Abstract
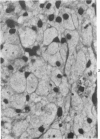
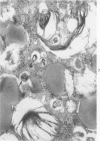
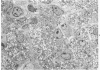
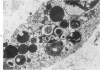
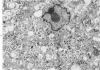
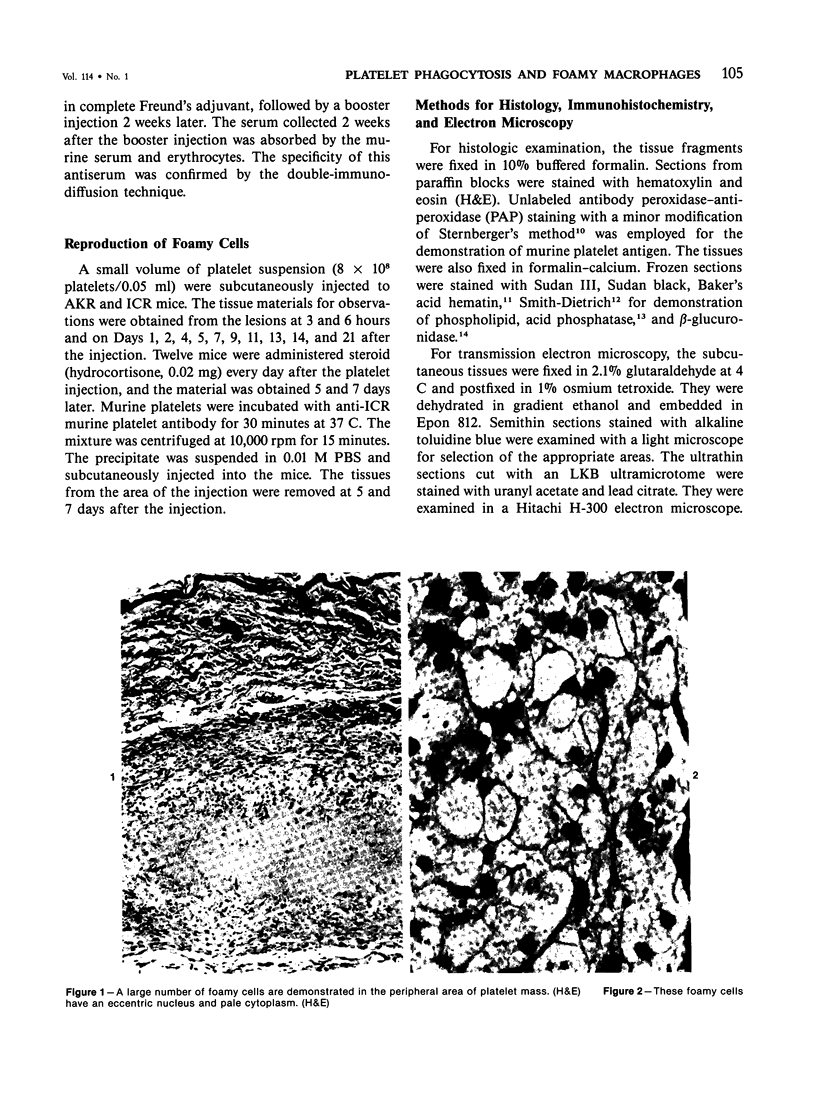
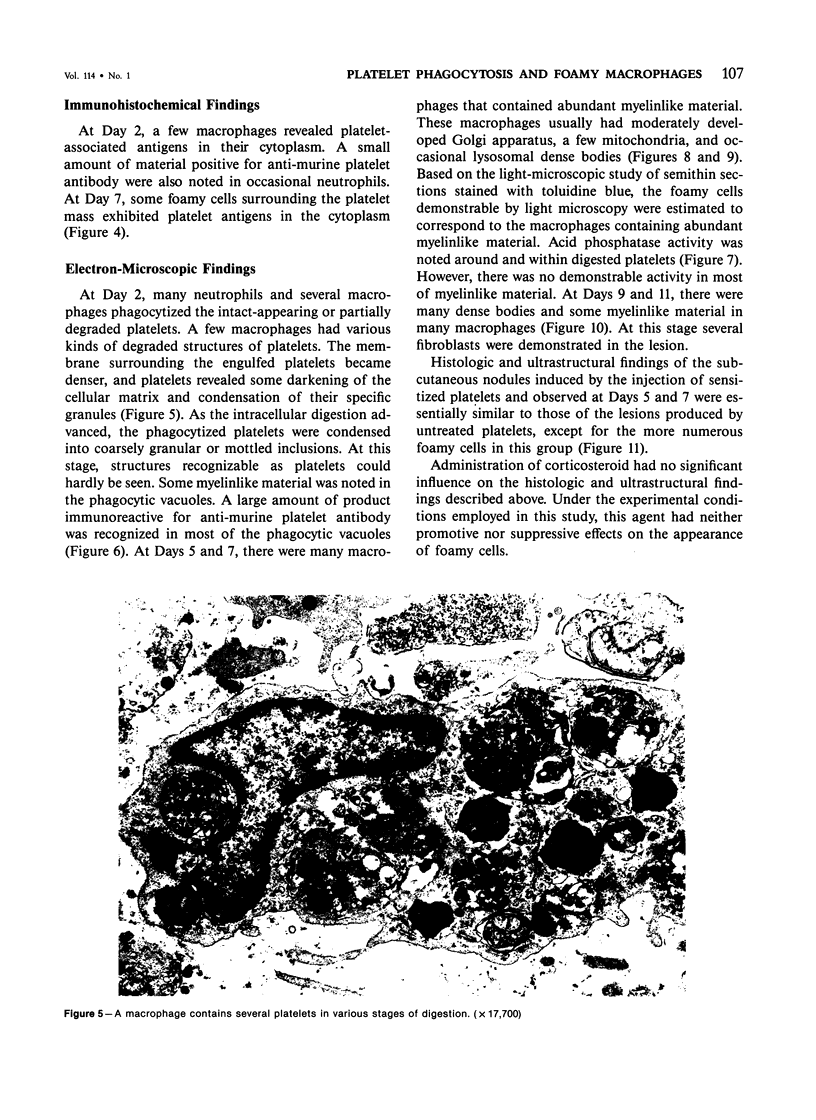
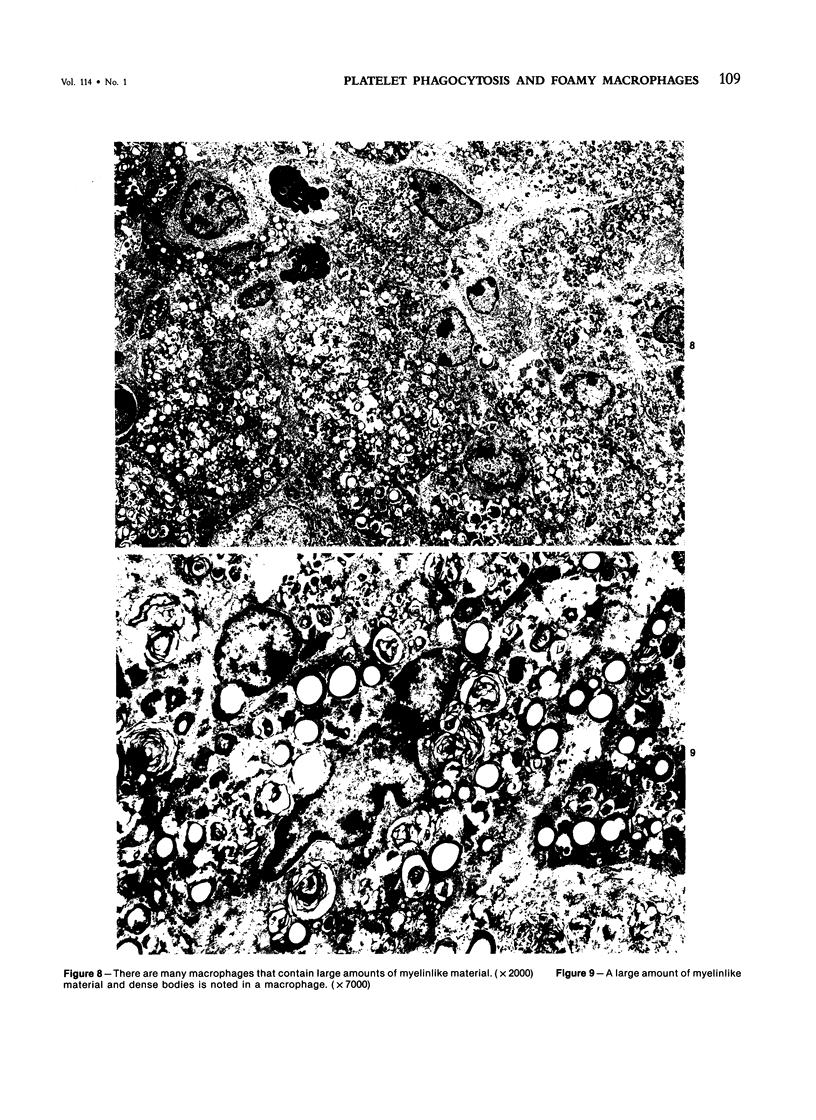
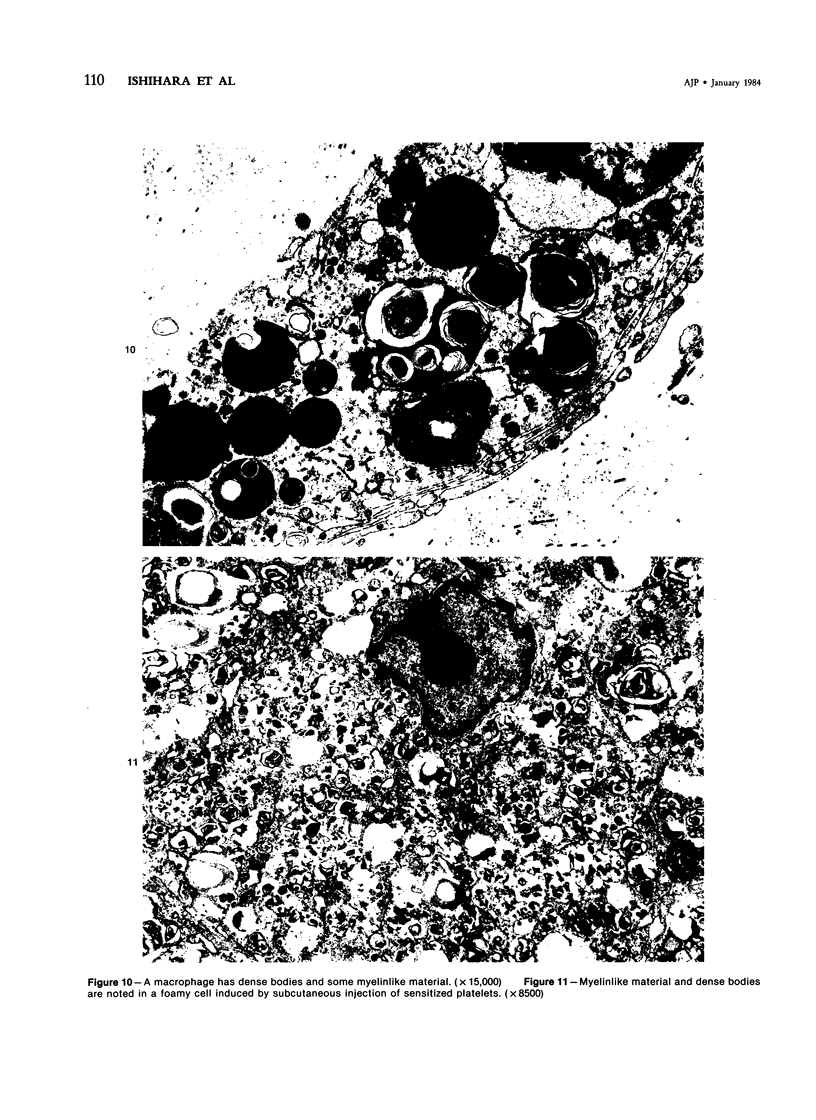
In order to gain an insight into the mechanism for the formation of foamy cells (macrophages with foamy cytoplasm) frequently seen in spleens affected by idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), these cells were experimentally induced in mice by subcutaneous injection of platelets with or without accompanied administration of corticosteroid. The light- and electron-microscopic features of experimentally reproduced foamy cells were essentially similar to those seen in the spleens of ITP patients. Corticosteroid had no significant effect on the formation of foamy cells. Most macrophages with foamy cytoplasm contained various amounts of phospholipids, which were derived from platelet membranes. By electron microscopy, myelinlike materials were frequently demonstrated in the