Abstract
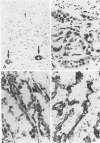
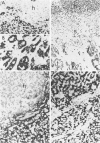
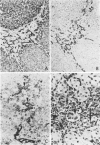
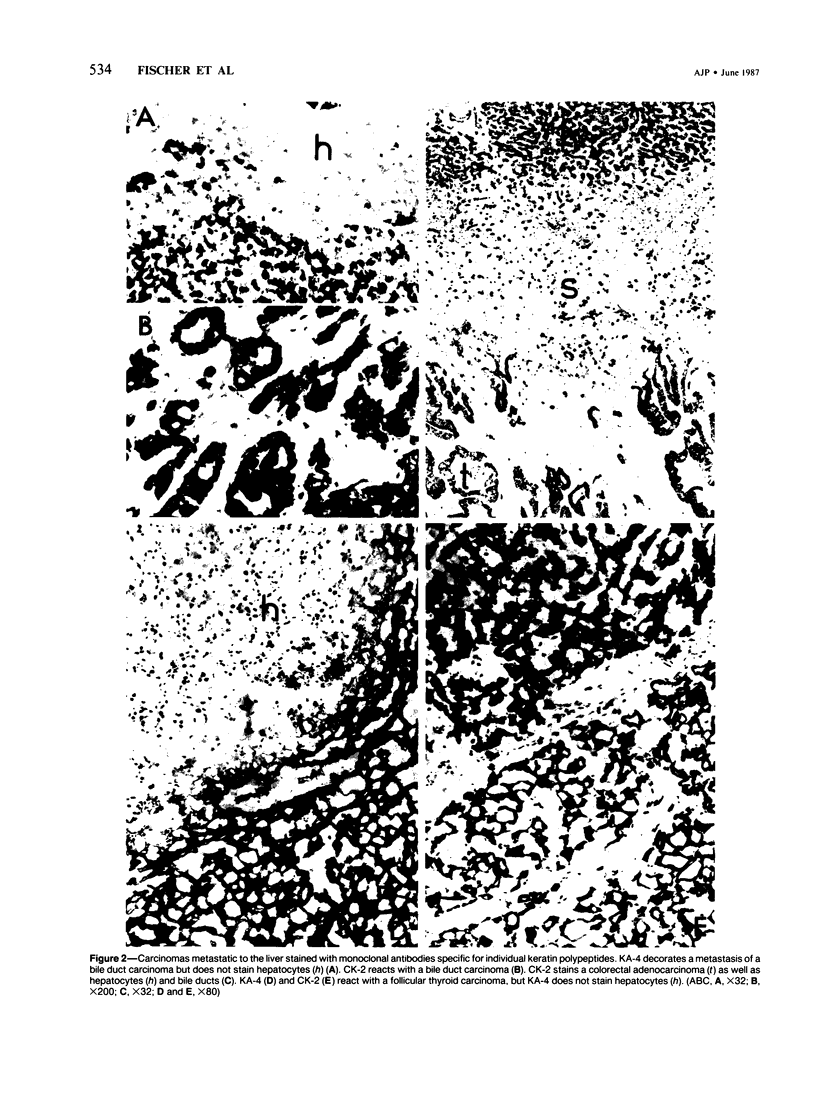
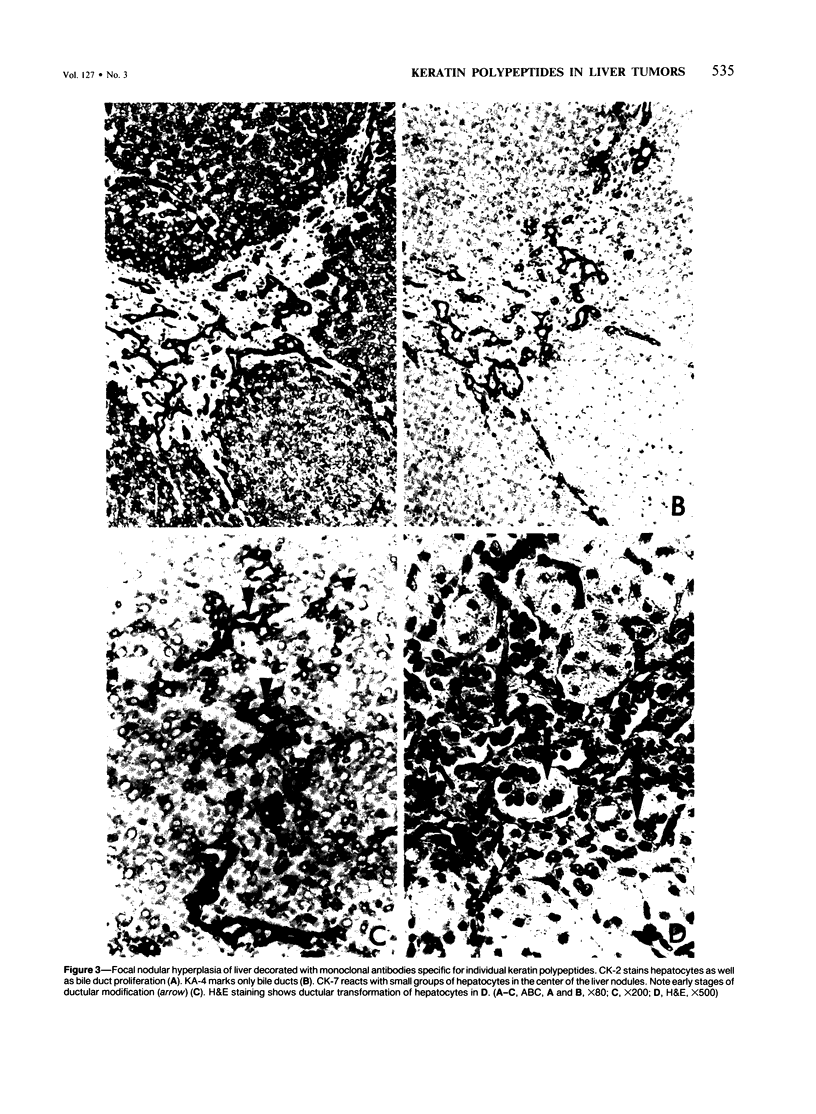
Five monoclonal antibodies recognizing different keratin polypeptides in immunoblotting or different epithelial cell types in complex tissues were studied for their suitability as reagents for the differential diagnosis of primary and secondary malignant epithelial liver tumors. The broad specificity keratin antibodies lu-5 and KL-1 stained all epithelial liver neoplasms. In contrast the antibodies CK-7 (Ker-7-specific), CK-2 (Ker-18-specific) and KA-4 (Ker-19-specific in liver) allow these neoplasms to be divided into three groups: Hepatocellular carcinomas were CK-2-positive and CK-7-negative. Cholangiocellular carcinomas, liver metastases of extrahepatic bile duct carcinomas, liver metastases of a ductal carcinoma of breast, and a follicular thyroid carcinoma were stained positively by CK-2, CK-7, and KA-4. In 1 of 6 hepatocellular carcinomas neoplastic hepatocytes were focally labeled by KA-4. In a focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver modified hepatocytes were decorated not only by CK-2 but also by CK-7 and KA-4. Liver metastases of colorectal adenocarcinomas and of a carcinoid tumor were stained positively by CK-2 and KA-4 but not by CK-7.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmannsberger M., Dirk T., Droese M., Weber K., Osborn M. Keratin polypeptide distribution in benign and malignant breast tumors: subdivision of ductal carcinomas using monoclonal antibodies. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1986;51(3):265–275. doi: 10.1007/BF02899036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D., Schermer A., Sun T. T. Classification of human epithelia and their neoplasms using monoclonal antibodies to keratins: strategies, applications, and limitations. Lab Invest. 1985 Mar;52(3):243–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Moll R., Franke W. W., Weber K., Osborn M. Immunohistochemical distinction of human carcinomas by cytokeratin typing with monoclonal antibodies. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jan;114(1):121–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Weber K., Osborn M. Monoclonal cytokeratin antibodies that distinguish simple from stratified squamous epithelia: characterization on human tissues. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1641–1647. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denk H., Krepler R., Lackinger E., Artlieb U., Franke W. W. Biochemical and immunocytochemical analysis of the intermediate filament cytoskeleton in human hepatocellular carcinomas and in hepatic neoplastic nodules of mice. Lab Invest. 1982 Jun;46(6):584–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enzan H., Okita T., Fujita H., Iijima S. Light and electron microscopic studies on the development of periportal bile ducts of the human embryo. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1974 Jul;24(4):427–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1974.tb00835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. B. Monoclonal antibodies provide specific intramolecular markers for the study of epithelial tonofilament organization. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):665–673. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapis K., Johannessen J. V. Pathology of primary liver cancer. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1979 Mar-May;5(2-3):315–355. doi: 10.1080/15287397909529752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle R. B., Lucas D. O., McDaniel K. M., Clark V. A., Schmalzel G. M. Paget's cells. New evidence linking mammary and extramammary Paget cells to a common cell phenotype. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Apr;83(4):431–438. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle R. B., Moll R., Weidauer H., Nemetschek H., Franke W. W. Different patterns of cytokeratin expression in the normal epithelia of the upper respiratory tract. Differentiation. 1985;30(2):130–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1985.tb00524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Altmannsberger M., Debus E., Weber K. Differentiation of the major human tumor groups using conventional and monoclonal antibodies specific for individual intermediate filament proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:649–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan R. A., Schiller D. L., Hatzfeld M., Achtstätter T., Moll R., Jorcano J. L., Magin T. M., Franke W. W. Patterns of expression and organization of cytokeratin intermediate filaments. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:282–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng S. C., Jarvinen M. J., Nelson W. G., Huang J. W., Woodcock-Mitchell J., Sun T. T. Correlation of specific keratins with different types of epithelial differentiation: monoclonal antibody studies. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tölle H. G., Weber K., Osborn M. Microinjection of monoclonal antibodies specific for one intermediate filament protein in cells containing multiple keratins allow insight into the composition of particular 10 nm filaments. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;38(2):234–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viac J., Reano A., Brochier J., Staquet M. J., Thivolet J. Reactivity pattern of a monoclonal antikeratin antibody (KL1). J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Oct;81(4):351–354. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12519941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEGMANN R., CORCOS V., CAROLI J. HISTOENZYMOLOGIE DES DUCTULES BILIAIRES CHEZ L'EMBRYON HUMAIN NORMAL ET AU COURS DES CIRRHOSES HUMAINES. Arch Mal Appar Dig Mal Nutr. 1965 Mar;54:215–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. J., Parker L. M., Binder N. E., Beckett M. A., Sinard J. H., Griffiths C. T., Rheinwald J. G. The mesothelial keratins: a new family of cytoskeletal proteins identified in cultured mesothelial cells and nonkeratinizing epithelia. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):693–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Overbeck J., Stähli C., Gudat F., Carmann H., Lautenschlager C., Dürmüller U., Takacs B., Miggiano V., Staehelin T., Heitz P. U. Immunohistochemical characterization of an anti-epithelial monoclonal antibody (mAB lu-5). Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1985;407(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00701324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]