Abstract
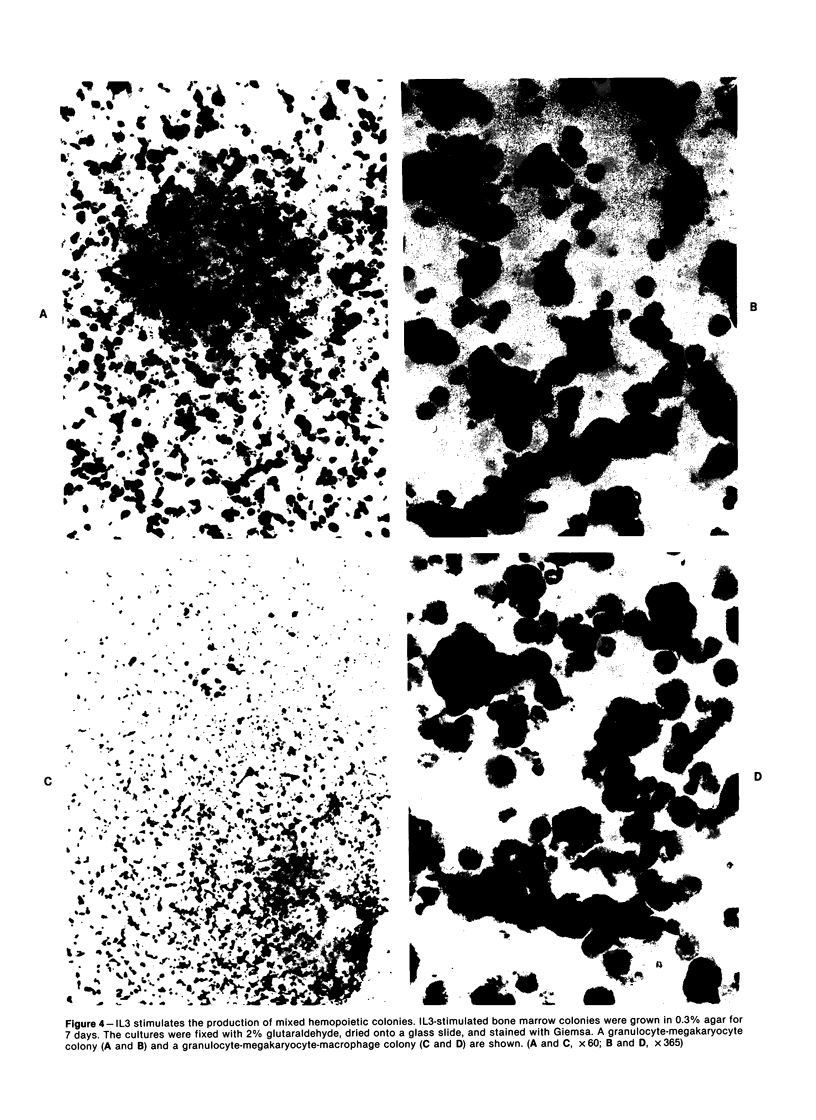
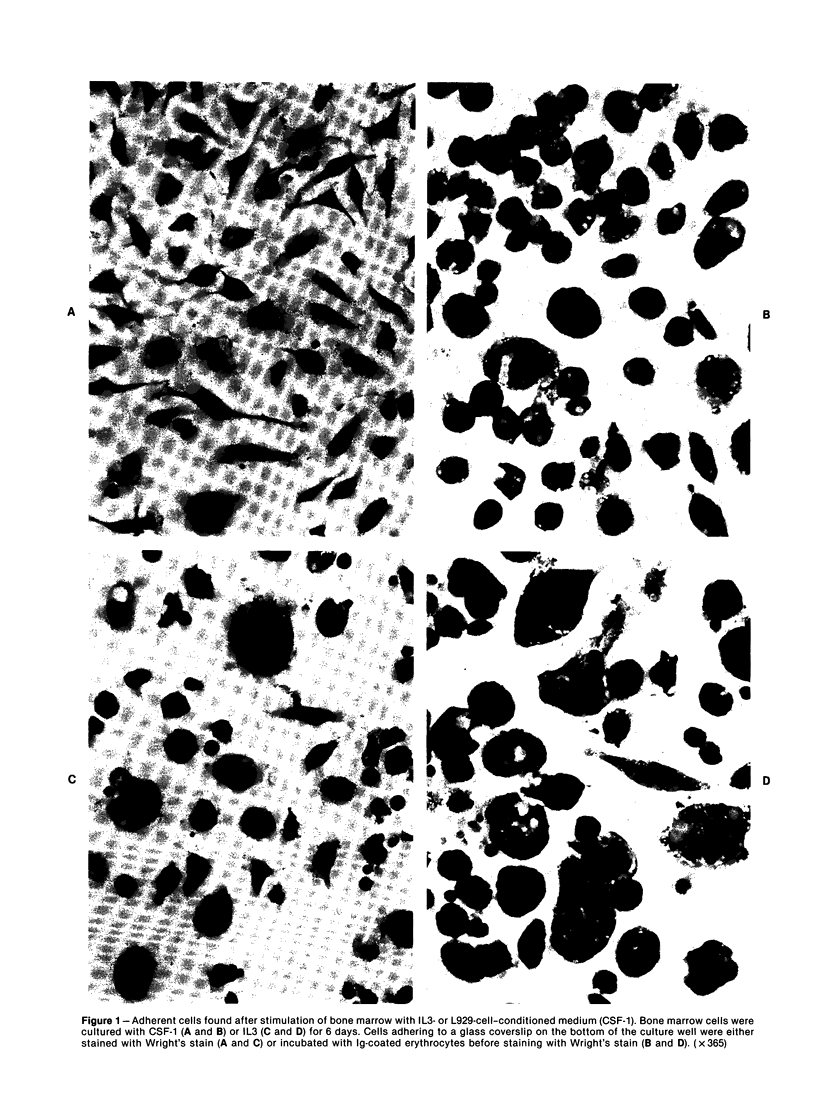
When the murine T-lymphocyte clone L2 is stimulated with concanavalin A, it secretes at least two distinct factors that affect hemopoietic precursor cells, interleukin 3 (IL3) and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). IL3 accounts for approximately 10% of the colony-stimulating activity in L2-cell-conditioned medium. The IL3 secreted by L2 cells is similar antigenically to the IL3 secreted by WEHI-3 cells. Like the IL3 from WEHI-3 cells, IL3 secreted by L2 cells does not bind to DEAE Sephacel and can be separated from the L2-cell GM-CSF, which does bind to DEAE. By assessment of the functional, morphologic, surface phenotypic, and cytochemical characteristics of bone marrow cells 6 days after stimulation with IL3 in liquid culture, four hemopoietic lineages were found, including macrophage, neutrophilic granulocyte, megakaryocyte, and basophil/mast cell. In addition, when bone marrow cells were stimulated with IL3 in semisolid medium, several types of colonies were found, including mixed colonies containing macrophage, megakaryocyte, and granulocyte lineages.
