Abstract
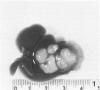
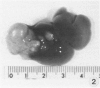
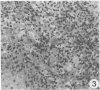
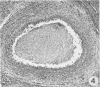
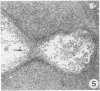
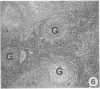
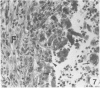
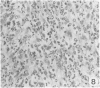
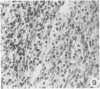
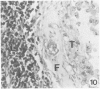
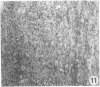
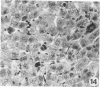
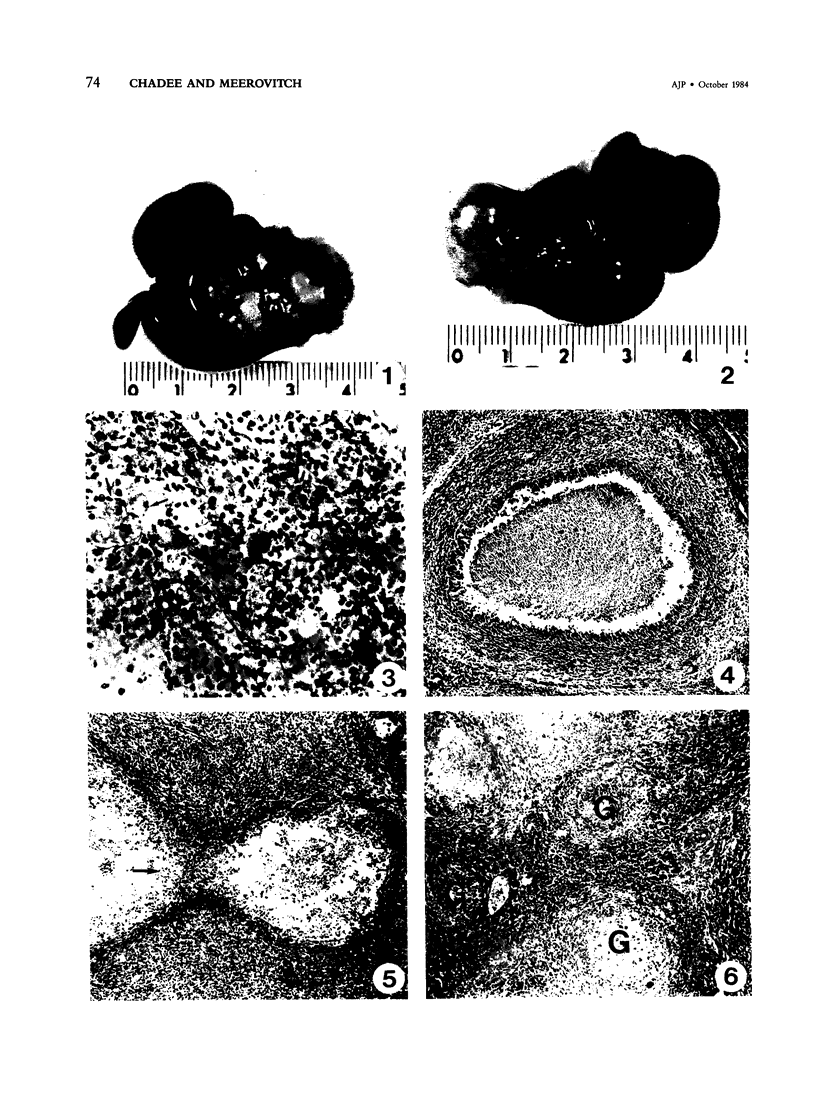
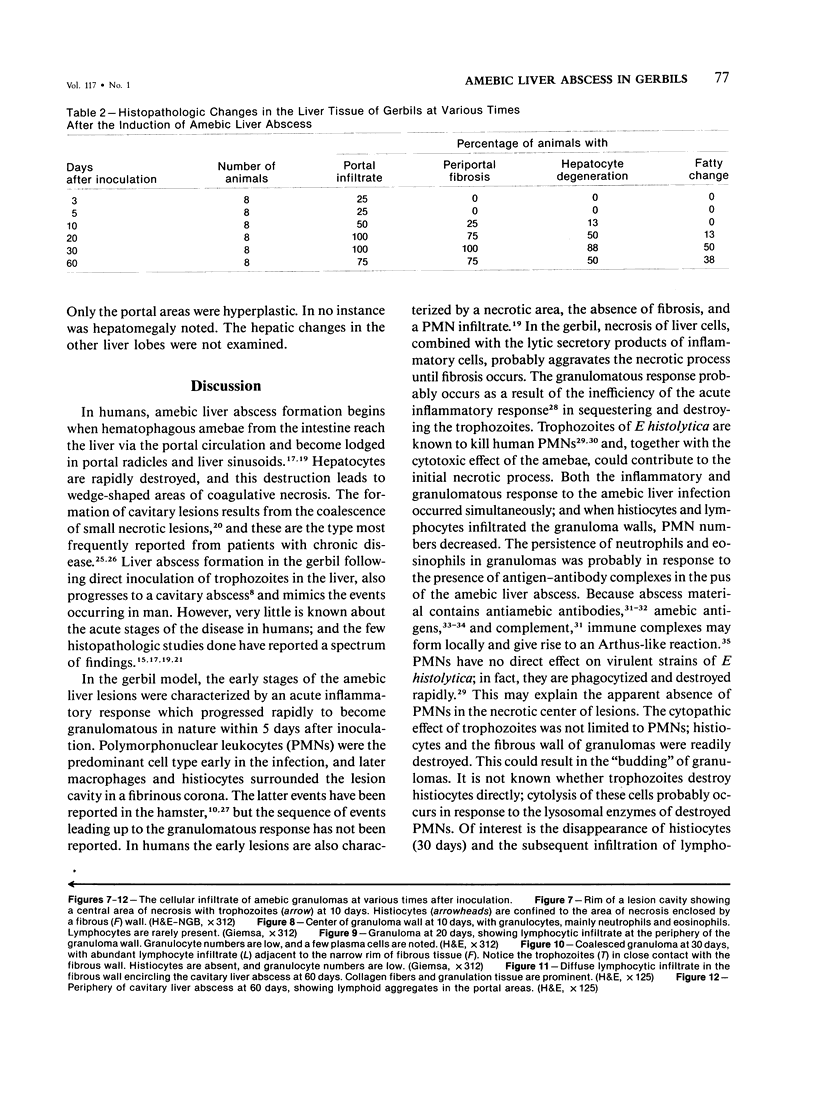
Sequential development and pathology of experimentally induced amebic liver abscess in the gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) were studied from 1 to 60 days after inoculation. Early lesions were characterized by an acute inflammatory response, which became granulomatous at 5 days. Early granulomas were discrete, with well-defined fibrohistiocytic walls. Trophozoite dissemination as a result of fibrolysis of granuloma wall was confined to the liver parenchyma. The granulomatous cellular infiltrate (less than 20 days) was characterized by granulocytes and histiocytes; older granulomas (greater than 30 days) were composed of lymphocytic infiltrate, plasma cells, and a few granulocytes, and were characterized by the absence of epithelioid histiocytes. The degree of pathologic change adjacent to liver granulomas followed the sequential development of the amebic liver abscess. Severe changes observed were portal canal lymphocytic infiltration, the presence of foreign body giant cells, periportal fibrosis, proliferation of bile duct epithelium, and hepatocyte anisonucleosis and ballooning degeneration. The pathogenesis of the infection and the usefulness of the gerbil model for the study of human amebiasis are discussed.
Full text
PDF



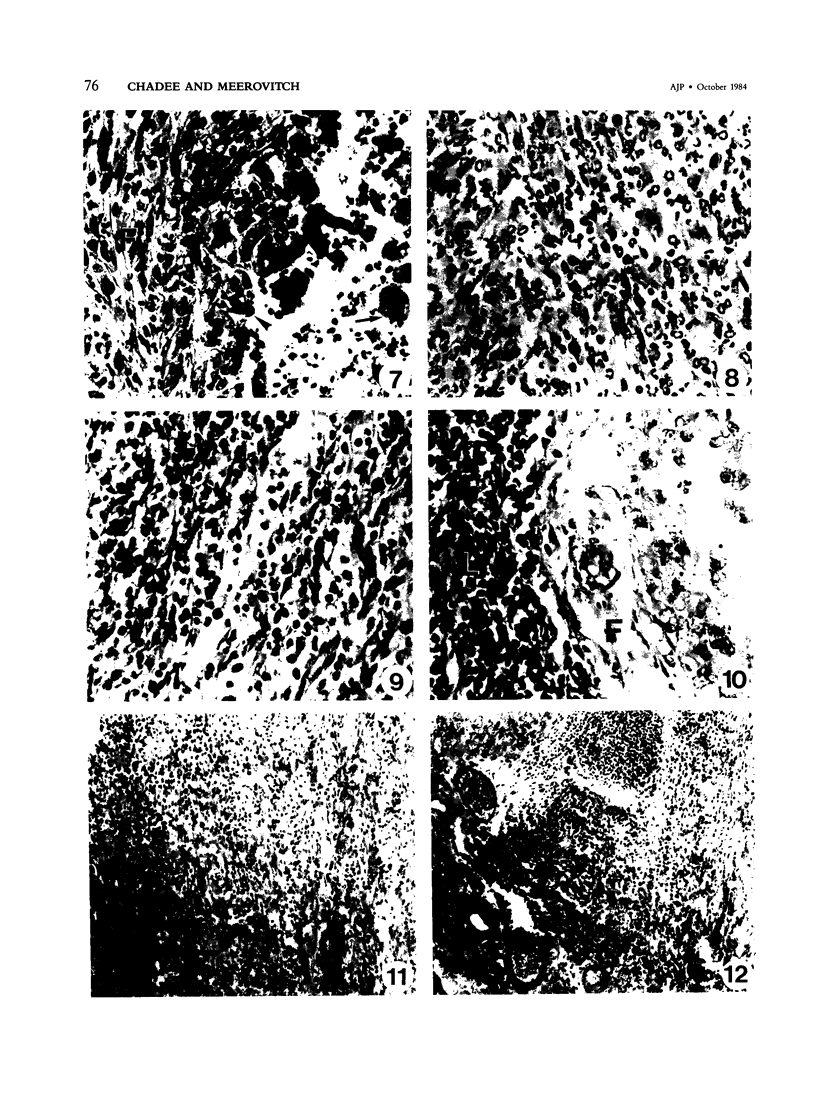
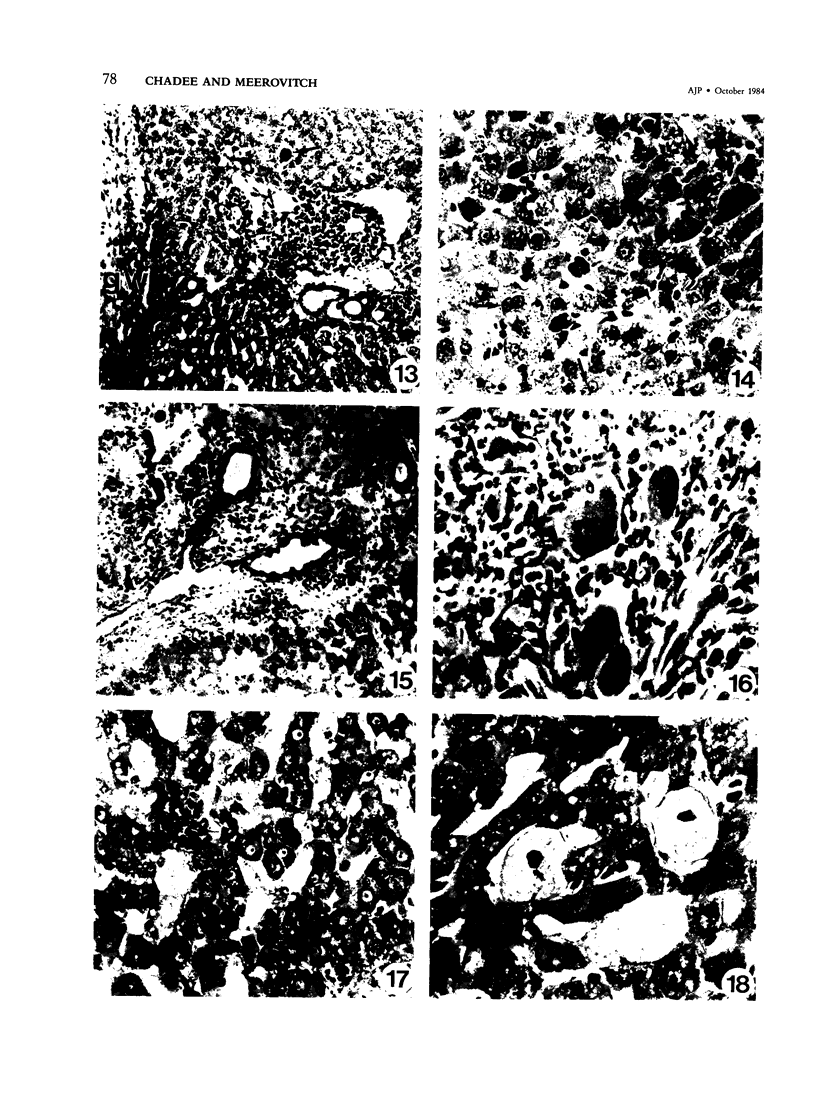


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O. The granulomatous inflammatory response. A review. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jul;84(1):164–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre-García J., Calderón P., Tanimoto-Weki M. Examen histopatológico de las lesiones hepáticas en hamsters inoculados con cultivo axénico de Entamoeba histolytica. