Abstract
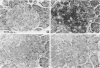
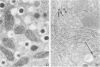
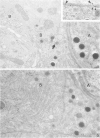
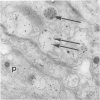
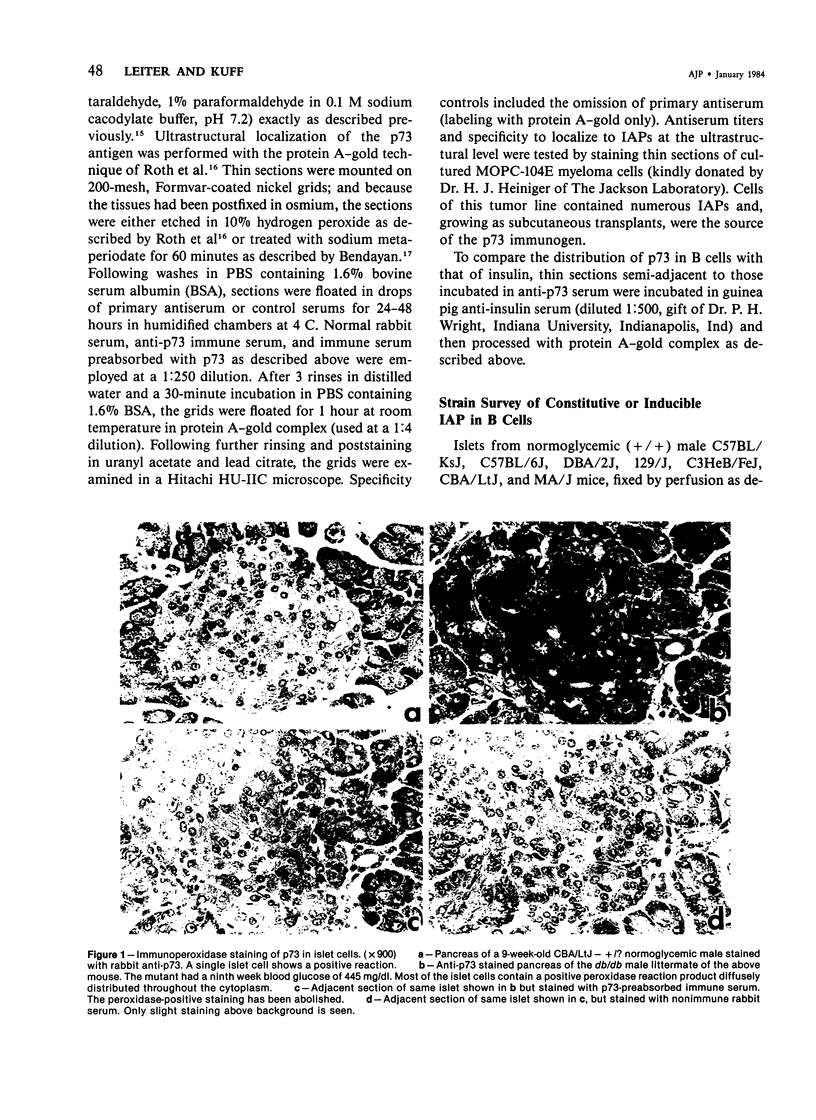
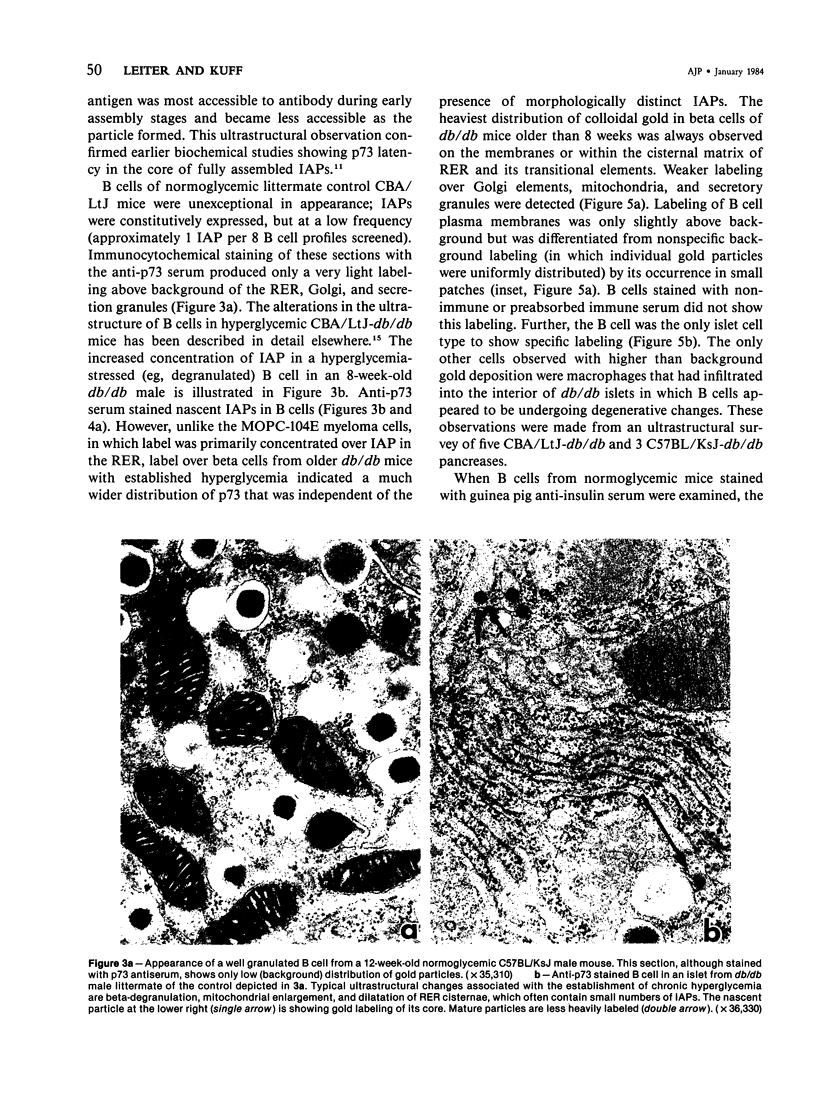
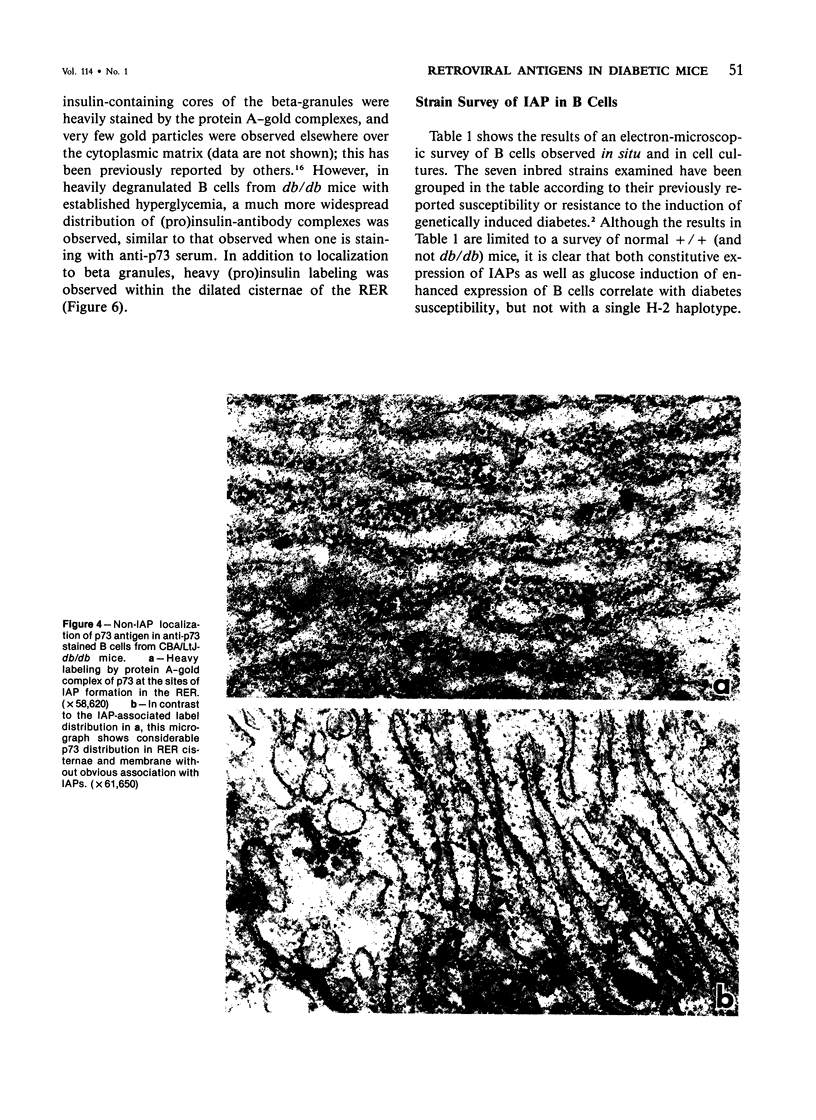
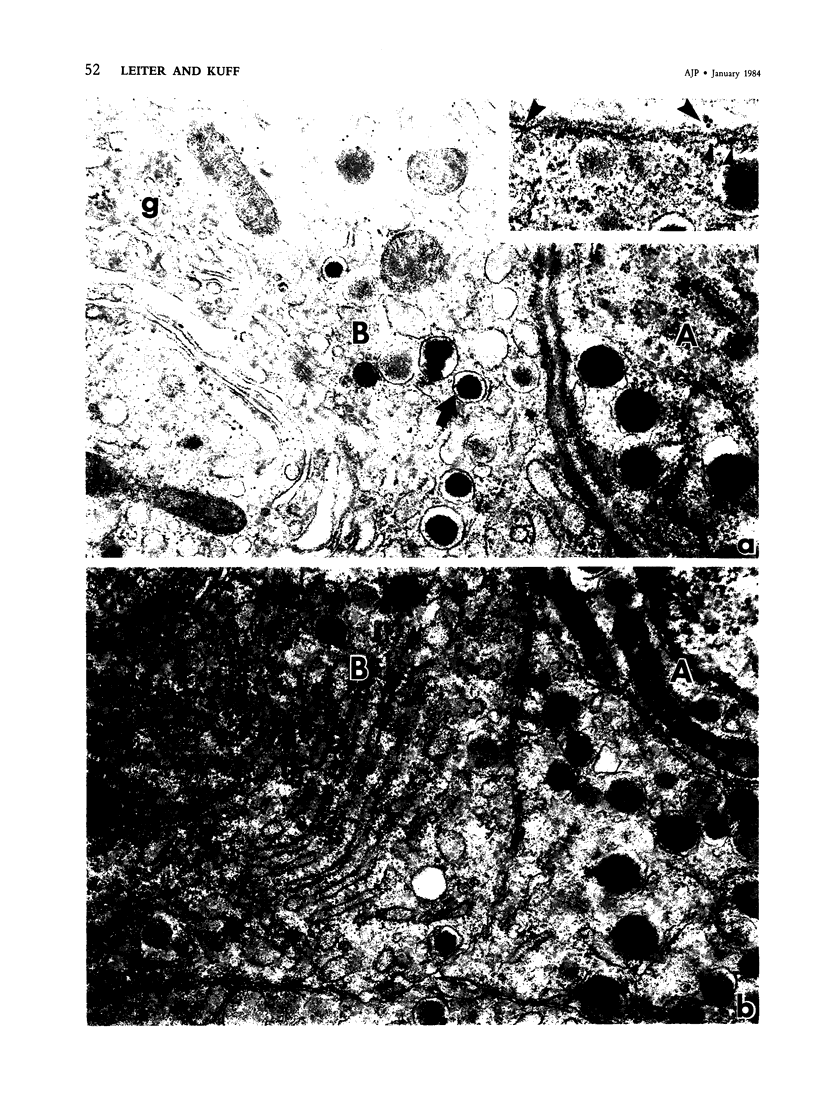
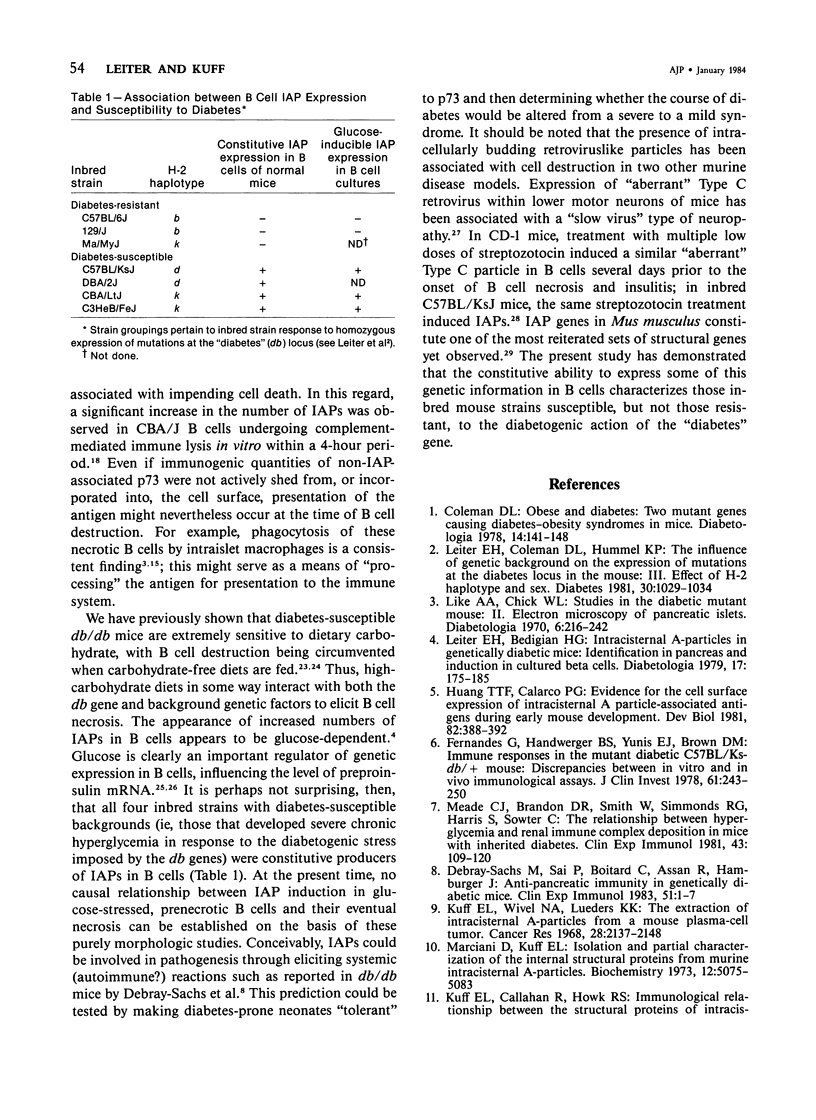
Intracisternal Type A particles (IAPs) are retroviruslike structures identified by a core protein antigen (p73) and found in mouse embryos, in many mouse tumor cells, and in pancreatic B cells of some strains of genetically diabetic mice. Using both peroxidase-antiperoxidase and protein A-gold immunocytochemical techniques to localize p73, the authors have observed differences in intracellular antigen distribution between MOPC-104E, a mouse tumor cell line rich in IAP, and B cells from genetically diabetic (db/db) mice of the CBA/LtJ and C57BL/KsJ strain. In MOPC-104E cells studied by electron microscopy, localization of protein A-gold complex label was almost exclusively limited to IAP and their sites of assembly on the rough endoplasmic reticulum. In contrast, p73 appeared widely distributed throughout the cytoplasm of B cells from hyperglycemic db/db mice but not normal littermate controls. In addition to distribution over budding IAP, label was also found dispersed through other cytoplasmic organelles involved in secretion, including Golgi complexes and secretory granules. Patch labeling of B cell surfaces was sometimes observed. An ultrastructural survey of islets isolated from normal mice of 7 inbred genetic backgrounds on which the "diabetes" (db) gene has been studied showed that constitutive ability to produce IAP was associated with strain susceptibility to severe diabetes (eg, C57BL/KsJ, DBA/2J, CBA/LtJ, and