Full text
PDF


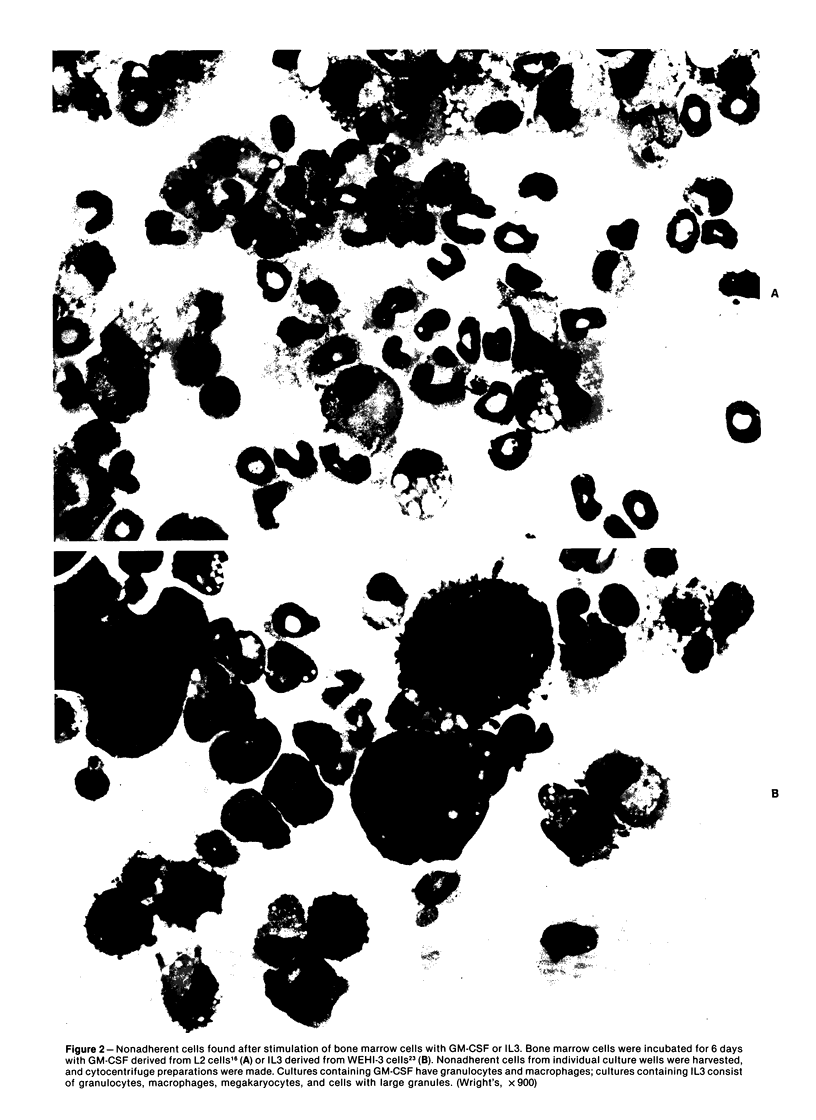



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess A. W., Metcalf D., Russell S. H., Nicola N. A. Granulocyte/macrophage-, megakaryocyte-, eosinophil- and erythroid-colony-stimulating factors produced by mouse spleen cells. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 1;185(2):301–314. doi: 10.1042/bj1850301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Metcalf D. The nature and action of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factors. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):947–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Engers H. D., Macdonald H. R., Brunner T. Generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vitro. I. Response of normal and immune mouse spleen cells in mixed leukocyte cultures. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):703–717. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Schrader J. W. Biochemical characterization of regulatory factors derived from T cell hybridomas and spleen cells. I. Separation of T cell growth factor and T cell replacing factor from granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):168–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S. K., Stanley E. R., Guilbert L. J., Forman L. W. Discrimination of a colony stimulating factor subclass by a specific receptor on a macrophage cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Sep;104(3):359–366. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041040309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely J. M., Prystowsky M. B., Eisenberg L., Quintans J., Goldwasser E., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. Alloreactive cloned T cell lines. V. Differential kinetics of IL 2, CSF, and BCSF release by a cloned T amplifier cell and its variant. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2345–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. Alloreactive cloned T cell lines. I. Interactions between cloned amplifier and cytolytic T cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):876–895. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. T-cell lines which cooperate in generation of specific cytolytic activity. Nature. 1979 Mar 8;278(5700):171–173. doi: 10.1038/278171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilfiker M. L., Moore R. N., Farrar J. J. Biologic properties of chromatographically separated murine thymoma-derived Interleukin 2 and colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1983–1987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Burgess A., McPhee D., Metcalf D. T-cell hybridoma secreting hemopoietic regulatory molecules: granulocyte-macrophage and eosinophil colony-stimulating factors. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90211-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. K., Eaves A. C., Eaves C. J. Self-renewal of hemopoietic stem cells during mixed colony formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3629–3633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Henderson L., Klein F., Palaszynski E. Procedures for the purification of interleukin 3 to homogeneity. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2431–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Oroszlan S., Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Fitch F., Prystowsky M. B., Goldwasser E., Schrader J. W., Palaszynski E. Biologic properties of homogeneous interleukin 3. I. Demonstration of WEHI-3 growth factor activity, mast cell growth factor activity, p cell-stimulating factor activity, colony-stimulating factor activity, and histamine-producing cell-stimulating factor activity. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Roitsch C. A., Williams N., Guilbert L. J. Molecules stimulating early red cell, granulocyte, macrophage, and megakaryocyte precursors in culture: similarity in size, hydrophobicity, and charge. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1982;1:65–78. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. W. Cholinesterase as a possible marker for early cells of the megakaryocytic series. Blood. 