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1972;2(Suppl):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aikat B. K., Bhusnurmath S. R., Pal A. K., Chhuttani P. N., Datta D. V. The pathology and pathogenesis of fatal hepatic amoebiasis--A study based on 79 autopsy cases. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(2):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amyx H. L., Asher D. M., Nash T. E., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Hepatic amebiasis in spider monkeys. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Sep;27(5):888–891. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos H. J., van de Griend R. J. Virulence and toxicity of axenic Entamoeba histolytica. Nature. 1977 Jan 27;265(5592):341–343. doi: 10.1038/265341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt H., Tamayo R. P. Pathology of human amebiasis. Hum Pathol. 1970 Sep;1(3):351–385. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(70)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARRERA G. M. Pathology of early amebic hepatitis. AMA Arch Pathol. 1950 Oct;50(4):440–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATGIDAKIS C. B. The pathology of hepatic amoebiasis as seen on the Witwatersrand. S Afr J Clin Sci. 1953 Sep;4(3):230–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadee K., Meerovitch E. The Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) as an experimental host for Entamoeba histolytica. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Jan;33(1):47–54. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOXIADES T., CANDREVIOTIS N., TILIAKOS M., POLYMEROPOULOS I. Chronic diffuse non-suppurative amoebic hepatitis. Br Med J. 1961 Feb 18;1(5224):460–462. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5224.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Phillips B. P., Bartgis I. L. The clawed jird (Meriones unguiculatus) as an experimental animal for the study of hepatic amebiasis. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1974;5(Suppl 2):465–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIDLEY M. F. A stain for Endamoeba histolytica in tissue sections. Am J Clin Pathol. 1954 Feb;24(2):243–244. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/24.2_ts.