Abstract
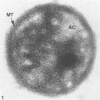
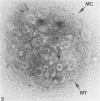
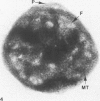
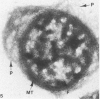
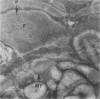
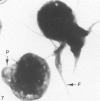
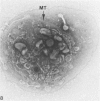
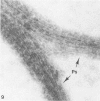
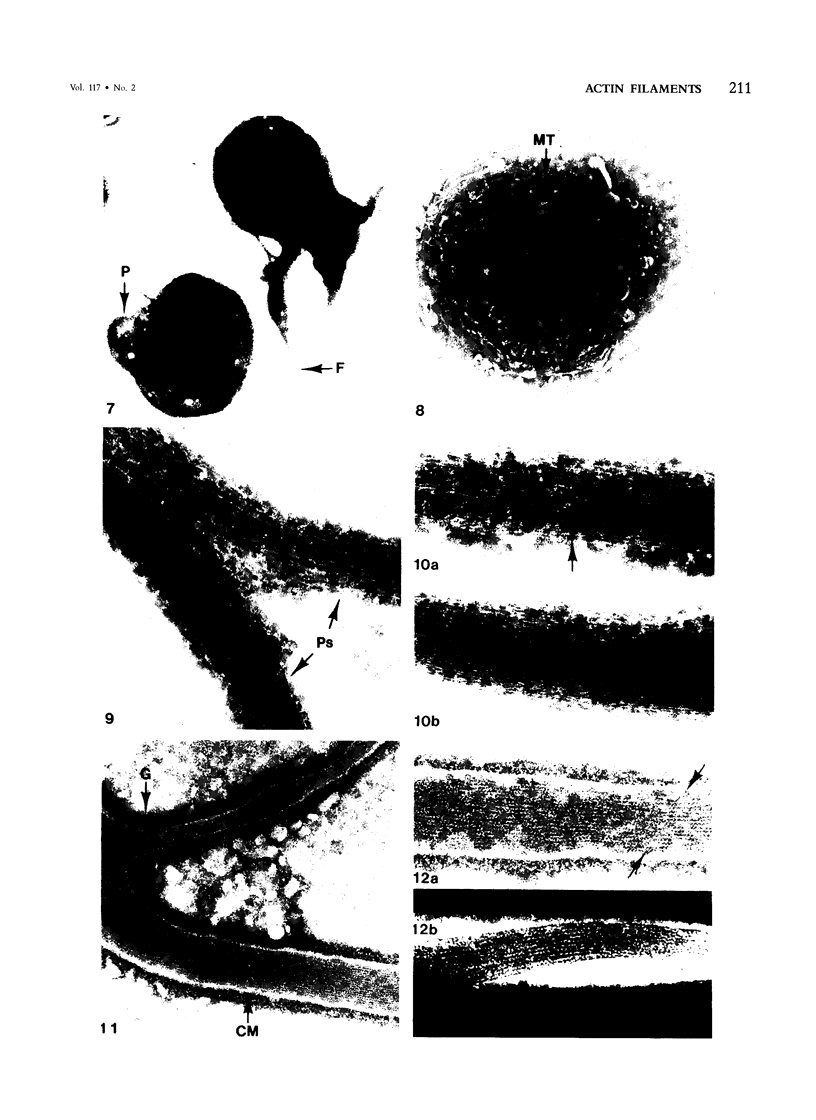
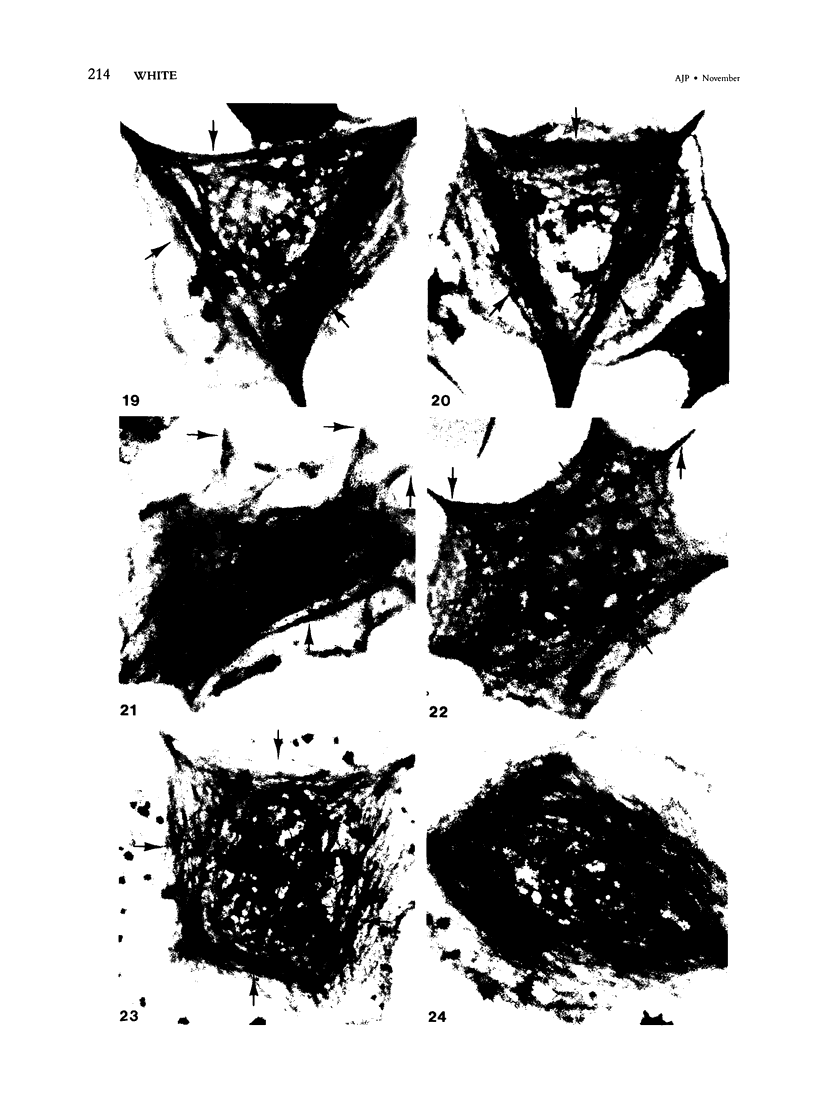
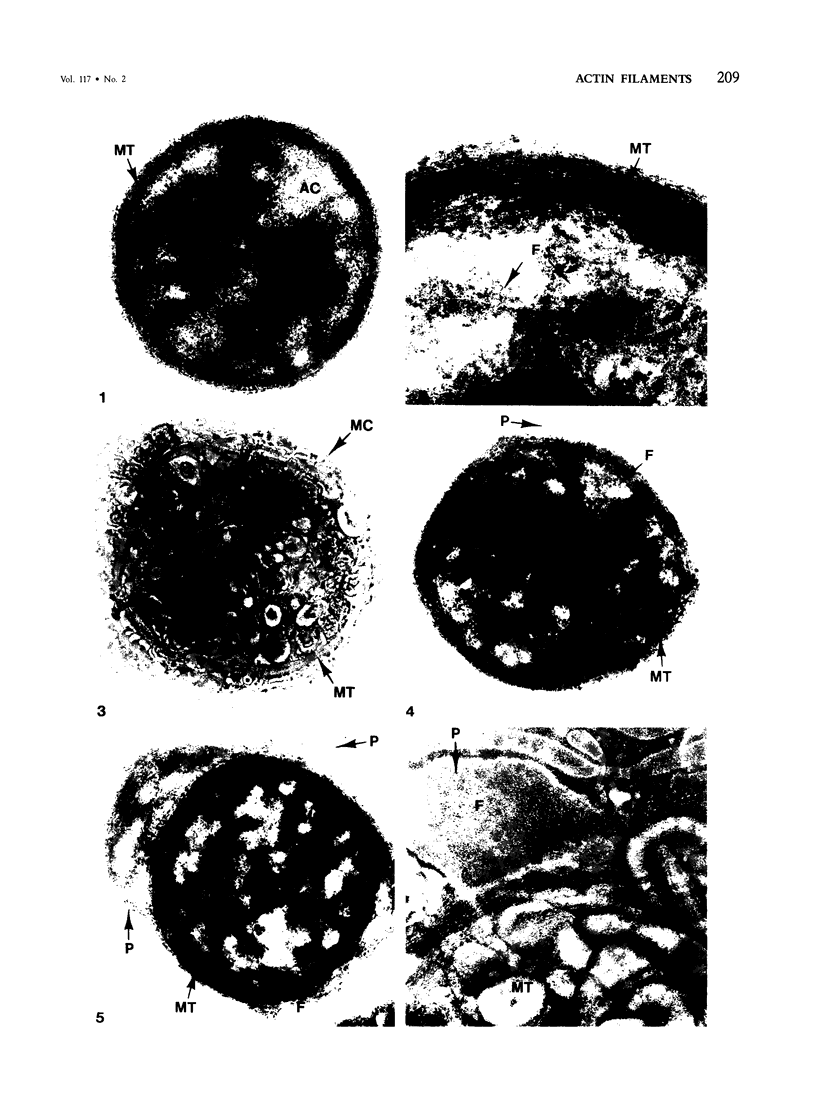
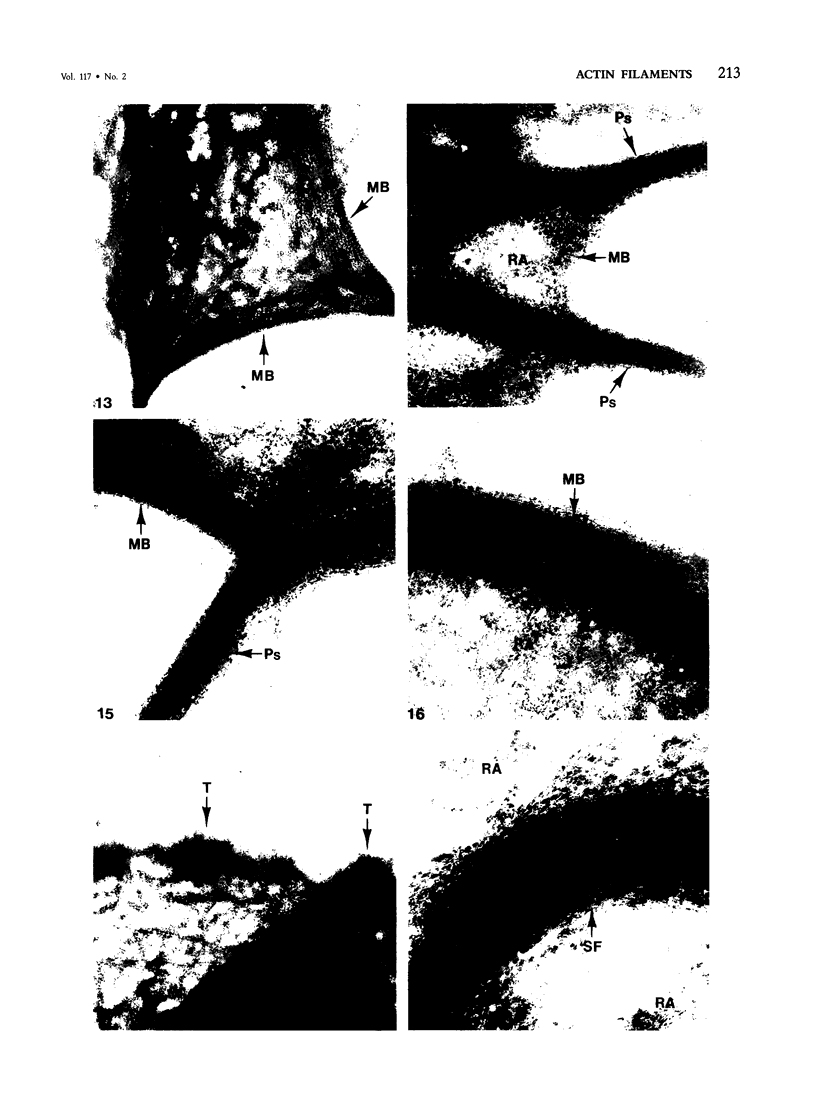
Assembly of actin molecules into filaments is closely associated with platelet shape change and exercise of contractile function. Since assembled actin filaments serve both as a framework for distortion of discoid shape and for generation of contractile force, it is important to determine the organizations of actin filaments capable of serving the two opposed functions of distortion and contraction. The present study has used negative staining alone and after combined glutaraldehyde fixation and detergent extraction to examine the arrangements of actin filaments in the cytoskeletons of surface activated platelets. Actin filament assembly developed as one of the earliest manifestations of platelet activation. Small protuberances containing random networks of actin filaments extending beyond the circumferential microtubules appeared to be an initial step in the response to stimulation. Transformation into dendritic forms was associated with development of parallel bundles of actin filaments organized into paracrystalline lattices with a periodicity of 5.5 nm at an angle of 60 degrees with the long axis of the pseudopod. Parallel bundles of actin filaments formed the concave borders of late dendritic forms and expanded to become the convex margin of most spread cells, suggesting a possible role in the spreading process. Other bundles of actin filaments resembled stress fibers radiating through the cytoplasm into pseudopods or organized in a variety of other apparently stable configurations. More loosely associated masses of actin filaments formed concentric layers around constricted rings of microtubules or a random network in the peripheral cytoplasm of spread cells. The arrangements of newly assembled actin filaments suggest their involvement in cell deformation, as well as contractile events.