cytoplasm of foamy cells. Although lysosomal enzyme activity was revealed in the macrophages that contained morphologically recognizable platelets, there was no demonstrable activity in the cells that contained myelinlike materials. From these results, the following conclusion has been suggested as the mechanism for the formation of foamy cells. Under the state of accelerated phagocytosis of platelets by the macrophages, such as in ITP, the amount of ingested platelet membranes is beyond the capacity of lysosomal digestion. Thus, the incompletely degraded membrane constituents, especially membrane-derived phospholipids, remain in the macrophages, and they are most responsible for the foamy appearance of these macrophages.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DOLLBERG L., CASPER J., DJALDETTI M., KLIBANSKY C., DEVRIES A. LIPID-LADEN HISTIOCYTES IN THE SPLEEN IN THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Jan;43:16–25. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/43.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firkin B. G., Wright R., Miller S., Stokes E. Splenic macrophages in thrombocytopenia. Blood. 1969 Feb;33(2):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYASHI M., NAKAJIMA Y., FISHMAN W. H. THE CYTOLOGIC DEMONSTRATION OF BETA-GLUCURONIDASE EMPLOYING NAPHTHOL AS-BI GLUCURONIDE AND HEXAZONIUM PARAROSANILIN; A PRELIMINARY REPORT. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Apr;12:293–297. doi: 10.1177/12.4.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL J. M., SPEER R. J., GEDIKOGLU H. Secondary lipidosis of spleen associated with thrombocytopenia and other blood dyscrasias treated with steroids. Am J Clin Pathol. 1963 Jun;39:607–615. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/39.6.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara T., Matsumoto N., Uchino F. Foamy histiocytes in the spleen associated with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1974 Mar;24(2):273–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1974.tb00822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDING B. H., STRAUSS L., CROCKER A. C., BRAUNSTEIN H., HENLEY W. L., WILL J. R., SANDERS M. Thrombocytopenic purpura with histiocytosis of the spleen. N Engl J Med. 1961 Sep 21;265:572–577. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196109212651203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk S. C., Musclow E., Simon G. T. Platelet phagocytosis in the spleen of patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). Histopathology. 1980 Mar;4(2):127–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1980.tb02906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTZSTEIN S. L. Phospholipid accumulation in histiocytes of splenic pulp associated with thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1961 Jul;18:73–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Hakozaki H., Terashima K., Kojima M. Two distinctive types of lipid histiocytes appearing in the spleen of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Sea-blue histiocyte and foam cell. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1977 Jul;27(4):447–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1977.tb00167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavassoli M., McMillan R. Structure of the spleen in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Aug;64(2):180–191. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/64.2.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]