Abstract
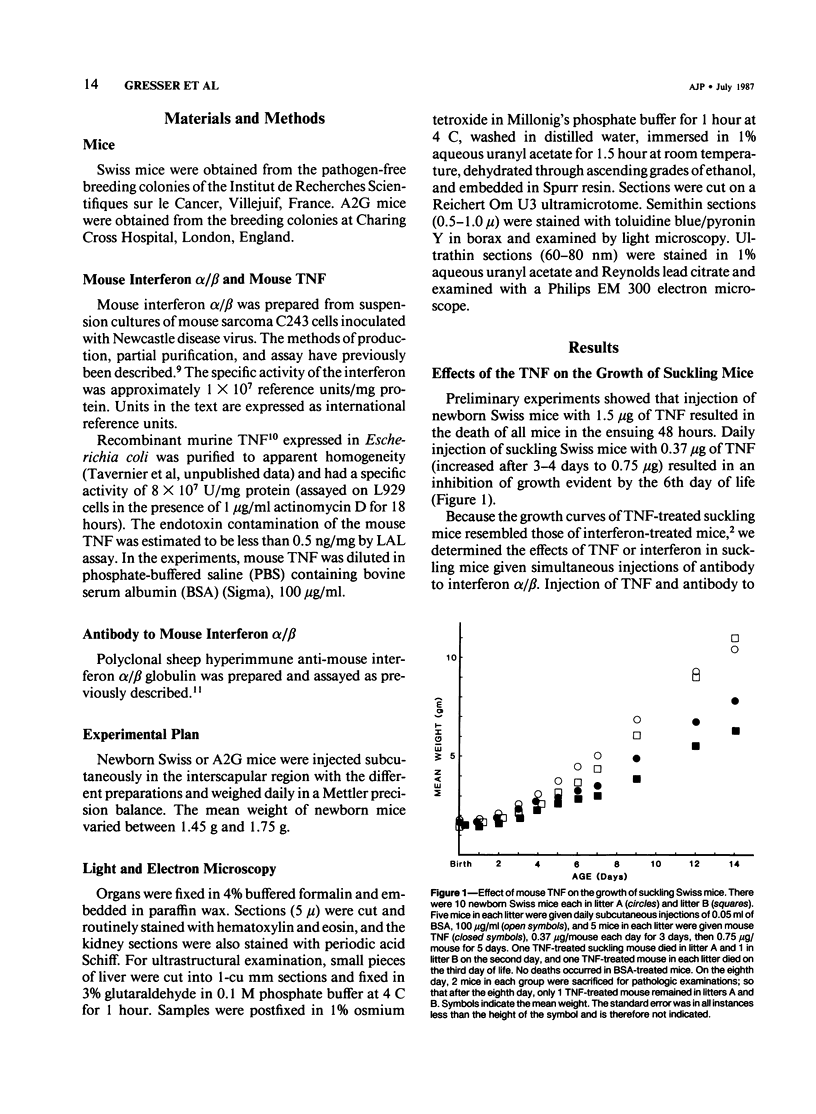
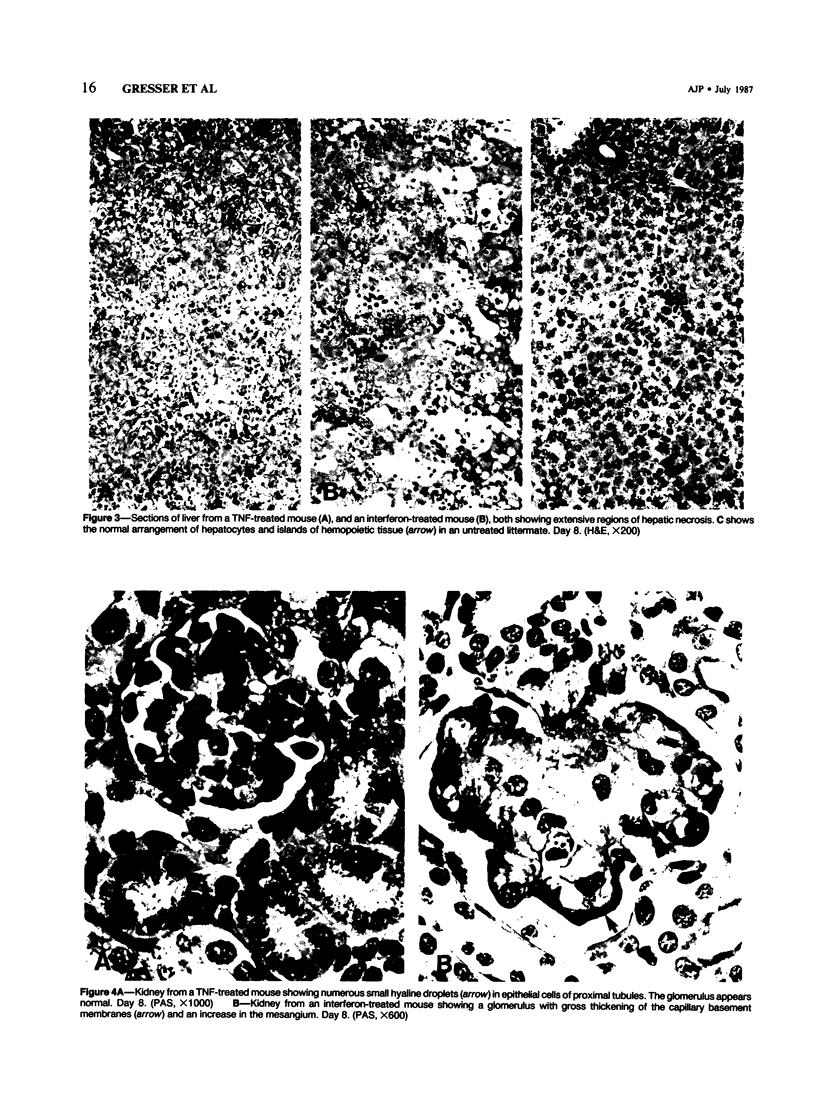
Newborn Swiss and A2G mice were given daily subcutaneous injections for 1 week of highly purified recombinant mouse tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or mouse interferon alpha/beta. Both treatments resulted in inhibition of growth of suckling mice and severe fatty changes and necrosis in the liver. The simultaneous injection of polyclonal antibody to interferon alpha/beta abrogated the effects of interferon but did not block the effects induced by TNF. The kidneys of TNF-treated suckling mice could be distinguished from interferon-treated mice by the absence of glomerular basement membrane abnormalities and the presence of numerous rounded eosinophilic hyaline granules within the cytoplasm of the proximal tubules. Treatment of suckling mice with TNF and interferon alpha/beta induced similar changes in the spleen and thymus. Interferon treatment of suckling A2G mice resulted in the appearance of pulmonary cysts, which were not observed in TNF-treated mice. It is concluded that the pattern of lesions induced in suckling mice by mouse TNF is both similar and different from that induced by mouse interferon alpha/beta.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Mahoney J., Le Trang N., Pekala P., Cerami A. Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):984–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen L., Müller R., Marmenout A., Tavernier J., Van der Heyden J., Kawashima E., Chollet A., Tizard R., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Vliet A. Molecular cloning of mouse tumour necrosis factor cDNA and its eukaryotic expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4417–4429. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Aguet M., Morel-Maroger L., Woodrow D., Puvion-Dutilleul F., Guillon J. C., Maury C. Electrophoretically pure mouse interferon inhibits growth, induces liver and kidney lesions, and kills suckling mice. Am J Pathol. 1981 Mar;102(3):396–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Belardelli F., Tavernier J., Fiers W., Podo F., Federico M., Carpinelli G., Duvillard P., Prade M., Maury C. Anti-tumor effects of interferon in mice injected with interferon-sensitive and interferon-resistant Friend leukemia cells. V. Comparisons with the action of tumor necrosis factor. Int J Cancer. 1986 Nov 15;38(5):771–778. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I. Can interferon induce disease? Interferon. 1982;4:95–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Maury C., Tovey M., Morel-Maroger L., Pontillon F. Progressive glomerulonephritis in mice treated with interferon preparations at birth. Nature. 1976 Sep 30;263(5576):420–422. doi: 10.1038/263420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Bandu M. E., Maury C., Brouty-Boyé D. Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases in mice as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. I. Rapid evolution of encephalomyocarditis virus infection. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1305–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Maury C., Chouroulinkov I. Lethality of interferon preparations for newborn mice. Nature. 1975 Nov 6;258(5530):76–78. doi: 10.1038/258076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel-Maroger L., Sloper J. C., Vinter J., Woodrow D., Gresser I. An ultrastructural study of the development of nephritis in mice treated with interferon in the neonatal period. Lab Invest. 1978 Nov;39(5):513–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Woodrow D. F., Sloper J. C., Rivière Y., Guillon J. C., Gresser I. Interferon as a cause of endoplasmic reticulum abnormalities within hepatocytes in newborn mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Feb;63(1):43–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strander H. Interferon treatment of human neoplasia. Adv Cancer Res. 1986;46:1–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M., Dieckmann B., Beutler B., Cerami A., Ringold G. M. A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.3839597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Begon-Lours J., Gresser I. A method for the large scale production of potent interferon preparations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jul;146(3):809–815. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodrow D., Moss J., Gresser I. Interferon induces pulmonary cysts in A2G mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7937–7940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwingelstein G., Meister R., Malak N. A., Maury C., Gresser I. Interferon alters the composition and metabolism of lipids in the liver of suckling mice. J Interferon Res. 1985 Spring;5(2):315–325. doi: 10.1089/jir.1985.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]