C3HeB/FeJ). Strains whose B cells failed to show constitutive expression in situ or glucose-inducible expression in cell culture were resistant to the diabetogenic action of db genes. The possibility is discussed that p73 may represent a "neoantigen" which sensitizes the diabetic mouse to reject, by autoimmune mechanisms, the B cells expressing it.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J. M., Gardner M. B. Lower motor neuron degeneration associated with type C RNA virus infection in mice: neuropathological features. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1974 Apr;33(2):285–307. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197404000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appel M. C., Rossini A. A., Williams R. M., Like A. A. Viral studies in streptozotocin-induced pancreatic insulitis. Diabetologia. 1978 Oct;15(4):327–336. doi: 10.1007/BF02573827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendayan M., Zollinger M. Ultrastructural localization of antigenic sites on osmium-fixed tissues applying the protein A-gold technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jan;31(1):101–109. doi: 10.1177/31.1.6187796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunstedt J., Chan S. J. Direct effect of glucose on the preproinsulin mRNA level in isolated pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1383–1389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia. 1978 Mar;14(3):141–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00429772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debray-Sachs M., Saï P., Boitard C., Assan R., Hamburger J. Anti-pancreatic immunity in genetically diabetic mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jan;51(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes G., Handwerger B. S., Yunis E. J., Brown D. M. Immune response in the mutant diabetic C57BL/Ks-dt+ mouse. Discrepancies between in vitro and in vivo immunological assays. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):243–250. doi: 10.1172/JCI108933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Chirgwin J., Permutt M. A. Effects of glucose on proinsulin messenger RNA in rats in vivo. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):624–629. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyderman E. Immunoperoxidase technique in histopathology: applications, methods, and controls. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Oct;32(10):971–978. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.10.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. T., Jr, Calarco P. G. Evidence for the cell surface expression of intracisternal A particle-associated antigens during early mouse development. Dev Biol. 1981 Mar;82(2):388–392. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90462-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Callahan R., Howk R. S. Immunological relationship between the structural proteins of intracisternal A-particles of Mus musculus and the M432 retrovirus of Mus cervicolor. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1211–1214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1211-1214.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Leuders K. K., Ozer H. L., Wivel N. A. Some structural and antigenic properties of intracisternal A particles occurring in mouse tumors (complement fixation-immunodiffusion-neuroblastoma-plasma-cell tumor). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):218–222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Smith L. A., Lueders K. K. Intracisternal A-particle genes in Mus musculus: a conserved family of retrovirus-like elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):216–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Wivel N. A., Lueders K. K. The extraction of intracisternal A-particles from a mouse plasma-cell tumor. Cancer Res. 1968 Oct;28(10):2137–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Bedigian H. G. Intracisternal A-particles in genetically diabetic mice: identification in pancreas and induction in cultured beta cells. Diabetologia. 1979 Sep;17(3):175–185. doi: 10.1007/BF01219746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Coleman D. L., Eisenstein A. B., Strack I. Dietary control of pathogenesis in C57BL/KsJ db/db diabetes mice. Metabolism. 1981 Jun;30(6):554–562. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Coleman D. L., Hummel K. P. The influence of genetic background on the expression of mutations at the diabetes locus in the mouse. III. Effect of H-2 haplotype and sex. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1029–1034. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Coleman D. L., Ingram D. K., Reynolds M. A. Influence of dietary carbohydrate on the induction of diabetes in C57BL/KsJ-db/db diabetes mice. J Nutr. 1983 Jan;113(1):184–195. doi: 10.1093/jn/113.1.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Simon D., Cherry M., Phillips C. A. Induction in C57BL/KsJ mice of complement-dependent antibody cytotoxic to cultured beta cells. Diabetes. 1981 Jan;30(1):30–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.1.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H. The influence of genetic background on the expression of mutations at the diabetes locus in the mouse IV. Male lethal syndrome in CBA/Lt mice. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1035–1044. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Chick W. L. Studies in the diabetic mutant mouse. II. Electron microscopy of pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1970 Jun;6(3):216–242. doi: 10.1007/BF01212232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Synthesis and turnover of intracisternal A-particle structural protein in cultured neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5192–5199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciani D. J., Kuff E. L. Isolation and partial characterization of the internal structural proteins from murine intracisternal A particles. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5075–5083. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade C. J., Brandon D. R., Smith W., Simmonds R. G., Harris S., Sowter C. The relationship between hyperglycaemia and renal immune complex deposition in mice with inherited diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jan;43(1):109–120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L. Macro- and micro-domains in the endocrine pancreas. Diabetes. 1982 Jun;31(6 Pt 1):538–565. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.6.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poffenbarger P. L., Chick W. L., Lavine R. L., Soeldner J. S., Flewelling J. H. Insulin biosynthesis in experimental hereditary diabetes. Diabetes. 1971 Oct;20(10):677–685. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.10.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Orci L. Ultrastructural localization of intracellular antigens by the use of protein A-gold complex. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Dec;26(12):1074–1081. doi: 10.1177/26.12.366014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]