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bessis M., Breton-Gorius J. Les microtubules et les fibrilles dans les plaquettes étalées. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1965 Jul-Aug;5(4):657–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson L., Markey F., Blikstad I., Persson T., Lindberg U. Reorganization of actin in platelets stimulated by thrombin as measured by the DNase I inhibition assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6376–6380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. C., Butler R. G., Morris P. A., Gerrard J. M. Separable assembly of platelet pseudopodal and contractile cytoskeletons. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson C. C., White J. G. Platelet interaction with bacteria. I. Reaction phases and effects of inhibitors. Am J Pathol. 1971 Nov;65(2):367–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Weber K., Osborn M. The cytoskeleton of blood platelets viewed by immunofluorescence microscopy. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;24(1):45–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Phillips D. R. Polymerization and organization of actin filaments within platelets. Semin Hematol. 1983 Oct;20(4):243–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Phillips D. R., Rao G. H., Plow E. F., Walz D. A., Ross R., Harker L. A., White J. G. Biochemical studies of two patients with the gray platelet syndrome. Selective deficiency of platelet alpha granules. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):102–109. doi: 10.1172/JCI109823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., White J. G. The structure and function of platelets, with emphasis on their contractile nature. Pathobiol Annu. 1976;6:31–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonnella P. A., Nachmias V. T. Platelet activation and microfilament bundling. J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;89(1):146–151. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman I. M., Crisona N. J., Pollard T. D. Relation between cell activity and the distribution of cytoplasmic actin and myosin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):84–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höglund A. S., Karlsson R., Arro E., Fredriksson B. A., Lindberg U. Visualization of the peripheral weave of microfilaments in glia cells. