Abstract
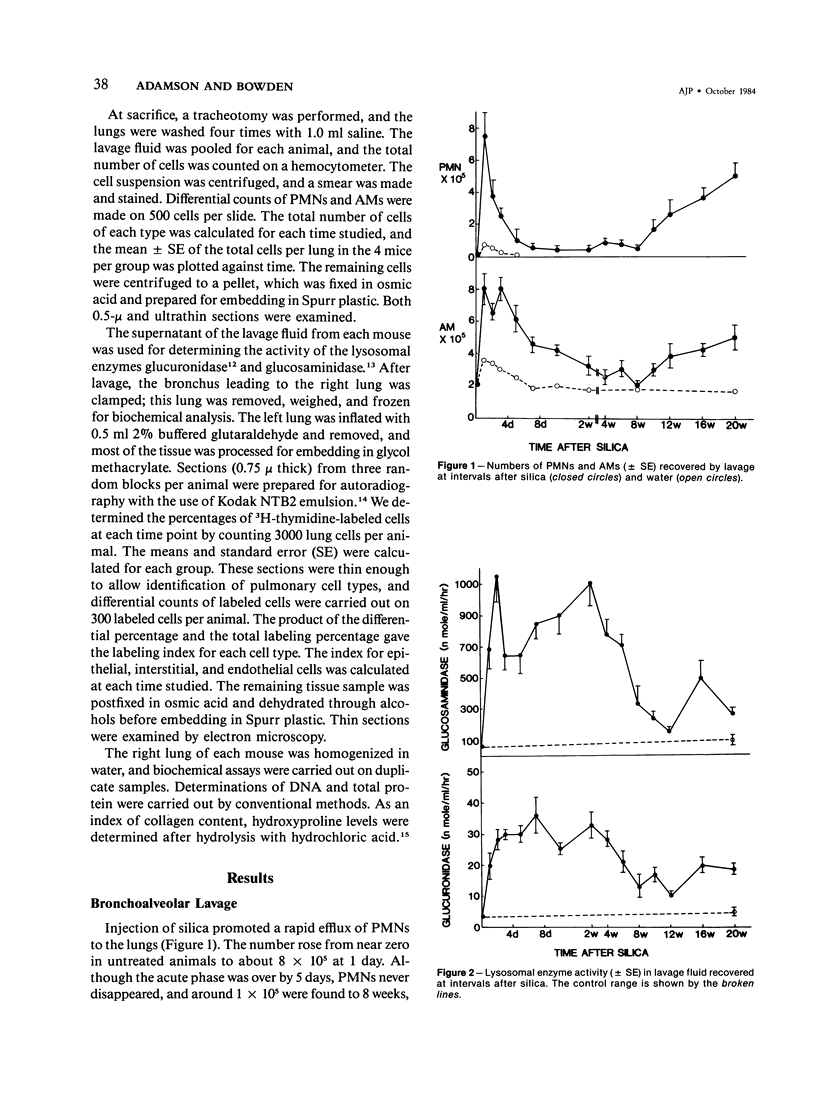
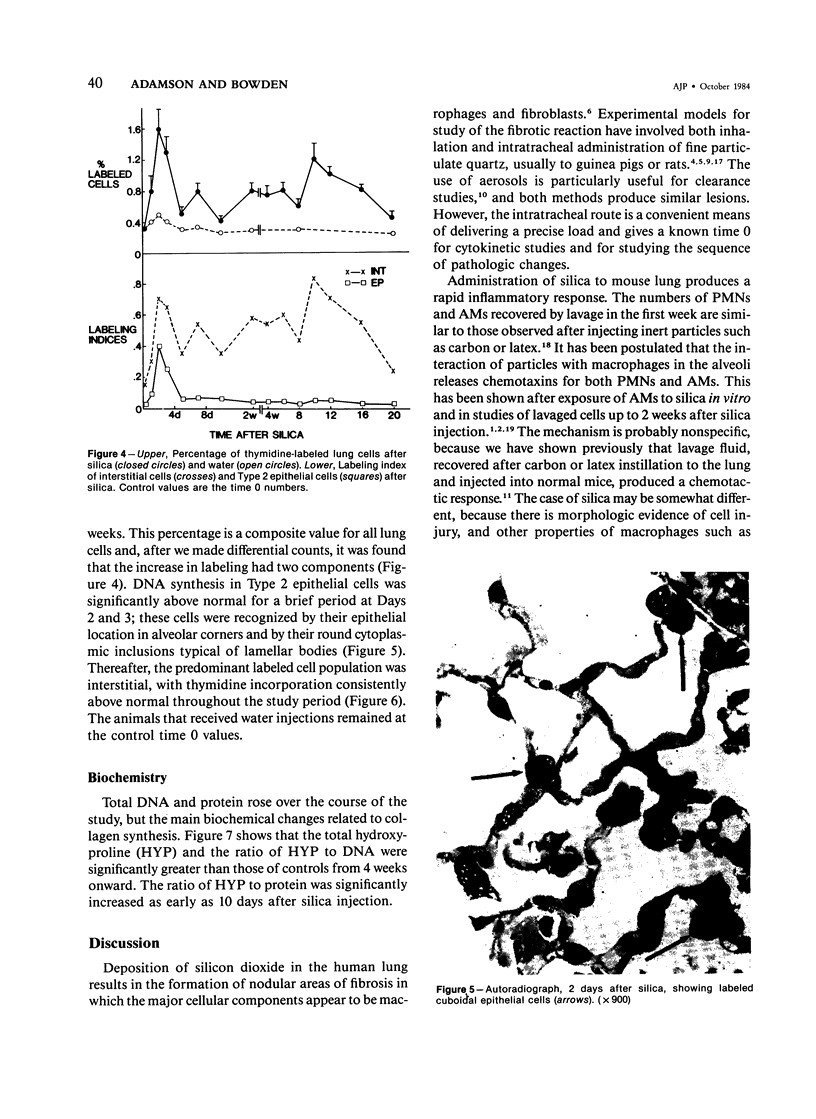
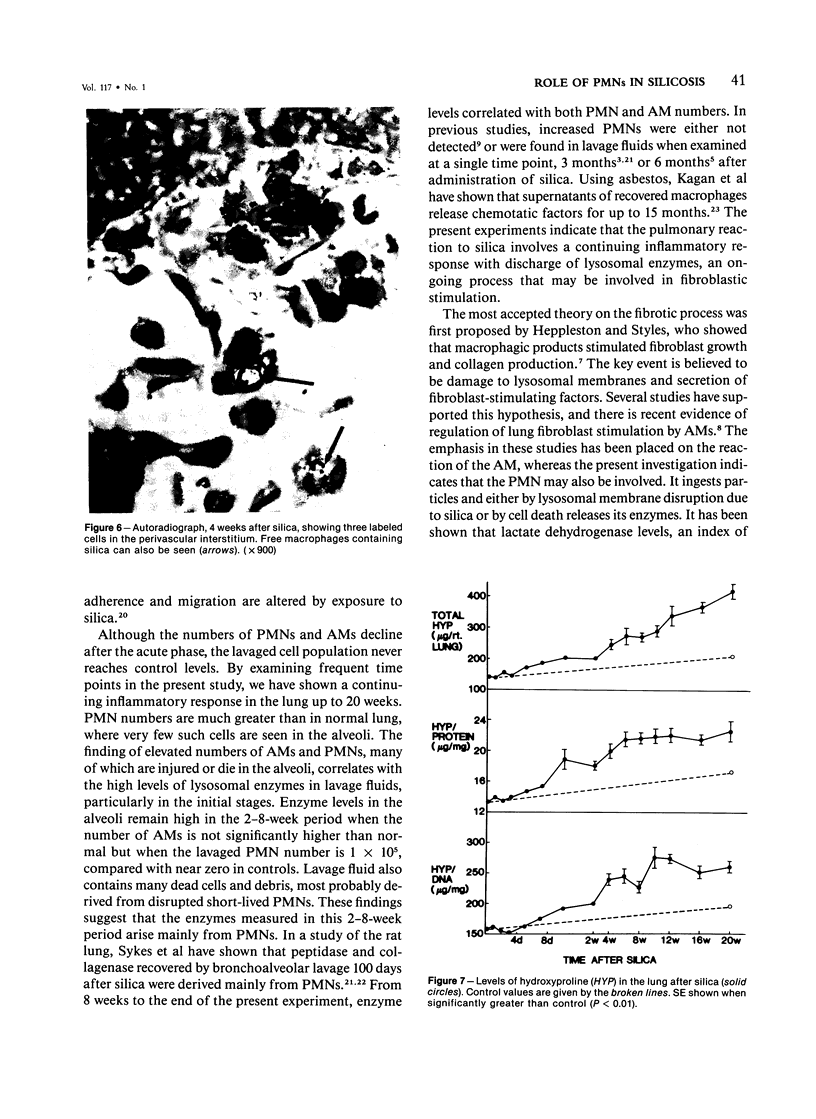
Silicosis is usually attributed to fibroblast stimulation by secretion of damaged alveolar macrophages (AMs), but the role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) and of continuing cell injury in the pathogenesis has not been fully studied. Mice given intratracheal injections of 2 mg of silica received 3H-thymidine 1 hour before death at intervals to 20 weeks. Cellular populations and lysosomal content of lavage fluids were correlated with morphology, DNA synthesis, and collagen content of the lung. The initial response involved rapid PMN and AM recruitment to the alveoli. Some free particles crossed Type 1 epithelial cells, and silica was found in interstitial macrophages. Focal Type 1 cell damage was rapidly repaired by Type 2 cell proliferation. Although PMN numbers dropped after a few days, they never reached control levels and rose again after 8 weeks; the number of AMs fell to control values from 2 to 8 weeks, then increased again. Glucosaminidase and glucuronidase levels in the lavage fluid were much higher than control levels throughout the study. Increased DNA synthesis by interstitial cells occurred from 2 days to 20 weeks; increased collagen synthesis was found from 4 weeks onward. The continuing inflammatory response of the lung to silica suggests may contribute to fibroblastic stimulation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. Chemotactic and mitogenic components of the alveolar macrophage response to particles ad neutrophil chemoattractant. Am J Pathol. 1982 Oct;109(1):71–77. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. Dose response of the pulmonary macrophagic system to various particulates and its relationship to transepithelial passage of free particles. Exp Lung Res. 1981 Aug;2(3):165–175. doi: 10.3109/01902148109052312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The type 2 cell as progenitor of alveolar epithelial regeneration. A cytodynamic study in mice after exposure to oxygen. Lab Invest. 1974 Jan;30(1):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B., Lockwood T., Morgan H. R. Surface biochemical changes accompanying primary infection with Rous sarcoma virus. II. Proteolytic and glycosidase activity and sublethal autolysis. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Jan;83(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90683-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody A. R., Roe M. W., Evans J. N., Davis G. S. Deposition and translocation of inhaled silica in rats. Quantification of particle distribution, macrophage participation, and function. Lab Invest. 1982 Dec;47(6):533–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauber J. H., Rossman M. D., Daniele R. P. Pulmonary fibrosis: bronchoalveolar cell types and impaired function of alveolar macrophages in experimental silicosis. Environ Res. 1982 Feb;27(1):226–236. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(82)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauber J. H., Rossman M. D., Pietra G. G., Jimenez S. A., Daniele R. P. Experimental silicosis: morphologic and biochemical abnormalities produced by intratracheal instillation of quartz into guinea pig lungs. Am J Pathol. 1980 Dec;101(3):595–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelmark B., Sjöstrand M., Bergström R., Rylander R. Pulmonary macrophage phagocytosis and enzyme production after in vivo exposure to silica dust. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1983 Mar 30;68(1):152–159. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(83)90364-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Styles J. A. Activity of a macrophage factor in collagen formation by silica. Nature. 1967 Apr 29;214(5087):521–522. doi: 10.1038/214521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan E., Oghiso Y., Hartmann D. P. Enhanced release of a chemoattractant for alveolar macrophages after asbestos inhalation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Oct;128(4):680–687. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.4.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugano E. M., Dauber J. H., Daniele R. P. Acute experimental silicosis. Lung morphology, histology, and macrophage chemotaxin secretion. Am J Pathol. 1982 Oct;109(1):27–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugano E. M., Dauber J. H., Daniele R. P. Silica stimulation of chemotactic factor release by guinea pig alveolar macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Nov;30(5):381–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSA B. U., DOE R. P., SEAL U. S. