321:85–93. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3448-8_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpelli D. G., Rao M. S., Reddy J. K. Are acinar cells involved in the pathogenesis of ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas? Cancer Cells. 1991 Jul;3(7):275–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldevila G., Buscema M., Marini V., Sutton R., James R. F., Bloom S. R., Robertson R. P., Mirakian R., Pujol-Borrell R., Bottazzo G. F. Transfection with SV40 gene of human pancreatic endocrine cells. J Autoimmun. 1991 Jun;4(3):381–396. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(91)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stork P., Loda M., Bosari S., Wiley B., Poppenhusen K., Wolfe H. Detection of K-ras mutations in pancreatic and hepatic neoplasms by non-isotopic mismatched polymerase chain reaction. Oncogene. 1991 May;6(5):857–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. E., Aguzzi A., Soriano P., Wagner E. F., Brugge J. S. Induction of tumor formation and cell transformation by polyoma middle T antigen in the absence of Src. Oncogene. 1993 Sep;8(9):2521–2529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Ruediger R., Slaughter C., Mumby M. Association of protein phosphatase 2A with polyoma virus medium tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2521–2525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):239–242. doi: 10.1038/315239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. L., Courtneidge S. A., Wagner E. F. Embryonic lethalities and endothelial tumors in chimeric mice expressing polyoma virus middle T oncogene. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90536-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa A., Kato Y., Ohtake K., Kitagawa T., Ohashi K., Hori M., Takagi K., Sugano H. c-Ki-ras point mutations in ductectatic-type mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1991 Oct;82(10):1057–1060. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1991.tb01756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonekura H., Nata K., Watanabe T., Kurashina Y., Yamamoto H., Okamoto H. Mosaic evolution of prepropancreatic polypeptide. II. Structural conservation and divergence in pancreatic polypeptide gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2990–2997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]