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. Behavior of axenic IP-106 strain of Entamoeba histolytica in the golden hamster. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Mar;27(2 Pt 1):241–247. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. In vitro amoebicidal activity of immune cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):243–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.243-246.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Barbosa M., Fastag de Shor A., De la Torre M., Villegas-González J. Secuencia de las lesiones hepáticas amibianas en el conejo. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1972;2(Suppl):349–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brush J., Ravdin J. I., Sullivan J. A., Mandell G. L. Interaction between Entamoeba histolytica and human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):83–93. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulati P. D., Gupta D. N., Chuttani H. K. Amoebic liver abscess and disturbances of portal circulation. Am J Med. 1967 May;42(5):852–854. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARUMILINTA R., KRADOLFER F. THE TOXIC EFFECT OF ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA ON LEUCOCYTES. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1964 Sep;58:375–381. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1964.11686259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenstein D., Rickerson V., Braude A. New concepts of amebic liver abscess derived from hepatic imaging, serodiagnosis, and hepatic enzymes in 67 consecutive cases in San Diego. Medicine (Baltimore) 1982 Jul;61(4):237–246. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198207000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lushbaugh W. B., Kairalla A. B., Hofbauer A. F., Pittman F. E. Sequential histopathology of cavitary liver abscess. Formation induced by axenically grown Entamoeba histolytica. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980 Nov;104(11):575–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lushbaugh W. B., Kairalla A. B., Loadholt C. B., Pittman F. E. Effect of hamster liver passage on the virulence of axenically cultivated Entamoeba histolytica. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Mar;27(2 Pt 1):248–254. