Abstract
The main objective of the present study is to define the expression and/or modulation of antigenic phenotypes in cells of the normal human kidney and urothelium according to cell type. Fourteen antibodies detecting differentiation and structural antigens expressed in the human urinary tract have been used to define the immunoanatomic distribution of these antigenic systems. They include urinary tract antigens (Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein and prostate-specific antigen), tissue-associated antigens (epithelial membrane antigen, Factor VIII antigen, and Protein S-100), and cytoskeletal antigens of the intermediate filament classes (cytokeratins, vimentin, desmin, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and neurofilaments. Immunofluorescence and immunoperoxidase analyses performed on normal human fetal and adult tissue sections have demonstrated that these antigens are expressed by different cell types and domains of the nephron. Studies correlating normal fetal and adult tissues reveal that some of the antigens appear at distinct stages of maturation, representing early and late antigenic expression events. These antibodies offer a wide range of potential applications that include studies of embryogenesis of the human urinary tract and immunopathologic analyses of neoplastic and nonneoplastic diseases of the human kidney and urothelium.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtstätter T., Moll R., Moore B., Franke W. W. Cytokeratin polypeptide patterns of different epithelia of the human male urogenital tract: immunofluorescence and gel electrophoretic studies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 May;33(5):415–426. doi: 10.1177/33.5.2580881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann S., Kriz W., Kuhn C., Franke W. W. Differentiation of cell types in the mammalian kidney by immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies to intermediate filament proteins and desmoplakins. Histochemistry. 1983;77(3):365–394. doi: 10.1007/BF00490899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bariéty J., Oriol R., Hinglais N., Zanetti M., Bretton R., Dalix A. M., Mandet C. Distribution of blood group antigen A in normal and pathologic human kidneys. Kidney Int. 1980 Jun;17(6):820–826. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Haglid K., Haiech J., Gérard D. Zinc ion binding to human brain calcium binding proteins, calmodulin and S100b protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 12;114(3):1138–1146. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90681-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher O., Kaissling B. Morphologie des juxtaglomerulären Apparates. Verh Anat Ges. 1972;67:109–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceriani R. L., Thompson K., Peterson J. A., Abraham S. Surface differentiation antigens of human mammary epithelial cells carried on the human milk fat globule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):582–586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D., Schermer A., Sun T. T. Classification of human epithelia and their neoplasms using monoclonal antibodies to keratins: strategies, applications, and limitations. Lab Invest. 1985 Mar;52(3):243–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Bander N. H., Fradet Y., Finstad C. L., Whitmore W. F., Lloyd K. O., Oettgen H. F., Melamed M. R., Old L. J. Immunoanatomic dissection of the human urinary tract by monoclonal antibodies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Oct;32(10):1035–1040. doi: 10.1177/32.10.6384360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donato R. The specific interaction of S-100 protein with synaptosomal particulate fractions. Site-site interactions among S-100 binding sites. J Neurochem. 1978 May;30(5):1105–1111. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P. Determination and differentiation of the nephron. Med Biol. 1981 Jun;59(3):139–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandson R. A., Cardon-Cardo C., Higgins P. J. Histogenesis of benign pleomorphic adenoma (mixed tumor) of the major salivary glands. An ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol. 1984 Nov;8(11):803–820. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198411000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finstad C. L., Cordon-Cardo C., Bander N. H., Whitmore W. F., Melamed M. R., Old L. J. Specificity analysis of mouse monoclonal antibodies defining cell surface antigens of human renal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2955–2959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