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF HUMAN LIVER BETA-GLUCURONIDASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:2811–2816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K., Calverley A., Kagan E. Evidence of a quartz-induced chemotactic factor for guinea pig alveolar macrophages. Environ Res. 1980 Jun;22(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(80)90116-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Moores S. R., Holmes A., Evans J. C., Evans N. H., Black A. The effect of quartz, administered by intratracheal instillation, on the rat lung. I. The cellular response. Environ Res. 1980 Jun;22(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(80)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser K. M., Haschek W. M., Hesterberg T. W., Last J. A. Experimental silicosis. II. Long-term effects of intratracheally instilled quartz on collagen metabolism and morphologic characteristics of rat lungs. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jan;110(1):30–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser K. M., Hesterberg T. W., Haschek W. M., Last J. A. Experimental silicosis. I. Acute effects of intratracheally instilled quartz on collagen metabolism and morphologic characteristics of rat lungs. Am J Pathol. 1982 May;107(2):176–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suratt P. M., Wilhoit S. C., Atkinson R. L. Elevated pulse flow resistance in awake obese subjects with obstructive sleep apnea. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Feb;127(2):162–165. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.2.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes S. E., Moores S. R., Jones S. T. Dose-dependent effects in the subacute response of the rat lung to quartz. II. Protease activities and levels of soluble hydroxyproline in lung lavage. Exp Lung Res. 1983 Dec;5(4):245–257. doi: 10.3109/01902148309061518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes S. E., Morgan A., Moores S. R., Jones S. T., Holmes A., Davison W. Evidence for a dose-dependent inflammatory response to quartz in the rat lung and its significance in early changes in collagen metabolism. Environ Health Perspect. 1983 Sep;51:141–146. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8351141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]