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan R. C., Ganguly N. K. Amoebic antigen in immunodiagnosis and prognosis of amoebic liver abscess. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(3):300–302. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan R. C., Ganguly N. K., Chitkara N. L., Dutta D. V., Chhuttani P. N. Detection of amoebic antigen in liver pus by counter immunoelectrophoresis--a preliminary report. Indian J Med Res. 1974 Oct;62(10):1462–1464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern C. F., Keister D. B. Experimental amebiasis. II. Hepatic amebiasis in the newborn hamster. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 May;26(3):402–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E. L. In memoriam. Fred L. Adair 1878-1972. J Reprod Med. 1972 Jun;8(6):348–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravi V. V., Mithal S., Malaviya A. N., Tandom B. N. Immunologic studies in amoebic liver abscess. Indian J Med Res. 1975 Dec;63(12):1732–1736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravi V. V., Tandon H. D., Tandon B. N. Morphological changes in the liver in hepatic amoebiasis. Indian J Med Res. 1974 Dec;62(12):1832–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G. L. The laboratory diagnosis of human parasitic amoebae. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1968;62(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(68)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Taylor R. G., Everett E. D., Owensby L., McNitt T. R. Amebic liver abscess. Report of a case presenting with nonreactive serologic tests for Entamoeba histolytica. Am J Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;72(3):234–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon B. N., Tandon H. D., Puri B. K. An electron microscopic study of liver in hepatomegaly presumably caused by amebiasis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1975 Feb;22(1):118–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(75)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl D. Immunology of Entamoeba histolytica in human and animal hosts. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):1154–1184. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.6.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]