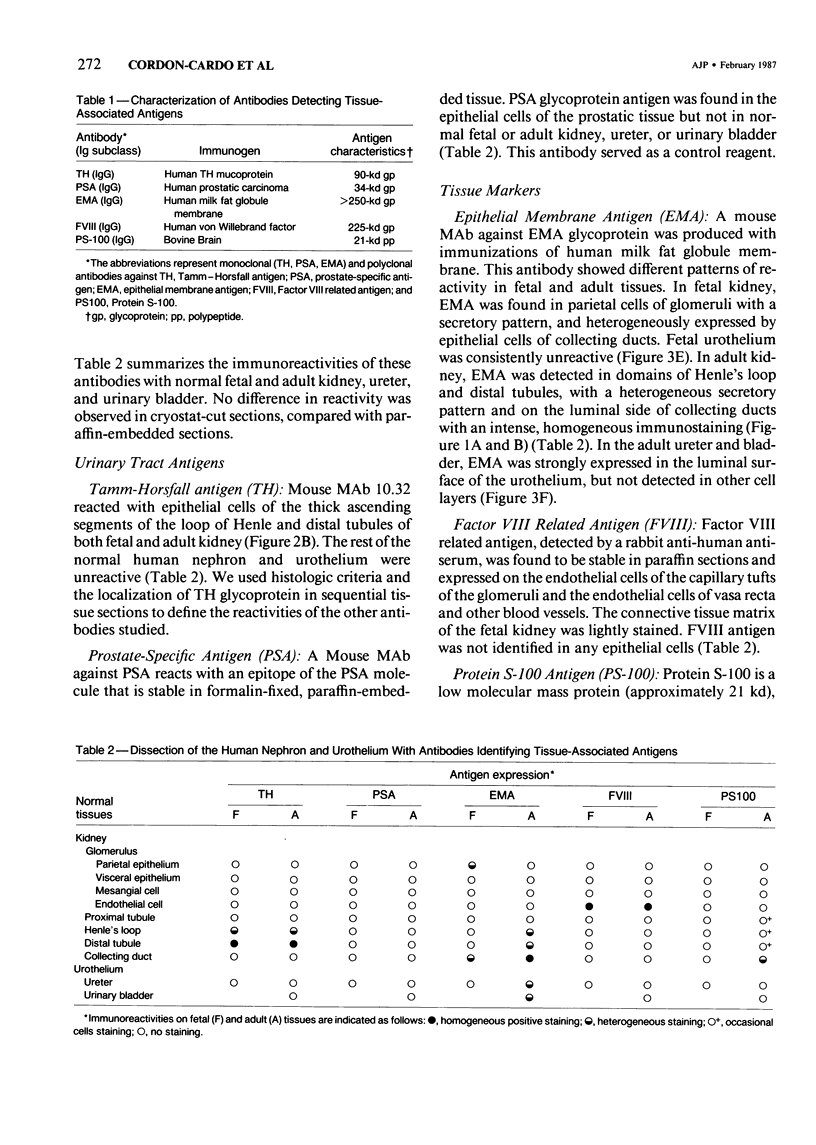
- Fleming S., Lindop G. B., Gibson A. A. The distribution of epithelial membrane antigen in the kidney and its tumours. Histopathology. 1985 Jul;9(7):729–739. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1985.tb02859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E. D., Tuszynski G. P., Warren L. Localization of vimentin and desmin in BHK21/C13 cells and in baby hamster kidney. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jun;139(2):235–247. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Different intermediate-sized filaments distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5034–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Weber K. The regulatory chain in the p36-kd substrate complex of viral tyrosine-specific protein kinases is related in sequence to the S-100 protein of glial cells. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2917–2920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Vogel A. M. Monoclonal antibodies to human intermediate filament proteins. II. Distribution of filament proteins in normal human tissues. Am J Pathol. 1984 Feb;114(2):309–321. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyderman E., Steele K., Ormerod M. G. A new antigen on the epithelial membrane: its immunoperoxidase localisation in normal and neoplastic tissue. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jan;32(1):35–39. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthöfer H., Miettinen A., Lehto V. P., Lehtonen E., Virtanen I. Expression of vimentin and cytokeratin types of intermediate filament proteins in developing and adult human kidneys. Lab Invest. 1984 May;50(5):552–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthöfer H., Miettinen A., Lehto V. P., Lehtonen E., Virtanen I. Expression of vimentin and cytokeratin types of intermediate filament proteins in developing and adult human kidneys. Lab Invest. 1984 May;50(5):552–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthöfer H., Virtanen I., Pettersson E., Törnroth T., Alfthan O., Linder E., Miettinen A. Lectins as fluorescence microscopic markers for saccharides in the human kidney. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Soban E. Color modification of diaminobenzidine (DAB) precipitation by metallic ions and its application for double immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Oct;30(10):1079–1082. doi: 10.1177/30.10.6182185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hydén H., Lange P. W., Larsson S. S100-glia regulation of GABA transport across the nerve cell membrane. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Mar;45(2-3):303–316. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe T., Okuyama T. The amino-acid sequence of the alpha subunit in bovine brain S-100a protein. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):79–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A. Synthesis of factor VIII by endothelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;401:163–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaissling B., Kriz W. Structural analysis of the rabbit kidney. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1979;56:1–123. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Rappaport J., Solter D. Murine embryonic antigen (SSEA-1) is expressed on human cells and structurally related human blood group antigen I is expressed on mouse embryos. Dev Biol. 1982 Sep;93(1):54–58. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments: a chemically heterogeneous, developmentally regulated class of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:219–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magil A. B. Histogenesis of glomerular crescents. Immunohistochemical demonstration of cytokeratin in crescent cells. Am J Pathol. 1985 Aug;120(2):222–229. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makin C. A., Bobrow L. G., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibody to cytokeratin for use in routine histopathology. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):975–983. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mani R. S., Boyes B. E., Kay C. M. Physicochemical and optical studies on calcium- and potassium-induced conformational changes in bovine brain S-100b protein. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2607–2612. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen A., Linder E. Membrane antigens shared by renal proximal tubules and other epithelia associated with absorption and excretion. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Mar;23(3):568–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molin S. O., Rosengren L., Baudier J., Hamberger A., Haglid K. S-100 alpha-like immunoreactivity in tubules of rat kidney. A clue to the function of a "brain-specific" protein. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Apr;33(4):367–374. doi: 10.1177/33.4.3884707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. W. A soluble protein characteristic of the nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 9;19(6):739–744. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Intermediate filaments: cell-type-specific markers in differentiation and pathology. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):303–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Tumor diagnosis by intermediate filament typing: a novel tool for surgical pathology. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):372–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., LeBien T. W., Michael A. F. Stages of renal ontogenesis identified by monoclonal antibodies reactive with lymphohemopoietic differentiation antigens. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):155–172. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Osborn M., Schimid E., Weber K., Bloemendal H., Franke W. W. Identification of the cytoskeletal proteins in lens-forming cells, a special epitheloid cell type. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jun;127(2):309–327. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90437-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudofsky U. H., Dilwith R. L., Lynes M., Flaherty L. Murine monoclonal antikidney autoantibodies. I. Anti-renal proximal tubular basement membrane autoantibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Nov;25(2):165–178. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinman J. I., Foidart J. M., Gehron-Robey P., Fish A. J., Michael A. F. The immunohistology of glomerular antigens. IV. Laminin, a defined noncollagen basement membrane glycoprotein. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Feb;15(2):175–189. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal G. M., Rowland R. G., Thomalla J. V., Rudolph R. A., Pfaff D. S., Kamer M., Eble J. N. A, B and H antigens in normal urothelium: an immunohistochemical study using monoclonal antibodies with the avidin-biotin complex technique. J Urol. 1985 Mar;133(3):513–516. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)49043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloane J. P., Ormerod M. G. Distribution of epithelial membrane antigen in normal and neoplastic tissues and it value in diagnostic tumor pathology. Cancer. 1981 Apr 1;47(7):1786–1795. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810401)47:7<1786::aid-cncr2820470711>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Isobe T., Ohtsuki Y., Akagi T., Sonobe H., Okuyama T. Immunohistochemical study on the distribution of alpha and beta subunits of S-100 protein in human neoplasm and normal tissues. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1984;45(4):385–396. doi: 10.1007/BF02889881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng S. C., Jarvinen M. J., Nelson W. G., Huang J. W., Woodcock-Mitchell J., Sun T. T. Correlation of specific keratins with different types of epithelial differentiation: monoclonal antibody studies. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanstapel M. J., Gatter K. C., de Wolf-Peeters C., Mason D. Y., Desmet V. D. New sites of human S-100 immunoreactivity detected with monoclonal antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Feb;85(2):160–168. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/85.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldherr R., Schwechheimer K. Co-expression of cytokeratin and vimentin intermediate-sized filaments in renal cell carcinomas. Comparative study of the intermediate-sized filament distribution in renal cell carcinomas and normal human kidney. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1985;408(1):15–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00739959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zager R. A., Cotran R. S., Hoyer J. R. Pathologic localization of Tamm-Horsfall protein in interstitial deposits in renal disease. Lab Invest. 1978 Jan;38(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]