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1980 Jun;1(2):127–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00711795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Rathke P. C., Hülsmann N., Franke W. W., Wohlfarth-Bottermann K. E. Cytoplasmic actomyosin fibrils in tissue culture cells: direct proof of contractility by visualization of ATP-induced contraction in fibrils isolated by laser micro-beam dissection. Cell Tissue Res. 1976 Feb 27;166(4):427–443. doi: 10.1007/BF00225909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Birchmeier W. Stress fiber sarcomeres of fibroblasts are contractile. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90365-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C., White M. S., Prater T., Taylor R. G., Davis K. S. Ultrastructural analysis of platelets in nonhuman primates. III. Stereo microscopy of microtubules during platelet adhesion and the release reaction. Exp Mol Pathol. 1982 Dec;37(3):370–381. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(82)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson J. C., Zuiches C. A. Elucidation of the platelet cytoskeleton. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:11–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. T. Cytoskeleton of human platelets at rest and after spreading. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):795–802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. T. Platelet and megakaryocyte shape change: triggered alterations in the cytoskeleton. Semin Hematol. 1983 Oct;20(4):261–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V., Sullender J., Asch A. Shape and cytoplasmic filaments in control and lidocaine-treated human platelets. Blood. 1977 Jul;50(1):39–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Ginsberg M. Concanavalin A induces interactions between surface glycoproteins and the platelet cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):565–573. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S., Stracher A., Lucas R. C. Isolation and characterization of actin and actin-binding protein from human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):201–211. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Horwitz S. B. Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1561–1565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schollmeyer J. V., Rao G. H., White J. G. An actin-binding protein in human platelets. Interactions with alpha-actinin on gelatin of actin and the influence of cytochalasin B. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):433–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V. Organization of actin in the leading edge of cultured cells: influence of osmium tetroxide and dehydration on the ultrastructure of actin meshworks. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):695–705. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wani M. C., Taylor H. L., Wall M. E., Coggon P., McPhail A. T. Plant antitumor agents. VI. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from Taxus brevifolia. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 May 5;93(9):2325–2327. doi: 10.1021/ja00738a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Burris S. M. Morphometry of platelet internal contraction. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jun;115(3):412–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Fine structural alterations induced in platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):604–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Gerrard J. M. Interaction of microtubules and microfilaments in platelet contractile physiology. Methods Achiev Exp Pathol. 1979;9:1–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Influence of taxol on the response of platelets to chilling. Am J Pathol. 1982 Aug;108(2):184–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Interaction of membrane systems in blood platelets. Am J Pathol. 1972 Feb;66(2):295–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Rao G. H. Effects of a microtubule stabilizing agent on the response of platelets to vincristine. Blood. 1982 Aug;60(2):474–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Rao G. H. Influence of a microtubule stabilizing agent on platelet structural physiology. Am J Pathol. 1983 Aug;112(2):207–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Sauk J. J. Microtubule coils in spread blood platelets. Blood. 1984 Aug;64(2):470–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosewick J. J., Porter K. R. Microtrabecular lattice of the cytoplasmic ground substance. Artifact or reality. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jul;82(1):114–139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]