Abstract
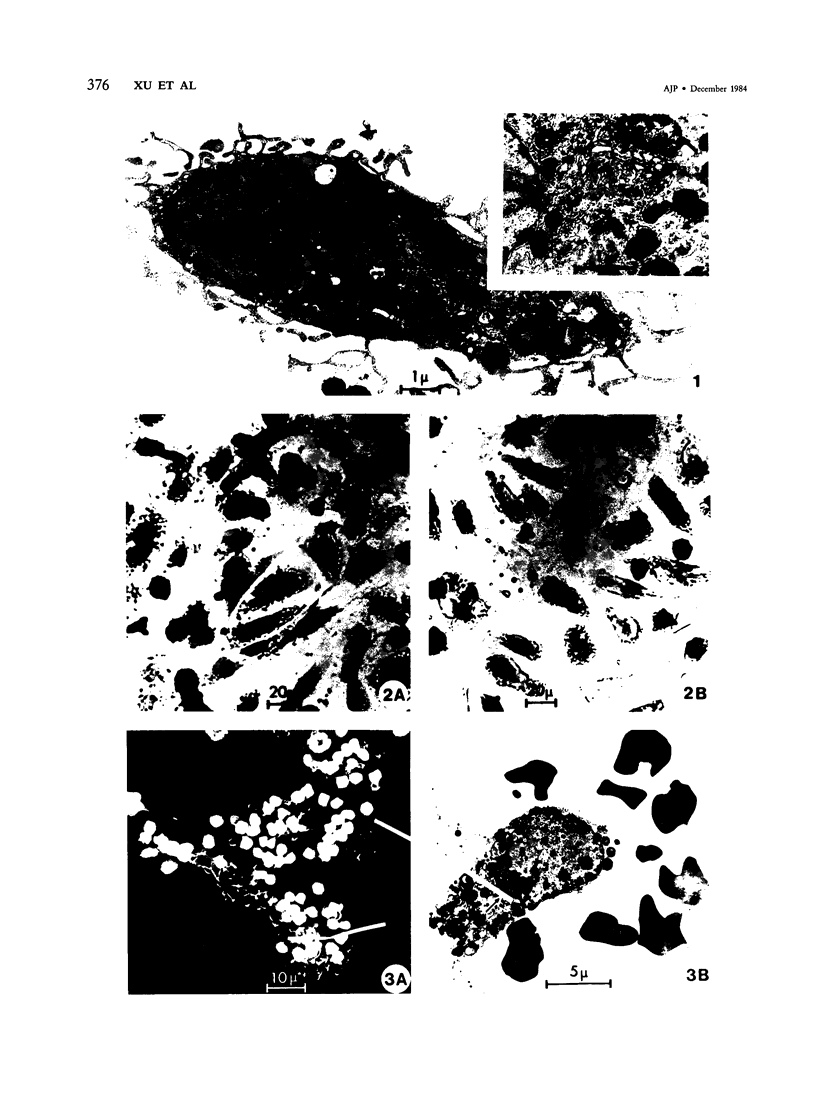
Murine Kupffer cells (RC) were isolated in sufficient number and purity to allow in vitro investigations of their tumoricidal capabilities. The identity of the adherent cells as KCs was established by morphologic, histochemical, and functional criteria. The yield of KCs varied from young (high) to old (low) mice but was not affected by the mouse strain. KCs activated in vitro by either endotoxins (lipopolysaccharide) or lymphokines were rendered highly cytotoxic against syngeneic melanoma or fibrosarcoma target cells. These studies indicate that KCs may indeed play a role in destruction of tumor cells in vivo and thus be important in host defense against developing hepatic cancer metastases.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg T., Munthe-Kaas A. C. Lysosomal enzymes in cultured rat Kupffer cells. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Oct 1;109(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar R., Schade U., Rietschel E. T., Decker K. Involvement of prostaglandin E and adenosine 3', 5'-monophosphate in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated collagenase release by rat Kupffer cells. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jun 15;125(1):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06659.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer A., Sleyster E. C., Duddridge R. J., Knook D. L. Activity of cathepsin D in rat liver Kupffer cells after phagocytosis in vivo and in vitro. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(10-11):1647–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. A., Salazar D., Nolan J. P. Natural cytotoxicity of isolated rat liver cells. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):495–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., Planqué B. Heterogeneity of cells isolated from rat liver by pronase digestion: ultrastructure, cytochemistry and cell culture. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Jul;20(1):11–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson S., Fraser J. R., Laurent T. C., Pertoft H., Smedsrød B. Endothelial cells are a site of uptake and degradation of hyaluronic acid in the liver. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Mar;144(1):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Darnell J. H., Budmen M. B. In vitro activation of mouse macrophages by rat lymphocyte mediators. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):666–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Recognition and destruction of target cells by tumoricidal macrophages. Isr J Med Sci. 1978 Jan;14(1):177–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogler W. E., Raz A., Fidler I. J. In situ activation of murine macrophages by liposomes containing lymphokines. Cell Immunol. 1980 Jul 15;53(1):214–219. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90440-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart I. R. The selection and characterization of an invasive variant of the B16 melanoma. Am J Pathol. 1979 Dec;97(3):587–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinerman E. S., Schroit A. J., Fogler W. E., Fidler I. J. Tumoricidal activity of human monocytes activated in vitro by free and liposome-encapsulated human lymphokines. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):304–315. doi: 10.1172/JCI110970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knook D. L., Seffelaar A. M., de Leeuw A. M. Fat-storing cells of the rat liver. Their isolation and purification. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jun;139(2):468–471. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90283-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kripke M. L. Latency, histology, and antigenicity of tumors induced by ultraviolet light in three inbred mouse strains. Cancer Res. 1977 May;37(5):1395–1400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. M., Zucker-Franklin D. Electron microscopic study of isolated Kupffer cells. Am J Pathol. 1969 Feb;54(2):147–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe-Kaas A. C., Berg T., Seglen P. O., Seljelid R. Mass isolation and culture of rat kupffer cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):1–10. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe-Kaas A. C. The accessory cell effects of liver macrophages in concanavalin A stimulation of rat spleen lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(5):523–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler P. I., Klingenstein R. J., Richman L. K., Ahmann G. B. The murine Kupffer cell. II. Accessory cell function in in vitro primary antibody responses, mitogen-induced proliferation, and stimulation of mixed lymphocyte responses. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2521–2525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praaning-Van Dalen D. P., Knook D. L. Quantitative determination of in vivo endocytosis by rat liver Kupffer and endothelial cells facilitated by an improved cell isolation method. FEBS Lett. 1982 May 17;141(2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reske S. N., Vyska K., Feinendegen L. E. In vivo assessment of phagocytic properties of Kupffer cells. J Nucl Med. 1981 May;22(5):405–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Klingenstein R. J., Richman J. A., Strober W., Berzofsky J. A. The murine Kupffer cell. I. Characterization of the cell serving accessory function in antigen-specific T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2602–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogoff T. M., Lipsky P. E. Antigen presentation by isolated guinea pig Kupffer cells. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1740–1744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogoff T. M., Lipsky P. E. Characterization of isolated guinea pig Kupffer cells: accessory cell function in mitogen-induced T lymphocyte activation. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):1920–1927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogoff T. M., Lipsky P. E. Role of the Kupffer cells in local and systemic immune responses. Gastroenterology. 1981 Apr;80(4):854–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleyster E. C., Knook D. L. Relation between localization and function of rat liver Kupffer cells. Lab Invest. 1982 Nov;47(5):484–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker S. B., Pierre R. V., Jordon R. E. Rapid identification of monocytes in a mixed mononuclear cell preparation. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters R. V., Ferraresi R. W. Muramyl dipeptide stimulation of particle clearance in several animal species. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Nov;28(5):457–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahlten R. N., Rogoff T. M., Steer C. J. Isolated Kupffer cells, endothelial cells and hepatocytes as investigative tools for liver research. Fed Proc. 1981 Aug;40(10):2460–2468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





