Abstract
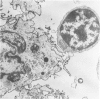
We have investigated cell subpopulations in frozen sections of thymus tissue obtained from myasthenic (MG) and control subjects. With the use of an avidin-biotin immunoperoxidase system with monoclonal antibodies, the following cell surface antigens were studied on frozen sections (12 MG and 3 control thymus); T11, T4, T6, T8, IgM, IgD, and Ia. The pattern of T cell phenotypes in MG thymus is similar to that of normal control thymus when examined by immunohistologic techniques. MG cortical thymocytes are virtually all T11+, T4+, T8+, and T6+. In the medulla, at least 45% of thymocytes are T11+, with T4+ cells predominating over T8+ cells. Approximately 10% of medullary thymocytes are T6+. Scattered medullary cells expressing surface IgM and IgD are identified in both MG and normal thymuses. However, unlike the normal thymus, the MG thymus has numerous secondary follicles containing IgM- and IgD-bearing cells. This finding supports the hypothesis that the MG thymus microenvironment is aberrant. The Ia antigen is found in similar tissue section localization patterns in MG and control thymus. Ultramicroscopic studies show the Ia antigen predominantly on epithelial and interdigitating dendritic cells. By immunoperoxidase techniques, numerous keratin-positive cells are demonstrated in MG and control thymus. This suggests that thymic epithelial cells, like epithelial cells elsewhere, contain keratin. Because these data differ in degree from our previous findings in suspensions of MG thymocytes, this study emphasizes the importance of examining tissue sections as well as cell suspensions when one is studying lymphocyte surface markers.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., Lisak R. P., Zweiman B., Abrahamsohn I., Penn A. S. The thymus in myasthenia gravis. Evidence for altered cell populations. N Engl J Med. 1974 Dec 12;291(24):1271–1275. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197412122912403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan A. K., Reinherz E. L., Poppema S., McCluskey R. T., Schlossman S. F. Location of T cell and major histocompatibility complex antigens in the human thymus. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):771–782. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner T., Abramsky O., Lisak R. P., Zweiman B., Tarrab-Hazdai R., Fuchs S. Radioimmunoassay of antibodies to acetylcholine receptor in serum of myasthenia gravis patients. Isr J Med Sci. 1978 Sep;14(9):986–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTLEMAN B., NORRIS E. H. The pathology of the thymus in myasthenia gravis; a study of 35 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1949 Feb;28(1):27–58. doi: 10.1097/00005792-194902000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. B. Myasthenia gravis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 19;298(3):136–142. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801192980305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr A. G., Nakane P. K. Cells bearing Ia antigens in the murine thymus. An ultrastructural study. Am J Pathol. 1983 Apr;111(1):88–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Thomas J. A., Bollum F. J., Granger S., Pizzolo G., Bradstock K. F., Wong L., McMichael A., Ganeshaguru K., Hoffbrand A. V. The human thymic microenvironment: an immunohistologic study. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):202–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Tidman N., Papageorgiou E. S., Kung P. C., Goldstein G. Distribution of t lymphocyte subsets in the human bone marrow and thymus: an analysis with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1608–1613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine G. D., Rosai J. Thymic hyperplasia and neoplasia: a review of current concepts. Hum Pathol. 1978 Sep;9(5):495–515. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(78)80131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisak R. P., Zweiman B., Skolnik P., Levinson A. I., Moskovitz A. R., Guerrero F. Thymic lymphocyte subpopulations in myasthenia gravis. Neurology. 1983 Jul;33(7):868–872. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.7.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton G. The incidence of follicular structures in the human thymus at autopsy. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1967 Apr;45(2):189–199. doi: 10.1038/icb.1967.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Watanabe S., Sato Y., Shimosato Y., Motoi M., Lennert K. S-100 protein in Langerhans cells, interdigitating reticulum cells and histiocytosis X cells. Gan. 1982 Jun;73(3):429–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsom-Davis J., Willcox N., Calder L. Thymus cells in myasthenia gravis selectively enhance production of anti-acetylcholine-receptor antibody by autologous blood lymphocytes. N Engl J Med. 1981 Nov 26;305(22):1313–1318. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198111263052203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. The differentiation and function of human T lymphocytes. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):821–827. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse R. V., Weissman I. L. Microanatomy of the thymus: its relationship to T cell differentiation. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;84:161–177. doi: 10.1002/9780470720660.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Banks-Schlegel S., Pinkus G. S. Immunohistochemical localization of keratin in normal human tissues. Lab Invest. 1980 Jan;42(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Willcox H. N., Newsom-Davis J. Immunohistological studies of the thymus in myasthenia gravis. Correlation with clinical state and thymocyte culture responses. J Neuroimmunol. 1982 Dec;3(4):319–335. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(82)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidman N., Janossy G., Bodger M., Granger S., Kung P. C., Goldstein G. Delineation of human thymocyte differentiation pathways utilizing double-staining techniques with monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Sep;45(3):457–467. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ewijk W., Rouse R. V., Weissman I. L. Distribution of H-2 microenvironments in the mouse thymus. Immunoelectron microscopic identification of I-A and H-2K bearing cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Oct;28(10):1089–1099. doi: 10.1177/28.10.6999083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetters M., Barclay R. S. The incidence of germinal centres in thymus glands of patients with congenital heart disease. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Aug;26(8):583–591. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.8.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]