1973 Sep;42(3):413–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. SIMPLIFIED MYELOPEROXIDASE STAIN USING BENZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J. THE LOCALIZATION OF CHOLINESTERASE ACTIVITY IN RAT CARDIAC MUSCLE BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Nov;23:217–232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder L. D. Diagnostic experiences with the naphthol AS-D chloroacetate esterase reaction. Blut. 1970 Jul;21(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF01633225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., Quon D. H., Golde D. W. Purification and characterization of a human T-lymphocyte-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1981 Jan;57(1):13–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Russell S., Burgess A. W. Production of hemopoietic stimulating factors by pokeweed-mitogen-stimulated spleen cells. Transplant Proc. 1978 Mar;10(1):91–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Greenberger J. S., Sakakeeny M. A., Cantor H. Multiple biologic activities of a cloned inducer T-cell population. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1157–1161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata T., Ogawa M. Clonal origin of murine hemopoietic colonies with apparent restriction to granuclocyte-macrophage-megakaryocyte (GMM) differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jun;111(3):239–246. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prystowsky M. B., Ely J. M., Beller D. I., Eisenberg L., Goldman J., Goldman M., Goldwasser E., Ihle J., Quintans J., Remold H. Alloreactive cloned T cell lines. VI. Multiple lymphokine activities secreted by helper and cytolytic cloned T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2337–2344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prystowsky M. B., Ely J. M., Naujokas M. F., Goldwasser E., Fitch F. W. Partial purification and characterization of a colony-stimulating factor secreted by a T lymphocyte clone. Exp Hematol. 1983 Nov;11(10):931–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prystowsky M. B., Ely J., Vogel S. N., Goldwasser E., Fitch F. W. Biochemical enrichment of lymphokines secreted by a cloned helper T lymphocyte. Fed Proc. 1983 Jul;42(10):2757–2761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prystowsky M. B., Naujokas M. F., Ihle J. N., Goldwasser E., Fitch F. W. A microassay for colony-stimulating factor based on thymidine incorporation. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jan;114(1):149–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Ihle J. N., Seldin D., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Katz H. R., LeBlanc P. A., Hein A., Caulfield J. P., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Interleukin 3: A differentiation and growth factor for the mouse mast cell that contains chondroitin sulfate E proteoglycan. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1479–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Clark-Lewis I. A T cell-derived factor stimulating multipotential hemopoietic stem cells: molecular weight and distinction from T cell growth factor and T cell-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):30–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Iscove N. N. Haematopoietic growth factors are released in cultures of H-2-restricted helper T cells, accessory cells and specific antigen. Nature. 1980 Sep 18;287(5779):228–230. doi: 10.1038/287228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R. Colony-stimulating factor (CSF) radioimmunoassay: detection of a CSF subclass stimulating macrophage production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2969–2973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Heard P. M. Factors regulating macrophage production and growth. Purification and some properties of the colony stimulating factor from medium conditioned by mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4305–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Metcalf D., Maritz J. S., Yeo G. F. Standardized bioassay for bone marrow colony stimulating factor in human urine: levels in normal man. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Apr;79(4):657–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]